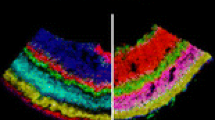
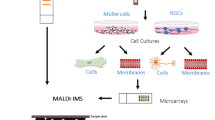
Abstract
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging (MALDI-MSI) is emerging as a powerful tool for the analysis of molecular distributions in biological samples in situ. When compared to classical histology, the major benefit of this method is the ability to identify and localize many molecules in a single tissue sample. MALDI-MSI spatial resolution currently falls short of traditional microscopic methods as it is limited by instrumentation and sample preparation. Tissue preparation steps, such as matrix deposition, are critical when considering strategies to further enhance the spatial resolution. The mammalian retina was selected as the tissue of choice for method development; its stratified anatomy renders it an ideal tissue to test high-resolution MALDI-MSI as the different layers correspond to specific neuronal classes and cellular structures. We compared alcohol-fixed, paraffin-embedded retina to fresh-frozen samples and matrix that had been deposited by spray or by sublimation. We present a lipid imaging method based on MALDI-MSI of frozen retinal sections with sublimated 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid matrix, which results in a highly advanced resolution compared to previous established methods. Hierarchical clustering of the primary data allows robust detection and differentiation of molecular distributions at a spatial resolution between 10 and 20 μm, thus approaching single-cell resolution.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DHB:
-
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
- GCL:
-
Ganglion cell layer
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- INL:
-
Inner nuclear layer
- MALDI-MSI:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging
- MALDI-TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight
- OCT:
-
Optimal cutting temperature compound
- OPL:
-
Outer plexiform layer
- PALDI:
-
Nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionization
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
References
Ablonczy Z, Higbee D, Anderson DM, Dahrouj M, Grey AC, Gutierrez D, Koutalos Y, Schey KL, Hanneken A, Crouch RK (2013) Lack of correlation between the spatial distribution of A2E and lipofuscin fluorescence in the human retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:5535–5542
Alexandrov T, Becker M, Deininger SO, Ernst G, Wehder L, Grasmair M, von Eggeling F, Thiele H, Maass P (2010) Spatial segmentation of imaging mass spectrometry data with edge-preserving image denoising and clustering. J Proteome Res 9:6535–6546
Alexandrov T, Meding S, Trede D, Kobarg JH, Balluff B, Walch A, Thiele H, Maass P (2011) Super-resolution segmentation of imaging mass spectrometry data: solving the issue of low lateral resolution. J Proteomics 75:237–245
Alexandrov T, Becker M, Guntinas-Lichius O, Ernst G, von Eggeling F (2013) MALDI-imaging segmentation is a powerful tool for spatial functional proteomic analysis of human larynx carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139:85–95
Angel PM, Spraggins JM, Baldwin HS, Caprioli R (2012) Enhanced sensitivity for high spatial resolution lipid analysis by negative ion mode matrix assisted laser desorption ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 84:1557–1564
Attia AS, Schroeder KA, Seeley EH, Wilson KJ, Hammer ND, Colvin DC, Manier ML, Nicklay JJ, Rose KL, Gore JC, Caprioli RM, Skaar EP (2012) Monitoring the inflammatory response to infection through the integration of MALDI IMS and MRI. Cell Host Microbe 11:664–673
Balluff B, Rauser S, Meding S, Elsner M, Schone C, Feuchtinger A, Schuhmacher C, Novotny A, Jutting U, Maccarrone G, Sarioglu H, Ueffing M, Braselmann H, Zitzelsberger H, Schmid RM, Hofler H, Ebert MP, Walch A (2011a) MALDI imaging identifies prognostic seven-protein signature of novel tissue markers in intestinal-type gastric cancer. Am J Pathol 179:2720–2729
Balluff B, Schone C, Hofler H, Walch A (2011b) MALDI imaging mass spectrometry for direct tissue analysis: technological advancements and recent applications. Histochem Cell Biol 136:227–244
Boggio KJ, Obasuyi E, Sugino K, Nelson SB, Agar NY, Agar JN (2011) Recent advances in single-cell MALDI mass spectrometry imaging and potential clinical impact. Expert Rev Proteomics 8:591–604
Buttery RG, Hinrichsen CF, Weller WL, Haight JR (1991) How thick should a retina be? A comparative study of mammalian species with and without intraretinal vasculature. Vision Res 31:169–187
Caprioli RM, Farmer TB, Gile J (1997) Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem 69:4751–4760
Chaurand P, Schwartz SA, Billheimer D, Xu BJ, Crecelius A, Caprioli RM (2004) Integrating histology and imaging mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:1145–1155
Chaurand P, Schriver KE, Caprioli RM (2007) Instrument design and characterization for high resolution MALDI-MS imaging of tissue sections. J Mass Spectrom 42:476–489
Chaurand P, Cornett DS, Angel PM, Caprioli RM (2011) From whole-body sections down to cellular level, multiscale imaging of phospholipids by MALDI mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 10(O110):004259
Crossman L, McHugh NA, Hsieh Y, Korfmacher WA, Chen J (2006) Investigation of the profiling depth in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:284–290
Deininger SO, Becker M, Suckau D (2010) Tutorial: multivariate statistical treatment of imaging data for clinical biomarker discovery. Methods Mol Biol 656:385–403
Deutskens F, Yang J, Caprioli RM (2011) High spatial resolution imaging mass spectrometry and classical histology on a single tissue section. J Mass Spectrom 46:568–571
Ergin B, Meding S, Langer R, Kap M, Viertler C, Schott C, Ferch U, Riegman P, Zatloukal K, Walch A, Becker KF (2010) Proteomic analysis of PAXgene-fixed tissues. J Proteome Res 9:5188–5196
Grey AC, Crouch RK, Koutalos Y, Schey KL, Ablonczy Z (2011) Spatial localization of A2E in the retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:3926–3933
Groseclose MR, Massion PP, Chaurand P, Caprioli RM (2008) High-throughput proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue microarrays using MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Proteomics 8:3715–3724
Guduric-Fuchs J, Ringland LJ, Gu P, Dellett M, Archer DB, Cogliati T (2009) Immunohistochemical study of pig retinal development. Mol Vis 15:1915–1928
Hankin JA, Barkley RM, Murphy RC (2007) Sublimation as a method of matrix application for mass spectrometric imaging. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 18:1646–1652
Hayasaka T, Goto-Inoue N, Sugiura Y, Zaima N, Nakanishi H, Ohishi K, Nakanishi S, Naito T, Taguchi R, Setou M (2008) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization quadrupole ion trap time-of-flight (MALDI-QIT-TOF)-based imaging mass spectrometry reveals a layered distribution of phospholipid molecular species in the mouse retina. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:3415–3426
Hayasaka T, Goto-Inoue N, Zaima N, Shrivas K, Kashiwagi Y, Yamamoto M, Nakamoto M, Setou M (2010) Imaging mass spectrometry with silver nanoparticles reveals the distribution of fatty acids in mouse retinal sections. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 21:1446–1454
Holle A, Haase A, Kayser M, Hohndorf J (2006) Optimizing UV laser focus profiles for improved MALDI performance. J Mass Spectrom 41:705–716
Jackson SN, Wang HY, Woods AS (2005) Direct profiling of lipid distribution in brain tissue using MALDI-TOFMS. Anal Chem 77:4523–4527
Kaletas BK, van der Wiel IM, Stauber J, Guzel C, Kros JM, Luider TM, Heeren RM (2009) Sample preparation issues for tissue imaging by imaging MS. Proteomics 9:2622–2633
Lagarrigue M, Becker M, Lavigne R, Deininger SO, Walch A, Aubry F, Suckau D, Pineau C (2011) Revisiting rat spermatogenesis with MALDI imaging at 20-microm resolution. Mol Cell Proteomics 10:M110 005991
Lakkaraju A, Finnemann SC, Rodriguez-Boulan E (2007) The lipofuscin fluorophore A2E perturbs cholesterol metabolism in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:11026–11031
Luxembourg SL, Mize TH, McDonnell LA, Heeren RM (2004) High-spatial resolution mass spectrometric imaging of peptide and protein distributions on a surface. Anal Chem 76:5339–5344
Ly A, Yee P, Vessey KA, Phipps JA, Jobling AI, Fletcher EL (2011) Early inner retinal astrocyte dysfunction during diabetes and development of hypoxia, retinal stress, and neuronal functional loss. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:9316–9326
Masland RH (2001) The fundamental plan of the retina. Nat Neurosci 4(9):877–886
Meding S, Balluff B, Elsner M, Schone C, Rauser S, Nitsche U, Maak M, Schafer A, Hauck SM, Ueffing M, Langer R, Hofler H, Friess H, Rosenberg R, Walch A (2012) Tissue-based proteomics reveals FXYD3, S100A11 and GSTM3 as novel markers for regional lymph node metastasis in colon cancer. J Pathol 228:459–470
Parker C, Smith D, Suckau D, Borchers C (2009) Mass spectrometry-based tissue imaging. In: Sensen C, Hallgrímsson B (eds) Advanced imaging in biology and medicine. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 131–146
Poetsch A, Schlusener D, Florizone C, Eltis L, Menzel C, Rogner M, Steinert K, Roth U (2008) Improved identification of membrane proteins by MALDI-TOF MS/MS using vacuum sublimated matrix spots on an ultraphobic chip surface. J Biomol Tech 19:129–138
Pol J, Strohalm M, Havlicek V, Volny M (2010) Molecular mass spectrometry imaging in biomedical and life science research. Histochem Cell Biol 134:423–443
Rompp A, Spengler B (2013) Mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space. Histochem Cell Biol 139:759–783
Roy MC, Nakanishi H, Takahashi K, Nakanishi S, Kajihara S, Hayasaka T, Setou M, Ogawa K, Taguchi R, Naito T (2011) Salamander retina phospholipids and their localization by MALDI imaging mass spectrometry at cellular size resolution. J Lipid Res 52:463–470
Sadeghi M, Vertes A (1998) Crystallite size dependence of volatilization in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization. Appl Surf Sci 127:226–234
Schwartz SA, Reyzer ML, Caprioli RM (2003) Direct tissue analysis using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: practical aspects of sample preparation. J Mass Spectrom 38:699–708
Seeley EH, Caprioli RM (2008) Molecular imaging of proteins in tissues by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:18126–18131
Thiery G, Shchepinov MS, Southern EM, Audebourg A, Audard V, Terris B, Gut IG (2007) Multiplex target protein imaging in tissue sections by mass spectrometry-TAMSIM. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 21:823–829
Thomas A, Charbonneau JL, Fournaise E, Chaurand P (2012) Sublimation of new matrix candidates for high spatial resolution imaging mass spectrometry of lipids: enhanced information in both positive and negative polarities after 1,5-diaminonapthalene deposition. Anal Chem 84:2048–2054
Yang J, Caprioli RM (2011) Matrix sublimation/recrystallization for imaging proteins by mass spectrometry at high spatial resolution. Anal Chem 83:5728–5734
Acknowledgments
Nicole Senninger from the Research Unit Protein Science and Claudia-Marieke Pflüger, Ulrike Buchholz, Gabriele Mettenleiter, and Andreas Voss from the Research Unit Analytical Pathology provided technical assistance. This project was funded by Ministry of Education and Research of the Federal Republic of Germany (BMBF) under Project Number 0315508A (SysTec-Verbund IMAGING) to MU and AW, and BMBF Grant Numbers 01IB10004E and 01ZX1310B, and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Grant Numbers HO 1258/3-1 and SFB824 TP Z02 to AW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
418_2014_1303_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplemenary Figure 1. a. Overall average mass spectra for OCT-embedded fresh-frozen mouse retina washed with 0.1 M phosphate buffer and coated with sublimated DHB matrix. b. Visualizations of individual m/z values from figure 4b. Measured at a 10 µm raster, the different m/z values clearly correspond to distinct retinal layers. Scale bars indicate 100 µm. (TIFF 4339 kb)
418_2014_1303_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplemenary Figure 2. a. Overall average mass spectra for fresh-frozen porcine retina coated with sublimated DHB matrix. b. Visualization of m/z 758. 64 from figure 5a. Scale bar indicates 100 µm. (TIFF 3214 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ly, A., Schöne, C., Becker, M. et al. High-resolution MALDI mass spectrometric imaging of lipids in the mammalian retina. Histochem Cell Biol 143, 453–462 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1303-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1303-1