Abstract
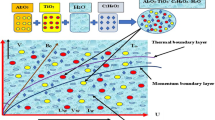
Herein, we examined the impact of Brownian motion and thermophoresis on MHD stagnation-point nanofluid flow toward vertical stretching surface using the non-Newtonian Prandtl fluid model. The governing mathematical model consists of a set of nonlinear partial differential equations along with associated boundary conditions. The similarity conversion technique is adopted to convert them to nonlinear ordinary differential equations, which are then solved numerically using the Finite-Difference Crank–Nicolson Method. The simulation is performed to examine flow, heat and mass transfer due to changes in physical parameters. The study revealed that, in the buoyancy opposing flow region, the heat transfer rate increases, and the mass transfer rate decreases due to an increase in Brownian motion. Moreover, augmentation in thermophoresis effects enhances the mass transfer rate, while the heat transfer rate is not dominantly affected. It is further noticed that the FDM-based Crank–Nicolson scheme is well matched and efficient to deal with the solution of such kinds of nonlinear physical models arising in mechanics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masuda, H., Ebata, A., Teramae, K., Hishinuma, N.: Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles. Netsu. Bussei. 7, 227–233 (1993)
Choi, S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: Siginer, D.A., Wang, H. P. (eds.) Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows, ASME, FED-Vol. 231/MD-Vol. 66, 99–105 (1995)
Kwak, K., Kim, C.: Viscosity and thermal conductivity of copper oxide nanofluid dispersed in ethylene glycol. Korea Aust. Rheol. J. 17, 35–40 (2005)
Wong, K.V., Leon, O.D.: Applications of nanofluids: current and future. Adv. Mech. Eng. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/519659
Eastman, J.A., Choi, S.U.S., Li, S., Yu, W., Thompson, L.J.: Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 718–720 (2001)
Das, S.K., Putra, N., Thiesen, P.H., Roetzel, W.: Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids. J. Heat Trans. 125, 567–574 (2003)
Tiwari, R.K., Das, M.K.: Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 50, 2002–2018 (2007)
Buongiorno, J.: Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006)
Soomro, F.A., Zaib, A., Haq, R.U., Sheikholeslami, M.: Dual nature solution of water functionalized copper nanoparticles along a permeable shrinking cylinder: FDM approach. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 129, 1242–1249 (2019)
Soomro, F.A., Haq, R.U., Khan, Z.H., Zhang, Q.: Numerical study of entropy generation in MHD water-based carbon nanotubes along an inclined permeable surface. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 412 (2017)
Lund, L.A., Omar, Z., Khan, I., Seikh, A.H., Sherif, E.S.M., Nisar, K.S.: Stability analysis and multiple solution of Cu–Al2O3/H2O nanofluid contains hybrid nanomaterials over a shrinking surface in the presence of viscous dissipation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 421–432 (2020)
Khan, U., Zaib, A., Khan, I., Baleanud, D., Sherif, E.S.M.: Comparative investigation on MHD nonlinear radiative flow through a moving thin needle comprising two hybridized AA7075 and AA7072 alloys nanomaterials through binary chemical reaction with activation energy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.02.008
Hamid, M., Usman, M., Zubair, T., Haq, R.U., Wang, W.: Shape effects of MoS2 nanoparticles on rotating flow of nanofluid along a stretching surface with variable thermal conductivity: a Galerkin approach. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 124, 706–714 (2018)
Usman, M., Hamid, M., Zubair, T., Haq, R.U., Wang, W.: Cu-Al2O3/Water hybrid nanofluid through a permeable surface in the presence of nonlinear radiation and variable thermal conductivity via LSM. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 126, 1347–1356 (2018)
Kata, S., Ganganapalli, S., Kuppalapalle, V.: Effect of thermophoresis and Brownian motion on the melting heat transfer of a Jeffrey fluid near a stagnation point towards a stretching surface: Buongiorno’s model. Heat Trans. Asian Res. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.21544
Ramana Reddy, J.V., Sugunamma, V., Sandeep, N.: Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on unsteady MHD nanofluid flow over a slendering stretching surface with slip effects. Alexandria Eng. J. 57, 2465–2473 (2017)
Mabood, F., Ibrahim, S.M., Khan, W.A.: Framing the features of Brownian motion and thermophoresis on radiative nanofluid flow past a rotating stretching sheet with magnetohydrodynamics. Results Phys. 6, 1015–1023 (2016)
Rafique, K., Anwar, M.I., Misiran, M., Khan, I., Seikh, A.H., Sherif, E.S.M., Nisar, K.S.: Brownian motion and thermophoretic diffusion effects on micropolar type nanofluid flow with soret and dufour impacts over an inclined sheet: keller-box simulations. Energies 12, 4191 (2019)
Ibrahim, W., Makinde, O.D.: Magnetohydrodynamic stagnation point flow of a power-law nanofluid towards a convectively heated stretching sheet with slip. Proc. Instit. Mech. Eng. E J. Process Mech. Eng. 230(5), 345–354 (2016)
Ahmed, J., Mahmood, T., Iqbal, Z., Shahzad, A., Ali, R.: Axisymmetric flow and heat transfer over an unsteady stretching sheet in power law fluid. J. Mol. Liquids 221, 386–393 (2016)
Hayat, T., Aziz, A., Muhammad, T., Ahmed, B.: On magnetohydrodynamic flow of second grade nanofluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet. J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 408, 99–106 (2016)
Khan, M., Rahman, M.U.: Flow and heat transfer to modified second grade fluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet. AIP Adv. 5, 087157 (2015)
Shehzad, S.A., Waqas, M., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T.: Flow and heat transfer over an unsteady stretching sheet in a Micro polar fluid with convective boundary conditions. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 9, 1437–1445 (2016)
Waqas, M., Farooq, M., Khan, M.I., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T., Yasmeen, T.: Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) mixed convection flow of micro polar liquid due to nonlinear stretched sheet with convective condition. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 102, 766–772 (2016)
Abbas, Z., Sheikh, M., Motsa, S.S.: Numerical solution of binary chemical reaction on stagnation point flow of Casson fluid over a stretching shrinking sheet with thermal radiation. Energy 95, 12–20 (2016)
Hayat, T., Khan, M.I., Waqas, M., Yasmeen, T., Alsaedi, A.: Viscous dissipation effect in flow of magneto nano fluid with variable properties. J. Mol. Liq. 22, 47–54 (2016)
Ali, M., Khan, W.A., Sultan, F., Shahzad, M.: Numerical investigation on thermally radiative time-dependent Sisko nanofluid flow for curved surface. Phys. A (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.124012
Khan, U., Zaib, A., Shah, Z., Baleanu, D., Sherif, E.S.M.: Impact of magnetic field on boundary-layer flow of Sisko liquid comprising nanomaterials migration through radially shrinking/stretching surface with zero mass flux. J. Mater. Res. Technol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.107
Akbar, N.S., Khan, Z.H., Haq, R.U., Nadeem, S.: Dual solutions in MHD stagnation-point flow of Prandtl fluid impinging on shrinking sheet. Appl. Math. Mech. Engl. Ed. 35, 813–820 (2014)
Akbar, N.S.: Blood flow analysis of Prandtl fluid model in tapered stenosed arteries. Ain Shams Eng. J. 5, 1267–1275 (2014)
Nadeem, S., Ijaz, S., Akbar, N.S.: Nanoparticle analysis for blood flow of Prandtl fluid model with stenosis. Int. Nano Lett. 3, 1–13 (2013)
Alsaedi, A., Batool, N., Yasmin, H., Hayat, T.: Convective heat transfer analysis on Prandtl fluid model with peristalsis. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 10, 197–208 (2013)
Akbar, N.S., Nadeem, S., Lee, C.H.: Peristaltic flow of a Prandtl fluid model in an asymmetric channel. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 7, 687–695 (2012)
Soomro, F.A., Haq, R.U., Khan, Z.H., Zhang, Q.: Passive control of nanoparticle due to convective heat transfer of Prandtl fluid model at the stretching surface. Chin. J. Phys. 55, 1561–1568 (2017)
Soomro, F.A., Khan, Z.H., Haq, R.U., Zhang, Q.: Heat transfer analysis of Prandtl liquid nano fluid in the presence of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. Results Phys. 10, 379–384 (2018)
Rehman, K.U., Khan, A.A., Malik, M.Y., Makinde, O.D.: Thermophysical aspects of stagnation point magnetonanofluid flow yields by an inclined stretching cylindrical surface: a non-Newtonian fluid model. J. Brazil Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39(9), 3669–3682 (2017)
Makinde, O.D., Khan, W.A., Khan, Z.H.: Stagnation point flow of MHD chemically reacting nanofluid over a stretching convective surface with slip and radiative heat. Proc. Instit. Mech. Eng. E J. Process Mech. Eng. 231(4), 695–703 (2017)
Makinde, O.D., Khan, W.A., Khan, Z.H.: Buoyancy effects on MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid past a convectively heated stretching/shrinking sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 62, 526–533 (2013)
Malik, M.Y., Makinde, O.D.: Parabolic curve fitting study subject to Joule heating in MHD thermally stratified mixed convection stagnation point flow of Eyring-Powell fluid induced by an inclined cylindrical surface. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 30(4), 440–449 (2018)
Hamid, M., Usman, M., Haq, R.U., Tian, Z.F.: A Galerkin approach to analyze MHD flow of nanofluid along converging/diverging channels. Arch. Appl. Mech. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01861-6
Soid, S.K., Merkin, J., Ishak, A., Pop, I.: Axisymmetric stagnation-point flow and heat transfer due to stretching/shrinking vertical plate with surface second-order velocity slip. Meccanica 52, 139–151 (2017)
Shoail, A., Uddin, M.J., Rashidi, M.M.: Numerical study of free convective flow of nanofluid over chemically reactive porous flat vertical plate with second-order slip model. J. Aerosp. Eng. 29, 1 (2016)
Wu, L.: A slip model for rarefied gas flows at arbitrary Knudsen number. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 253103 (2008)
Jing, L., Zheng, L.C., Liu, L.: MHD viscoelastic flow and heat transfer over a vertical stretching sheet with Cattaneo-Christov heat flux effects. J. Mol. Liq. 221, 19–25 (2016)
Noor, M.F.M., Haq, R.U., Nadeem, S., Hashim, I.: Mixed convection stagnation-point flow of a micro polar nanofluid along a vertically stretching surface with slip effects. Meccanica 50, 2007–2022 (2015)
Hamid, M., Usman, M., Khan, Z.H., Haq, R.U., Wang, W.: Numerical study of unsteady MHD flow of Williamson nanofluid in a permeable channel with heat source/sink and thermal radiation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133(12), 527 (2018)
Hamid, M., Zubair, T., Usman, M., Haq, R.U.: Numerical investigation of fractional-order unsteady natural convective radiating flow of nanofluid in a vertical channel. AIMS Math. 4(5), 1416 (2019)
Hamid, M., Zubair, T., Usman, M., Khan, Z.H., Wang, W.: Natural convection effects on heat and mass transfer of slip flow of time-dependent Prandtl fluid. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 6(4), 584–592 (2019)
Carstens, S., Kuhl, D.: Higher-order accurate implicit time integration schemes for transport problem. Arch. Appl. Mech. 82, 1007–1039 (2012)
Hamid, M., Usman, M., Wang, W., Tian, Z.F.: A stable computational approach to analyze semi-relativistic behavior of fractional evolutionary problems. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/num.22617
Khan, W.A., Pop, I.: Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 53, 2477–2483 (2010)
Wang, C.Y.: Free convection on a vertical stretching surface. J. Appl. Math. Mech. (ZAMM) 69, 418–420 (1989)
Gorla, R.S.R., Sidawi, I.: Free convection on a vertical stretching surface with suction and blowing. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 52, 247–257 (1994)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the referees for their valuable suggestions that help improve the manuscript's content. The corresponding author (M. Hamid) is sincerely grateful to Fudan University for providing research opportunities through the Postdoctoral International Exchange Fellowship. China Postdoctoral Science Foundation supported this work (No. 2020M681135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soomro, F.A., Haq, R.U. & Hamid, M. Brownian motion and thermophoretic effects on non-Newtonian nanofluid flow via Crank–Nicolson scheme. Arch Appl Mech 91, 3303–3313 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-01966-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-01966-6