Abstract
Our previous study has confirmed that IL-7δ5 (an IL-7 variant lacking exon 5) promotes breast cancer growth. However, whether IL-7δ5 is involved in tumor cell EMT and metastasis remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the preclinical effects and molecular mechanisms of IL-7δ5 on EMT and metastasis in human MCF-7 and BT-20 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that IL-7δ5 induced EMT and invasion in tumor cells, associated with up-regulation of N-cadherin and the down-regulation of E-cadherin. Furthermore, we found that IL-7δ5 induced the activation of Akt. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway by LY294002 reversed the EMT transition in breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and BT-20 induced by IL-7δ5. In addition, IL-7δ5 enhanced cancer metastasis and shortened survival time, with increased level changes of activated Akt in nude mice with breast cancer. In conclusion, our findings demonstrate that IL-7δ5 induces human breast cancer cell lines EMT and metastasis via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Thus, IL-7δ5 may be a potential target against human breast cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barata JT, Silva A, Brandao JG, Nadler LM, Cardoso AA, Boussiotis VA (2004) Activation of PI3K is indispensable for interleukin 7-mediated viability, proliferation, glucose use, and growth of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. J Exp Med 200:659–669
Caceres JF, Kornblihtt AR (2002) Alternative splicing: multiple control mechanisms and involvement in human disease. Trends Genet 18:186–193
Chen J, Lan T, Hou J, Zhang J, An Y, Tie L, Pan Y, Liu J, Li X (2012) Atorvastatin sensitizes human non-small cell lung carcinomas to carboplatin via suppression of AKT activation and upregulation of TIMP-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:759–769
Christiansen JJ, Rajasekaran AK (2006) Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 66:8319–8326
Cook RS, Garrett JT, Sanchez V, Stanford JC, Young C, Chakrabarty A, Rinehart C, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Greenberger L, Horak ID, Arteaga CL (2011) ErbB3 ablation impairs PI3K/Akt-dependent mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 71:3941–3951
Cosenza L, Gorgun G, Urbano A, Foss F (2002) Interleukin-7 receptor expression and activation in nonhaematopoietic neoplastic cell lines. Cell Signal 14:317–325
Dietel M, Hafner N, Jansen L, Durst M, Runnebaum IB (2011) Novel splice variant CAR 4/6 of the coxsackie adenovirus receptor is differentially expressed in cervical carcinogenesis. J Mol Med (Berl) 89:621–630
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J, Klein-Szanto AJ, van Roy F, Lee-Kwon W, Donowitz M, Tsichlis PN, Larue L (2003) The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal transition and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res 63:2172–2178
Grosso AR, Martins S, Carmo-Fonseca M (2008) The emerging role of splicing factors in cancer. EMBO Rep 9:1087–1093
Hu H, Yang Y, Ji Q, Zhao W, Jiang B, Liu R, Yuan J, Liu Q, Li X, Zou Y, Shao C, Shang Y, Wang Y, Gong Y (2012) CRL4B catalyzes H2AK119 monoubiquitination and coordinates with PRC2 to promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 22:781–795
Julien S, Puig I, Caretti E, Bonaventure J, Nelles L, van Roy F, Dargemont C, de Herreros AG, Bellacosa A, Larue L (2007) Activation of NF-kappaB by Akt upregulates Snail expression and induces epithelium mesenchyme transition. Oncogene 26:7445–7456
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2009) The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Investig 119:1420–1428
Kim WH, Chon CY, Moon YM, Kang JK, Park IS, Choi HJ (1993) Effect of anticancer drugs and desferrioxamine in combination with radiation on hepatoma cell lines. Yonsei Med J 34:45–56
Kim E, Goren A, Ast G (2008a) Alternative splicing and disease. RNA Biol 5:17–19
Kim E, Goren A, Ast G (2008b) Insights into the connection between cancer and alternative splicing. Trends Genet 24:7–10
Korner M, Miller LJ (2009) Alternative splicing of pre-mRNA in cancer: focus on G protein-coupled peptide hormone receptors. Am J Pathol 175:461–472
Kroemer RT, Kroncke R, Gerdes J, Richards WG (1998) Comparison of the 3D models of four different human IL-7 isoforms with human and murine IL-7. Protein Eng 11:31–40
Larue L, Bellacosa A (2005) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene 24:7443–7454
Liu B, Wang G, Yang J, Pan X, Yang Z, Zang L (2011) Berberine inhibits human hepatoma cell invasion without cytotoxicity in healthy hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 6:e21416
Maeurer MJ, Walter W, Martin D, Zitvogel L, Elder E, Storkus W, Lotze MT (1997) Interleukin-7 (IL-7) in colorectal cancer: IL-7 is produced by tissues from colorectal cancer and promotes preferential expansion of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol 45:182–192
Ming J, Jiang G, Zhang Q, Qiu X, Wang E (2012) Interleukin-7 up-regulates cyclin D1 via activator protein-1 to promote proliferation of cell in lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:79–88
O’Neill LA (2006) Targeting signal transduction as a strategy to treat inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:549–563
Pan D, Liu B, Jin X, Zhu J (2012) IL-7 splicing variant IL-7delta5 induces human breast cancer cell proliferation via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 422:727–731
Pettigrew CA, Brown MA (2008) Pre-mRNA splicing aberrations and cancer. Front Biosci 13:1090–1105
Qiao M, Sheng S, Pardee AB (2008) Metastasis and AKT activation. Cell Cycle 7:2991–2996
Saltzman AL, Kim YK, Pan Q, Fagnani MM, Maquat LE, Blencowe BJ (2008) Regulation of multiple core spliceosomal proteins by alternative splicing-coupled nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Mol Cell Biol 28:4320–4330
Schluns KS, Kieper WC, Jameson SC, Lefrancois L (2000) Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naive and memory CD8 T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol 1:426–432
Silva A, Laranjeira AB, Martins LR, Cardoso BA, Demengeot J, Yunes JA, Seddon B, Barata JT (2011) IL-7 contributes to the progression of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Cancer Res 71:4780–4789
Sourbier C, Lindner V, Lang H, Agouni A, Schordan E, Danilin S, Rothhut S, Jacqmin D, Helwig JJ, Massfelder T (2006) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway: a new target in human renal cell carcinoma therapy. Cancer Res 66:5130–5142
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Thiery JP (2003) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:740–746
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142
Tilli TM, Franco VF, Robbs BK, Wanderley JL, da Silva FR, de Mello KD, Viola JP, Weber GF, Gimba ER (2011) Osteopontin-c splicing isoform contributes to ovarian cancer progression. Mol Cancer Res 9:280–293
Tokunaga E, Oki E, Egashira A, Sadanaga N, Morita M, Kakeji Y, Maehara Y (2008) Deregulation of the Akt pathway in human cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8:27–36
Trinder P, Seitzer U, Gerdes J, Seliger B, Maeurer M (1999) Constitutive and IFN-gamma regulated expression of IL-7 and IL-15 in human renal cell cancer. Int J Oncol 14:23–31
Vudattu NK, Magalhaes I, Hoehn H, Pan D, Maeurer MJ (2009) Expression analysis and functional activity of interleukin-7 splice variants. Genes Immun 10:132–140
Wofford JA, Wieman HL, Jacobs SR, Zhao Y, Rathmell JC (2008) IL-7 promotes Glut1 trafficking and glucose uptake via STAT5-mediated activation of Akt to support T-cell survival. Blood 111:2101–2111
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81260324 and 81200308), Ministry of Education Colleges and Universities Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program class of new teachers (20124503120008), Youth Foundation of Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of (No. 2012GXNSFBA053096), Youth Science Foundation of Guangxi Medical University (No. GXMUYSF14).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Yang and Zhi Zeng have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
418_2014_1222_MOESM1_ESM.tif
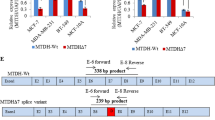
Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of IL-7R detected in MCF-7 and BT-20 cells. A, Immunocytochemical staining assay showing the expression and cellular location of IL-7R in MCF-7 and BT-20 cell lines. B, Western blotting data showing the expression of IL-7R in MCF-7 and BT-20 cell lines. The expression of IL-7R in HeLa cells was served as positive control. (TIFF 2390 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Zeng, Z., Peng, Y. et al. IL-7 splicing variant IL-7δ5 induces EMT and metastasis of human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and BT-20 through activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Histochem Cell Biol 142, 401–410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1222-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1222-1