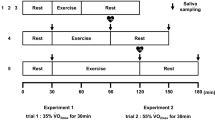
Abstract
Physical exercise is associated with elevation of serum levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) because of its production in the muscles. The use of IL-6 measurements in saliva has been proposed in the field of immunopathology, mainly involving salivary gland disease. We evaluated the responses of serum and salivary IL-6 in two different groups of athletes submitted to different types of controlled strenuous exercise (spinning activity and maximal isokinetic test). Serum and salivary samples for IL-6 measurements, and serum samples for lactate and myoglobin determination before and after exercise, were obtained. Salivary IL-6 was measured by ELISA after dilution experiments and compared with results obtained by immunoradiometric assay. Spinning activity elicited significant increases in all the variables, and no correlation was found among the respective variations. A significant response to the isokinetic exercise was observed for serum IL-6, lactate and myoglobin only; no correlation was found between serum and salivary IL-6. Our study demonstrated that serum and salivary IL-6 responses to exercise are dissociated, possibly in relation to the lack of relationships between the systemic/muscular and the salivary routes of IL-6 production. Analytical issues that concern IL-6 measurement in saliva deserve attention, notably regarding the collection method used to absorb saliva. Concomitant monitoring of serum markers of inflammation, muscle metabolism and damage can provide information about muscle function properties and adaptations to physical effort in different types of athletes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard P, Andersen JL (1998) Correlation between contractile strength and myosin heavy chain isoform composition in human skeletal muscle. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30:1217–1222
Baumann H, Gauldie J (1994) The acute phase response. Immunol Today 15:74–80
Bertoldo U, Nicodemo A, Pallavicini J, Massè A (2003) Acute bilateral compartment syndrome of the thigh induced by spinning training. Injury 34:791–792
Bidwell JP, Gibbons CE, Godsiff S (1996) Acute compartment syndrome of the thigh after weight training. Br J Sports Med 30:264–265
Boppart MD, Aronson D, Gibson L, Roubenoff R, Abad LW, Bean J, Goodyear LJ, Fielding RA (1999) Eccentric exercise markedly increases c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase activity in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 87:1668–1673
Bosco C, Komi PV (1979) Mechanical characteristics and fiber composition of human leg extensor muscles. Eur J Appl Physiol 41:275–284
Brodsky M, Bongiovanni MS (2000) Bilateral lower leg acute exertional compartment syndrome. Orthopedics 23:607–609
Chrousos GP (1995) The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N Engl J Med 332:1351–1362
Convertino VA, Keil LC, Bernauer EM, Greenleaf JE (1981) Plasma volume, osmolality, vasopressin, and renin activity during graded exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 50:123–128
Croisier JL, Camus G, Venneman I, Deby-Dupont G, Juchmes-Ferir A, Lamy M, Crielaard JM, Deby C, Duchateau J (1999) Effects of training on exercise-induced muscle damage and interleukin 6 production. Muscle Nerve 22:208–212
Essen B, Haggmark T (1975) Lactate concentration in type I and II muscle fibres during muscular contraction in man. Acta Physiol Scand 95:344–346
Essen B, Jansson E, Henriksson J, Taylor AW, Saltin B (1975) Metabolic characteristics of fibre types in human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 95:153–165
Fehlandt A Jr, Micheli L (1995) Acute exertional anterior compartment syndrome in an adolescent female. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27:3–7
Flamm SD, Taki J, Moore R, Lewis SF, Keech F, Maltais F (1990) Redistribution of regional and organ blood volume and effect on cardiac function in relation to upright exercise intensity in healthy human subjects. Circulation 81:1550–1559
Gudmundsson A, Ershler WB, Goodman B, Lent SJ, Barczi S, Carnes M (1997) Serum concentrations of interleukin-6 are increased when sampled through an indwelling venous catheter. Clin Chem 43:2199–2201
Harrison MH (1985) Effects on thermal stress and exercise on blood volume in humans. Physiol Rev 65:149–209
Hiscock N, Chan MH, Bisucci T, Darby IA, Febbraio MA (2004) Skeletal myocytes are a source of interleukin-6 mRNA expression and protein release during contraction: evidence of fiber type specificity. FASEB J 18:992–994
Jonsdottir IH, Schjerling P, Ostrowski K, Asp S, Richter EA, Pedersen BK (2000) Muscle contractions induce interleukin-6 mRNA production in rat skeletal muscles. J Physiol (Lond) 528:157–163
Kahan JS, McClellan RT, Burton DS (1994) Acute bilateral compartment syndrome of the thigh induced by exercise. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76:1068–1071
Kuklo TR, Tis JE, Moores LK, Schaefer RA (2000) Fatal rhabdomyolysis with bilateral gluteal, thigh, and leg compartment syndrome after the Army Physical Fitness Test. A case report. Am J Sports Med 28:112–116
Leach RE, Hammond G, Stryker WS (1967) Anterior tibial compartment syndrome. Acute and chronic. J Bone Joint Surg Am 49:451–462
Ljungberg G, Ericson T, Ekblom B, Birkhed D (1997) Saliva and marathon running. Scand J Med Sci Sports 7:214–219
Lonka L, Pedersen RS (1987) Fatal rhabdomyolysis in marathon runner. Lancet 1(8537):857–858
Lyson K, McCann SM (1991) The effect of interleukin-6 on pituitary hormone release in vivo and in vitro. Neuroendocrinology 54:262–266
MacDonald C, Wojtaszewski JF, Pedersen BK, Kiens B, Richter EA (2003) Interleukin-6 release from human skeletal muscle during exercise: relation to AMPK activity. J Appl Physiol 95:2273–2237
Mastorakos G, Chrousos GP, Weber JS (1993) Recombinant interleukin-6 activates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 77:1690–1694
McHale KM, Prahinski JR (1994) Acute exertional compartment syndrome occurring after performance of the army physical fitness test. Orthop Rev 23:749–753
McKee MD, Jupiter JB (1995) Acute exercise-induced bilateral anterolateral leg compartment syndrome in a healthy young man. Am J Orthop 24:862–864
Nau T, Menth-Chiari WA, Seitz H, Vecsei V (2000) Acute compartment syndrome of the thigh associated with exercise. Am J Sports Med 28:120–122
Nieman DC, Henson DA, Smith LL, Utter AC, Vinci DM, Davis JM, Kaminsky DE, Shute M. (2001) Cytokine changes after a marathon race. J Appl Physiol 91:109–114
O’Connor PJ, Corrigan DL (1987) Influence of short-term cycling on salivary cortisol levels. Med Sci Sports Exerc 19:224–228
Ostrowski K, Hermann C, Bangash A, Schjerling P, Nielsen JN, Pedersen BK (1998a) A trauma-like elevation of plasma cytokines in humans in response to treadmill running. J Physiol (Lond) 513:889–894
Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Zacho M, Asp S, Pedersen BK (1998b) Evidence that interleukin-6 is produced in human skeletal muscle during prolonged running. J Physiol (Lond) 508:949–953
Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Asp S, Schjerling P, Pedersen BK (1999) Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine balance in strenuous exercise in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 515:287–291
Ostrowski K, Schjerling P, Pedersen BK (2000) Physical activity and plasma interleukin-6 in humans—effect of intensity of exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 83:512–515
Papanicolaou DA, Vgontzas AN (2000) Interleukin-6: the endocrine cytokine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:1331–1333
Papanicolaou DA, Petrides JS, Tsigos C, Bina S, Kalogeras KT, Wilder R, Gold PW, Deuster PA, Chrousos GP (1996) Exercise stimulates interleukin-6 secretion: inhibition by glucocorticoids and correlation with catecholamines. Am J Physiol 271:E601–E605
Pedersen BK (2000) Special feature for the Olympics: effects of exercise on the immune system: exercise and cytokines. Immunol Cell Biol 78:532–535
Port K (1991) Serum and saliva cortisol responses and blood lactate accumulation during incremental exercise testing. Int J Sports Med 12:490–494
Power RA, Greengross P (1991) Acute lower leg compartment syndrome. Br J Sports Med 25:218–220
Presnal BP, Heavilon JA (1995) Exercise-induced acute compartment syndrome of the thigh. Case report. Am J Knee Surg 8:77–79
Rhodus N, Dahmer L, Lindemann K, Rudney J, Mathur A, Bereuter J (1998) s-IgA and cytokine levels in whole saliva of Sjogren’s syndrome patients before and after oral pilocarpine hydrochloride administration: a pilot study. Clin Oral Investig 2:191–196
Riad-Fahmy D, Read GF, Walker RF, Walker SM, Griffiths K (1987) Determination of ovarian steroid hormone levels in saliva. An overview. J Reprod Med 32:254–272
Robinson SJ (2000) Acute quadriceps compartment syndrome and rhabdomyolysis in a weight lifter using high-dose creatine supplementation. J Am Board Fam Pract 13:134–137
Rohde T, MacLean DA, Richter EA, Kiens B, Pedersen BK (1997) Prolonged submaximal eccentric exercise is associated with increased levels of plasma IL-6. Am J Physiol 273:E85–E91
Ronsen O, Lea T, Bahr R, Pedersen BK (2002) Enhanced plasma IL-6 and IL-1ra responses to repeated vs. single bouts of prolonged cycling in elite athletes. J Appl Physiol 92:2547–2553
Shirtcliff EA, Granger DA, Schwartz E, Curran MJ (2001) Use of salivary biomarkers in biobehavioral research: cotton-based sample collection methods can interfere with salivary immunoassay results. Psychoneuroendocrinology 26:165–173
Smith LL, Anwar A, Fragen M, Rananto C, Johnson R, Holbert D (2000) Cytokines and cell adhesion molecules associated with high-intensity eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 82:61–67
Starkie RL, Arkinstall MJ, Koukoulas I, Hawley JA, Febbraio MA (2001) Carbohydrate ingestion attenuates the increase in plasma interleukin-6, but not skeletal muscle interleukin-6 mRNA, during exercise in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 533:585–591
Steensberg A, van Hall G, Osada T, Sacchetti M, Saltin B, Klarlund Pedersen B (2000) Production of interleukin-6 in contracting human skeletal muscles can account for the exercise-induced increase in plasma interleukin-6. J Physiol (Lond) 529:237–242
Steensberg A, Febbraio MA, Osada T, Schjerling P, van Hall G, Saltin B, Pedersen BK (2001) Interleukin-6 production in contracting human skeletal muscle is influenced by pre-exercise muscle glycogen content. J Physiol (Lond) 537:633–639
Streckfus C, Bigler L, Navazesh M, Al-Hashimi I (2001) Cytokine concentrations in stimulated whole saliva among patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome, secondary Sjogren’s syndrome, and patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome receiving varying doses of interferon for symptomatic treatment of the condition: a preliminary study. Clin Oral Investig 5:133–135
Stupnicki R, Obminski Z (1992) Glucocorticoid response to exercise as measured by serum and salivary cortisol. Eur J Appl Physiol 65:546–549
Tesch P, Sjodin B, Thorstensson A, Karlsson J (1978) Muscle fatigue and its relation to lactate accumulation and LDH activity in man. Acta Physiol Scand 103:413–420
Thorstensson A, Karlsson J (1976) Fatiguability and fibre composition of human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 98:318–322
Thuma JR, Gilders R, Verdun M, Loucks AB (1995) Circadian rhythm of cortisol confounds cortisol responses to exercise: implications for future research. J Appl Physiol 78:1657–1664
Tishler M, Yaron I, Shirazi I, Yaron M (1999) Hydroxychloroquine treatment for primary Sjogren’s syndrome: its effect on salivary and serum inflammatory markers. Ann Rheum Dis 58:253–256
Turnbull AV, Rivier CL (1999) Regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis by cytokines: actions and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev 79:1–71
Vgontzas AN, Papanicolaou DA, Bixler EO, Lotsikas A, Zachman K, Kales A, Prolo P, Wong ML, Licinio J, Gold PW, Hermida RC, Mastorakos G, Chrousos GP (1999) Circadian interleukin-6 secretion and quantity and depth of sleep. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:2603–2607
Vining RF, McGinley RA, Symons RG (1983) Hormones in saliva: mode of entry and consequent implications for clinical interpretation. Clin Chem 29:1752–1756
Wise JJ, Fortin PT (1997) Bilateral, exercise-induced thigh compartment syndrome diagnosed as exertional rhabdomyolysis. A case report and review of the literature. Am J Sports Med 25:126–129
Worthman CM, Stallings JF, Hofman LF (1990) Sensitive salivary estradiol assay for monitoring ovarian function. Clin Chem 36:1769–1773
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by grants of University of Turin (“fondi ex-60%”) and by MIUR Project “ENERME” (2003062904_002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minetto, M., Rainoldi, A., Gazzoni, M. et al. Differential responses of serum and salivary interleukin-6 to acute strenuous exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 93, 679–686 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1241-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1241-z