Abstract
The perichromatin region is an elusive zone of the cell nucleus located at the periphery of the condensed chromatin areas. This region is visible at the electron microscope level under special staining treatments, otherwise it is merged with the border of condensed chromatin. In this 200 nm-thick area, several fundamental cell processes take place, such as replication, DNA repair and transcription. In addition, RNA processing occurs in the perichromatin region, including 5′-capping and 3′-polyadenylation as well as splicing. Recently, it has become clear that also some epigenetics modifications take place there, such as methylation of DNA and RNA on cytosine and adenosine. In summary, this thin interface between chromatin and the interchromatinic space represents the zone where the majority of the functions of DNA in interphase occur, in a place where there is no steric hindrance of condensed chromatin, the products can easily move away toward their target and the enzymes can freely dock.


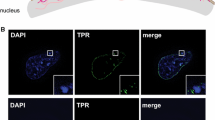
Reprinted from Trentani et al. Eur J Histochem 47:195–200, 2003, with permission. Bar = 30 nm, b Rat thymocyte, anti-5mC labelling. Most of the labelling occurs at the surface of chromatin, while the more distant few grains most probably label methylated RNA. c Hep-2 cell. After a short pulse of BrdU, beginning of replication is indicated by the labelling (green dots) present at the periphery of the chromatin. d Hep-2 cell. Labelling with an anti-DNA/RNA hybrid. The gold grains localized at the sites of transcription where the hybrids are present. Bar 200 nm
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allfrey VG (1966) Control mechanisms in ribonucleic acid synthesis. Cancer Res 26(9):2026–2040
Bernhard W (1969) A new staining procedure for electron microscopical cytology. J Ultrastruct Res 27(3):250–265
Bernhard W, Granboulan N (1963) The fine structure of the cancer cell nucleus. Exp Cell Res 24:19–53
Biggiogera M, Fakan S (1998) Fine structural specific visualization of RNA on ultrathin sections. J Histochem Cytochem 46:389–395
Biggiogera M, Masiello I (2017) Visualizing RNA at electron microscopy by terbium citrate. Methods Mol Biol 1560:277–283
Bouchet-Marquis C, Dubochet J, Fakan S (2006) Cryoelectron microscopy of vitrified sections: a new challenge for the analysis of functional nuclear architecture. Histochem Cell Biol 125(1–2):43–51
Cardinale S, Cisterna B, Bonetti P, Aringhieri C, Biggiogera M, Barabino SM (2007) Subnuclear localization and dynamics of the Pre-mRNA 3′ end processing factor mammalian cleavage factor I 68-kDa subunit. Mol Biol Cell 18(4):1282–1292
Chaudhury A, Chander P, Howe PH (2010) Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) in cellular processes: focus on hnRNP E1’s multifunctional regulatory roles. RNA 16:1449–1462
Cmarko D, Verschure PJ, Martin TE, Dahmus ME, Krause S, Fu XD, Fakan S (1999) Ultrastructural analysis of transcription and splicing in the cell nucleus after bromo-UTP microinjection. Mol Bio Cell 10:211–223
Cmarko D, Verschure PJ, Otte AP, van Driel R, Fakan S (2002) Polycomb group gene silencing proteins are concentrated in the perichromatin compartment of the mammalian nucleus. J Cell Sci 116:335–343
Cortini R, Filion GJ (2018) Theoretical principles of transcription factor traffic on folded chromatin. Nat Commun 9(1):1740
De Boni U (1994) The interphase nucleus as a dynamic structure. Int Rev Cytol 150:149–171
Fakan S (1994) Perichromatin fibrils are in situ forms of nascent transcripts. Trends Cell Biol 4:86–90
Fakan S, Bernhard W (1971) Localisation of rapidly and slowly labelled nuclear RNA as visualized by high resolution autoradiography. Exp Cell Res 67:129–141
Fakan S, Hankok R (1974) Localization of newly-synthesized DNA in a mammalian cell as visualized by high resolution autoradiography. Exp Cell Res 81:95–102
Fakan S, Puvion E (1980) The ultrastructural visualization of nucleolar and extranucleolar RNA synthesis and distribution. Int Rev Cytol 65:255–299
Fakan S, van Driel R (2007) The perichromatin region: a functional compartment in the nucleus that determines large-scale chromatin folding. Semin Cell Dev Biol 18:676–681
Fakan S, Puvion E, Sphor G (1976) Localization and characterization of newly synthesized nuclear RNA in isolate rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res 99:155–164
Fakan S, Leser G, Martin TE (1986) Immunoelectron microscope visualization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigens within spread transcription complexes. J Cell Biol 103:1153–1157
Gall JG, Callan HG (1962) H3 uridine incorporation in lampbrush chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 48:562–570
Görnemann J, Kotovic KM, Hujer K, Neugebauer KM (2005) Cotranscriptional spliceosome assembly occurs in a stepwise fashion and requires the cap binding complex. Mol Cell 19:53–63
Hancock R (2012) Structure of metaphase chromosomes: a role for effects of macromolecular crowding. PLoS One 7(4):e36045
Hozak P, Hassan AB, Jackson DA, Cook PR (1993) Visualization of replication factories attached to a nucleoskeleton. Cell 73:361–373
Huang S, Deerinck TJ, Ellisman MH, Spector DL (1994) In vivo analysis of the stability and transport of nuclear poly(A) + RNA. J Cell Biol 126:877–899
Jaunin F, Visser AE, Cmarko D, Aten JA, Fakan S (2000) Fine structural in situ analysis of nascent DNA movement following DNA replication. Exp Cell Res 260:313–323
Kasowitz SD, Ma J, Anderson SJ, Leu NA, Xu Y, Gregory BD, Wang PJ (2018) Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and splicing during mouse oocyte development. PLOS Genet 14:e1007412
Knuckles P, Bühler M (2018) Adenosine methylation as a molecular imprint defining the fate of RNA. FEBS Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13107. (Epub ahead of print)
Knuckles P, Carl SH, Musheev M, Niehrs C, Wenger A, Bühler M (2017) RNA fate determination through cotranscriptional adenosine methylation and microprocessor binding. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24:561–569
Manders EMM, Stap J, Strackee J, van Driel R, Aten JA (1996) Dynamic behavior of DNA replication do- mains. Exp Cell Res 226:328 – 335
Markaki Y, Gunkel M, Schermelleh L, Beichmanis S, Neumann J, Heidemann M, Leonahardt H, Eick D, Cremer C, Cremer T (2011) Functional nuclear organization of transcription and DNA replication: a topographical marriage between chromatin domains and the interchromatin compartment. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Bio 75:475–492
Masiello I, Biggiogera M (2017) Ultrastructural localization of 5-methylcytosine on DNA and RNA. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:3057–3064
Mazzotti G, Gobbi P, Manzoli L, Falconi M (1998) Nuclear morphology during the S phase. Microsc Res Tech 40:418–431
Monneron A, Bernhard W (1969) Fine structural organization of the interphase nucleus in some mammalian cells. J Ultrastruct Res 27(3):266–288
Morlando M, Ballarino M, Gromak N, Pagano F, Bozzoni I, Proudfoot NJ (2008) Primary microRNA transcripts are processed co-transcriptionally. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:902–909
Müller WG, Rieder D, Karpova TS, John S, Trajanoski Z, McNally JG (2007) Organization of chromatin and histone modifications at a transcription site. J Cell Biol 177:957–967
Nash RE, Puvion E, Bernhard W (1975) Perichromatin fibrils as components of rapidly labeled extranucleolar RNA. J Ultrastr Res 53:395–405
Niedojadlo J, Perret-Vivancos C, Kalland KH, Cmarko D, Cremer T, Van Driel R, Fakan S (2011) Transcribed DNA is preferentially located in the perichromatin region of mammalian cell nuclei. Exp Cell Res 317:433–444
Puvion E, Bernhard W (1975) Ribonucleoprotein components in liver cell nuclei as visualized by cryoultramicrotomy. J Cell Biol 67(1):200–214
Puvion E, Viron A, Assens C, Leduc EH, Jeanteur P (1984) Immunocytochemical identification of nuclear structures containing snRNPs in isolated rat liver cells. J Ultrast Res 87:180–189
Raska I, Michel LS, Jarnik M, Dundr M, Fakan S, Gasser S, Gassmann M, Hübscher U, Izaurralde E, Martinez E et al (1991) Ultrastructural cryoimmunocytochemistry is a convenient tool for the study of DNA replication in cultured cells. J Electron Microsc Tech 18:91–105
Ris H (1961) Ultrastructure and molecular organization of genetic systems. Can J Genet Cytol 3:95–120
Rouquette J, Genoud C, Vazquez-Nin GH, Kraus B, Cremer T, Fakan S (2009) Revealing the high-resolution three-dimensional network of chromatin and interchromatin space: a novel electron-microscopic approach to reconstructing nuclear architecture. Chromosome Res 17:801–810
Ruthenburg AJ, Allis CD, Wysocka J (2007) Methylation of lysine 4 on histone H3: intricacy of writing and reading a single epigenetic mark. Mol Cell 25:15–30
Sobczak-Thepot J, Harper F, Florentin Y, Zindy F, Brechot C, Puvion E (1993) Localization of cyclin A at the sites of cellular DNA replication. Exp Cell Res 206:43–48
Solimando L, Luijsterburg MS, Vecchio L, Vermeulen W, van Driel R, Fakan S (2009) Spatial organization of nucleotide excision repair proteins after UV-induced DNA damage in the human cell nucleus. J Cell Sci 122:83–91
Spector DL, Fu XD, Maniatis T (1991) Associations between distinct pre-mRNA splicing components and the cell nucleus. EMBO J 10:3467–3481
Spedito A, Cisterna B, Malatesta M, Biggiogera M (2014) Use of halogenated precursors to define a transcription time window after treatment with hypometabolizing molecules. Histochem Cell Biol 141:243–249
Swift H (1959) Studies on nuclear fine structure. Brookhaven Symp Biol 12:134–152
Testillano PS, Gorab E, Risueno MC (1994) A new approach to map transcription sites at the ultrastructural level. J Histochem Cytochem 42:1–10
Trentani A, Testillano PS, Risueño MC, Biggiogera M (2003) Visualization of transcription sites at the electron microscope. Eur J Histochem 47:195–200
Vázquez Nin GH, Echeverría OM, Ortiz R, Ubaldo E, Fakan S (1997) Effects of hypophyseal hormones on transcription and RNA export to the cytoplasm. Exp Cell Res 236:519–526
Visa N, Puvion-Dutilleul F, Harper F, Bachellerie JP, Puvion E (1993) Intranuclear distribution of poly(A) RNA determined by electron microscope in situ hybridization. Exp Cell Res 208:19–34
von Schack ML, Fakan S, Villiger W (1991) Some applications of cryosubstitution in ultrastructural studies of the cell nucleus. Biol Cell 72(1–2):113–119
Watson M (1962) Observations on a granule associated with chromatin in the nuclei of cells of rat and mouse. J Cell Biol 13:162–167
Wee CL, Teo S, Oey NE, Wright GD, VanDongen HMA, VanDongen AMJ (2014) Nuclear Arc interacts with the histone acetyltransferase Tip60 to modify H4K12 acetylation. eNeuro. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0019-14.2014
Xu K, Yang Y, Feng GH, Sun BF, Chen JQ, Li YF, Li W (2017) Metl3-mediated m6A regulates spermatogonial differentiation and meiosis initiation. Cell Res 27:1100–1114
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS, Yang YG (2018) Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res 28:616–624
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR): Dipartimenti di Eccellenza Program (2018–2022)—Dept. of Biology and Biotechnology “L. Spallanzani”, University of Pavia (to M.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masiello, I., Siciliani, S. & Biggiogera, M. Perichromatin region: a moveable feast. Histochem Cell Biol 150, 227–233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-018-1703-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-018-1703-8