Abstract
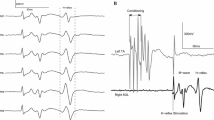
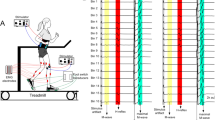
The behaviour of the soleus H-reflex is considered to be motor task-dependent. However, the speed of movements as well as the motor recruitment level is altered when motor tasks are changed. Therefore it is ambiguous to what extent the motor task-dependent changes found between walking and running, for example, are simply due to changes in these two parameters. The purpose of this study was to investigate how movement speed and motor recruitment level separately influence the soleus H-reflex behaviour when the motor task is unchanged. Soleus H-reflexes were elicited during pedalling at different cadences and crank loads, by which movement speed and muscle recruitment level were modified separately. The H-reflex gain was expressed as the slope of the linear relation between the reflex amplitudes and the background electromyelogram (EMG), and the reflex threshold was expressed by the intercept. The results showed a decrease in reflex gain by 54% ( P =0.001) when the speed of movement was doubled from 40 to 80 rpm (repetitions per minute) without changes in the level of soleus EMG activity. Reflex gain decreased 40% ( P =0.002) when the soleus EMG level was increased by 47% without changing the speed of movement. No significant changes were found in the reflex threshold. We conclude that as speed of movement and motor recruitment level influence the gain of the soleus H-reflex, it is significant that these two parameters are comparable before changes in H-reflexes are stated to be task-dependent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avela J, Kyrolainen H, Komi PV (2001) Neuromuscular changes after long-lasting mechanically and electrically elicited fatigue. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:317–325
Boorman G, Becker WJ, Morrice BL, Lee RG (1992) Modulation of the soleus H-reflex during pedalling in normal humans and in patients with spinal spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:1150–1156
Broker J, Gregor R (1990) A dual piezoelectric force pedal for kinetic analysis of cycling. Int J Sports Biomech 6:394–403
Brooke JD, McIlroy WE, Collins DF (1992) Movement features and H-reflex modulation. I. Pedalling versus matched controls. Brain Res 582:78–84
Brooke JD, Cheng J, Collins DF, McIlroy WE, Misiaszek JE, Staines WR (1997) Sensori-sensory afferent conditioning with leg movement: gain control in spinal reflex and ascending paths. Prog Neurobiol 51:393–421
Capaday C (1995) The effects of baclofen on the stretch reflex parameters of the cat. Exp Brain Res 104:287–296
Capaday C (1997) Neurophysiological methods for studies of the motor system in freely moving human subjects. J Neurosci Methods 74:201–218
Capaday C, Stein RB (1986) Amplitude modulation of the soleus H-reflex in the human during walking and standing. J Neurosci 6:1308–1313
Capaday C, Stein RB (1987a) A method for simulating the reflex output of a motoneuron pool. J Neurosci Methods 21:91–104
Capaday C, Stein RB (1987b) Difference in the amplitude of the human soleus H reflex during walking and running. J Physiol (Lond) 392:513–522
Capaday C, Stein RB (1989) The effects of postsynaptic inhibition on the monosynaptic reflex of the cat at different levels of motoneuron pool activity. Exp Brain Res 77:577–584
Cheng J, Brooke JD, Misiaszek JE, Staines WR (1995) The relationship between the kinematics of passive movement, the stretch of extensor muscles of the leg and the change induced in the gain of the soleus H reflex in humans. Brain Res 672:89–96
Crenna P, Frigo C (1987) Excitability of the soleus H-reflex arc during walking and stepping in man. Exp Brain Res 66:49–60
Crone C, Hultborn H, Jespersen B, Nielsen J (1987) Reciprocal Ia inhibition between ankle flexors and extensors in man. J Physiol (Lond) 389:163–185
Crone C, Johnsen LL, Hultborn H, Orsnes GB (1999) Amplitude of the maximum motor response (Mmax) in human muscles typically decreases during the course of an experiment. Exp Brain Res 124:265–270
Curtis DR, Lacey G (1998) Prolonged GABA(B) receptor-mediated synaptic inhibition in the cat spinal cord: an in vivo study. Exp Brain Res 121:319–333
Edamura M, Yang JF, Stein RB (1991) Factors that determine the magnitude and time course of human H-reflexes in locomotion. J Neurosci 11:420–427
Faist M, Dietz V, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1996) Modulation, probably presynaptic in origin, of monosynaptic Ia excitation during human gait. Exp Brain Res 109:441–449
Ferris DP, Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Farley CT, Dyhre-Poulsen P (2001) Soleus H-reflex gain in humans walking and running under simulated reduced gravity. J Physiol (Lond) 530:167–180
Garland SJ, McComas AJ (1990) Reflex inhibition of human soleus muscle during fatigue. J Physiol (Lond) 429:17–27
Garrett M, Kerr T, Caulfield B (1999) Phase-dependent inhibition of H-reflexes during walking in humans is independent of reduction in knee angular velocity. J Neurophysiol 82:747–753
Gosgnach S, Quevedo J, Fedirchuk B, McCrea DA (2000) Depression of group Ia monosynaptic EPSPs in cat hindlimb motoneurones during fictive locomotion. J Physiol (Lond) 526:639–652
Gossard JP (1996) Control of transmission in muscle group IA afferents during fictive locomotion in the cat. J Neurophysiol 76:4104–4112
Gottlieb GL, Agarwal GC (1971) Effects of initial conditions on the Hoffman reflex. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:226–230
Gregor RJ, Broker JP, Ryan MM (1991) The biomechanics of cycling. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 19:127–169
Hull ML, Jorge M (1985) A method for biomechanical analysis of bicycle pedalling. J Biomech 18:631–644
Kautz S, Feltner M, Coyle E, Baylor A (1991) The pedaling technique of elite endurance cyclists: changes with increasing workload at constant cadence. Int J Sports Biomech 7:29–53
Lepers R, Maffiuletti NA, Rochette L, Brugniaux J, Millet GY (2002) Neuromuscular fatigue during a long-duration cycling exercise. J Appl Physiol 92:1487–1493
Llewellyn M, Yang JF, Prochazka A (1990) Human H-reflexes are smaller in difficult beam walking than in normal treadmill walking. Exp Brain Res 83:22–28
Marsden CD, Merton PA, Morton HB (1976) Servo action in the human thumb. J Physiol (Lond) 257:1–44
McIlroy WE, Collins DF, Brooke JD (1992) Movement features and H-reflex modulation. II. Passive rotation, movement velocity and single leg movement. Brain Res 582:85–93
Menard A, Leblond H, Gossard JP (1999) The modulation of presynaptic inhibition in single muscle primary afferents during fictive locomotion in the cat. J Neurosci 19:391–400
Misgeld U, Bijak M, Jarolimek W (1995) A physiological role for GABAB receptors and the effects of baclofen in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 46:423–462
Petersen N, Morita H, Nielsen J (1999) Modulation of reciprocal inhibition between ankle extensors and flexors during walking in man. J Physiol (Lond) 520:605–619
Rossignol S (1998) Presynaptic inhibition and neural control. Oxford University Press, New York
Schieppati M (1987) The Hoffmann reflex: a means of assessing spinal reflex excitability and its descending control in man. Prog Neurobiol 28:345–376
Schneider C, Lavoie BA, Capaday C (2000) On the origin of the soleus H-reflex modulation pattern during human walking and its task-dependent differences. J Neurophysiol 83:2881–2890
Simonsen EB, Dyhre-Poulsen P (1999) Amplitude of the human soleus H reflex during walking and running. J Physiol (Lond) 515: 929–939
Stein RB, Yang JF, Belanger M, Pearson KG (1993) Modification of reflexes in normal and abnormal movements. Prog Brain Res 97:189–196
Voigt M, Chelli F, Frigo C (1998a) Changes in the excitability of soleus muscle short latency stretch reflexes during human hopping after 4 weeks of hopping training. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 78:522–532
Voigt M, Dyhre-Poulsen P, Simonsen EB (1998b) Modulation of short latency stretch reflexes during human hopping. Acta Physiol Scand 163:181–194
Voigt M, Vanwanseele B, Riso RR (1998c) The human soleus H-reflex modulation during the transition from relaxed sitting to walking. Soc Neurosci 838:12
Winter DA (1991) Biomechanics and motor control of human movement. Wiley, New York
Zehr P (2002) Considerations for use of the Hoffmann reflex in exercise studies. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:455–468
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Danish National Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, B., Voigt, M. Changes in the gain of the soleus H-reflex with changes in the motor recruitment level and/or movement speed. Eur J Appl Physiol 93, 19–29 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1152-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1152-z