Abstract
In this paper, a comprehensive analysis is presented to investigate a codimension two bifurcation that exists in a nonlinear railway bogie dynamic system combining theoretical analysis with numerical investigation. By using the running velocity V and the primary longitudinal stiffness \(K_{1x}\) as bifurcation parameters the first and second Lyapunov coefficients are calculated to determine which kind of Hopf bifurcation can happen and how the system states change with the variance of the bifurcation parameters. It is found that multiple solution branches both stable and unstable coexist in a range of the bifurcation parameters which can lead to jumps in the lateral oscillation amplitude of the railway bogie system. Furthermore, reduce the values of the bifurcation parameters gradually. Firstly, the supercritical Hopf bifurcation turns into a subcritical one with multiple limit cycles both stable and unstable near the Hopf bifurcation point. With a further reduction in the bifurcation parameters two saddle-node bifurcation points emerge, resulting in the loss of the stable limit cycle between these two bifurcation points.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kingel, W.: Über den Lauf der Eisenbahnwagen auf gerader Bahn. Organ für die Fortchritte des Eisenbahnwesens in technischer Beziehung. Neue Folge 20(4), 113–123 (1883)
Huilgol, R.R.: Hopf-Friedrichs bifurcation and the hunting of a railway axle. Q. J. Appl. Mech. 36(1), 85–94 (1978)
Cooperrider, N.K.: The hunting behavior of conventional railway trucks. J. Eng. Ind. 94(2), 752–761 (1972)
True, H.: Railway vehicle chaos and asymmetric hunting. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 20(sup1), 625–637 (1992)
Isaksen, P., True, H.: On the ultimate transition to chaos in the dynamics of Cooperrider’s bogie. Chaos Solitons Fractals 8(4), 559–581 (1997)
Polach, O.: On non-linear methods of bogie stability assessment using computer simulations. Inst. Mech. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 220(1), 13–27 (2006)
Polach, O.: Characteristic parameters of nonlinear wheel/rail contact geometry. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 48(S1), 19–36 (2010)
Polach, O., Kaiser, I.: Comparison of methods analyzing bifurcation diagram and hunting of complex rail vehicle models. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 7(4), 041005 (2012)
True, H., Jensen, J.: Chaos and asymmetry in railway vehicle dynamics. Period. Polytechn. Ser. Transp. Eng. 22(1), 55–68 (1994)
Gao, X.J., True, H., Li, Y.H.: Lateral dynamic features of a railway vehicle. Inst. Mech. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 230(3), 909–923 (2016)
Petersen, D., Hoffmann, M.: Curving dynamics of railway vehicles. Report, The Technical University of Denmark, Denmark (2002)
True, H., Hansen, T.G. and Lundell, H.: On the quasi-stationary curving dynamics of a railroad truck. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ASME/IEEE Joint Rail Conference, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp 131–138 (2005)
Rezvani, M., Mazraeh, A.: Dynamics and stability analysis of a freight wagon subjective to the railway track and wheelset operational conditions. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 61, 22–34 (2017)
De Pater, A.D.: The approximation determination of the hunting movement of a railway vehicle by aid of the method of Krylov and Bogoljubov. Appl. Sci. Res. 10(1), 205–228 (1961)
Law, E.H., Brand, R.S.: Analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of a railway vehicle wheelset. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 95, 28–35 (1973)
Knudsen, C., Feldberg, R., Jaschinski, A.: Nonlinear dynamic phenomena in the behavior of a railway wheelset model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2(5), 389–404 (1991)
Kaas-Petersen, C.: PATH-User’s Guide. Department of Applied Mathematical Studies and Centre for Nonlinear Studies, University of Leeds, Leeds (1987)
Zeng, J.: Numerical computations of the hunting bifurcation and limit cycles for railway vehicle system. J. China Railw. Soc. 15(3), 13–18 (1996)
Gao, X.J.: The “resultant bifurcation diagram” method and its application to bifurcation behaviors of a symmetric railway bogie system. Nonlinear Dyn. 70(1), 363–380 (2012)
Kalker, J.J.: A fast algorithm for the simplified theory of rolling contact. Int. J. Veh. Styst. Dyn. 11(1), 1–13 (1982)
Shabana, A.A., Zaazaa, K.E., Sugiyama, H.: Railroad Vehicle Dynamics: A Computational Approach. CRC Press, London (2007)
von Wagner, U.: Nonlinear dynamic behaviour of a railway wheelset. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 47(5), 627–640 (2009)
Kuznetsov, Y.A.: Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory. Springer, New York (2004)
Wickens, A.H.: The dynamic stability of railway vehicle wheelsets and bogies having profiled wheels. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1(3), 319–334 (1965)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the China Railway Corporation under Grant No. YS2016J-40 and the Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC) Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
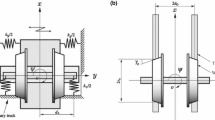
Appendix: Description and values of the railway bogie system parameters
Appendix: Description and values of the railway bogie system parameters
Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
\(M_{t}\) | Mass of the bogie frame | 2056 kg |
\(J_{tz}\) | Yaw moment of inertia of the bogie frame | \(3800~\mathrm{kg\,{m}}^2\) |
\(M_{w}\) | Mass of the wheelset | 1627 kg |
\(J_{wz}\) | Yaw moment of inertia of the wheelset | \(830~\mathrm{kg\,{m}}^2\) |
\(K_{1x}\) | Primary longitudinal stiffness (per axle box) | – |
\(K_{1y}\) | Primary lateral stiffness (per axle box), | \(7.0~\mathrm{MN\,{m}}^{-1}\) |
\(C_{1x}\) | Primary longitudinal damper (per axle box) | \(0.0~\mathrm{MN\,{s}\,{m}}^{-1}\) |
\(C_{1y}\) | Primary lateral damper (per axle box), | \(0.0~\mathrm{MN\,{s}\,{m}}^{-1}\) |
\(K_{2x}\) | Secondary longitudinal stiffness (per side of bogie) | \(0.133~\mathrm{MN\,{m}}^{-1}\) |
\(K_{2y}\) | Primary lateral stiffness (per side of bogie), | \(0.133~\mathrm{MN\,{m}}^{-1}\) |
\(C_{2x}\) | Primary longitudinal damper (per side of bogie) | \(0.0~\mathrm{MN\,{s}\,{m}}^{-1}\) |
\(C_{2y}\) | Primary lateral damper (per side of bogie), | \(0.015~\mathrm{MN\,{s}\,{m}}^{-1}\) |
\(r_0\) | Centered wheel rolling radius | 0.46 m |
b | Half of the rolling cycle gauge | 0.7465 m |
\(b_1\) | Half of the swing arm | 1.02 m |
\(b_2\) | Half distance of the secondary springs | 0.95 m |
\(b_3\) | Half distance of the secondary dampers | 1.275 m |
l | Half of the axle distance | 1.25 m |
v | Running speed of the bogie | – |
\(f_{11}\) | Longitudinal creep coefficient | 12 MN |
\(f_{22}\) | Lateral creep coefficient | 12 MN |
W | Axle load | 103.936 kN |
\(\lambda \) | Conicity of the wheel when \(y_{wi}=0\) | 0.2 |
\(\delta _1\) | Nonlinear coefficient of wheel–rail contact force | \(-1.6\times 10^{11}~\mathrm{N\,{m^{-3}}}\) |
\(\delta _2\) | Nonlinear coefficient of wheel–rail contact force | \(1.6\times 10^{15}~\mathrm{N\,{m^{-5}}}\) |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., True, H. & Dai, H. A codimension two bifurcation in a railway bogie system. Arch Appl Mech 88, 391–404 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-017-1314-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-017-1314-1