Abstract
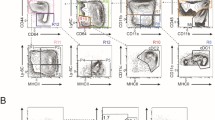
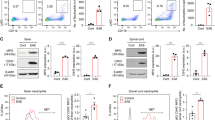
To determine the possible involvement of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), we examined their infiltration pattern during the course of MOG35–55-induced EAE in the C57BL/6 mice. Using immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry, we found that the number of neutrophils was significantly increased during onset of disease, remained high at the peak stage and dramatically declined thereafter. Moreover, dual labeling provided anatomical evidence of a prominent accumulation of neutrophils in the center and vicinity of lesion areas of demyelination, axonal loss or axonal degeneration at early stages of EAE. These observations provide evidence that neutrophils are one of the major sources of inflammatory cells to initiate EAE, which suggest that neutrophils may contribute to demyelination and axonal degeneration in the acute phase of EAE and play a greater role than previously thought in the pathogenesis of EAE.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen SJ, Baker D, O’Neill JK, Davison AN, Turk JL (1993) Isolation and characterization of cells infiltrating the spinal cord during the course of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Biozzi AB/H mouse. Cell Immunol 146:335–350
Altin JG, Sloan EK (1997) The role of CD45 and CD45-associated molecules in T cell activation. Immunol Cell Biol 75:430–445
Batten M, Li J, Yi S, Kljavin NM, Danilenko DM, Lucas S, Lee J, de Sauvage FJ, Ghilardi N (2006) Interleukin 27 limits autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing the development of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat Immunol 7:929–936
Beaufays J, Adam B, Menten-Dedoyart C, Fievez L, Grosjean A, Decrem Y, Prévôt PP, Santini S, Brasseur R, Brossard M, Vanhaeverbeek M, Bureau F, Heinen E, Lins L, Vanhamme L, Godfroid E (2008) Ir-LBP, an ixodes ricinus tick salivary LTB4-binding lipocalin, interferes with host neutrophil function. PLoS One 3:e3987
Brown A, McFarlin DE, Raine CS (1982) Chronologic neuropathology of relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Lab Invest 46:171–185
Bruck W (2005) The pathology of multiple sclerosis is the result of focal inflammatory demyelination with axonal damage. J Neurol 252(Suppl 5):v3–v9
Butcher EC (1991) Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell 67:1033–1036
Gold R, Linington C, Lassmann H (2006) Understanding pathogenesis and therapy of multiple sclerosis via animal models: 70 years of merits and culprits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis research. Brain 129:1953–1971
Gutcher I, Urich E, Wolter K, Prinz M, Becher B (2006) Interleukin 18-independent engagement of interleukin 18 receptor-alpha is required for autoimmune inflammation. Nat Immunol 7:946–953
Hartung HP, Kieseier BC, Hemmer B (2005) Purely systemically active anti-inflammatory treatments are adequate to control multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 252(Suppl 5):v30–v37
Hemmer B, Archelos JJ, Hartung HP (2002) New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev 3:291–301
Javed A, Reder AT (2006) Therapeutic role of beta-interferons in multiple sclerosis. Pharmacol Ther 110:35–56
Kelly MN, Kolls JK, Happel K, Schwartzman JD, Schwarzenberger P, Combe C, Moretto M, Khan IA (2005) Interleukin-17/interleukin-17 receptor-mediated signaling is important for generation of an optimal polymorphonuclear response against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infect Immun 73:617–621
Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Sudo K, Iwakura Y (2006) IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 177:566–573
Lafaille JJ (1998) The role of helper T cell subsets in autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 9:139–151
Lampert P (1967) Electron microscopic studies on ordinary and hyperacute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol 9:99–126
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ (2005) IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 201:233–240
Lappe-Siefke C, Goebbels S, Gravel M, Nicksch E, Lee J, Braun PE, Griffiths IR, Nave KA (2003) Disruption of Cnp1 uncouples oligodendroglial functions in axonal support and myelin. Nat Genet 33:366–374
Levine S (1974) Hyperacute, neutrophilic, and localized forms of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: a review. Acta Neuropathol 28:179–189
Maatta JA, Eralinna JP, Roytta M, Salmi AA, Hinkkanen AE (1996) Physical state of the neuroantigen in adjuvant emulsions determines encephalitogenic status in the BALB/c mouse. J Immunol Methods 190:133–141
Maatta JA, Sjoholm UR, Nygardas PT, Salmi AA, Hinkkanen AE (1998) Neutrophils secreting tumor necrosis factor alpha infiltrate the central nervous system of BALB/c mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 90:162–175
Mayer-Scholl A, Averhoff P, Zychlinsky A (2004) How do neutrophils and pathogens interact? Curr Opin Microbiol 7:62–66
McColl SR, Staykova MA, Wozniak A, Fordham S, Bruce J, Willenborg DO (1998) Treatment with anti-granulocyte antibodies inhibits the effector phase of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 161:6421–6426
Nyland H, Mork S, Matre R (1982) In situ characterization of mononuclear cell infiltrates in lesions of multiple sclerosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 8:403–411
Okuda Y, Okuda M, Bernard CA (2002) Gender does not influence the susceptibility of C57BL/6 mice to develop chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. Immunol Lett 81:25–29
Pagany M, Jagodic M, Bourquin C, Olsson T, Linington C (2003) Genetic variation in myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein expression and susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 139:1–8
Raine CS (1984) Biology of disease. Analysis of autoimmune demyelination: its impact upon multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest 50:608–635
Scapini P, Lapinet-Vera JA, Gasperini S, Calzetti F, Bazzoni F, Cassatella MA (2000) The neutrophil as a cellular source of chemokines. Immunol Rev 177:195–203
Shin K, Nigrovic PA, Crish J, Boilard E, McNeil HP, Larabee KS, Adachi R, Gurish MF, Gobezie R, Stevens RL, Lee DM (2009) Mast cells contribute to autoimmune inflammatory arthritis via their tryptase/heparin complexes. J Immunol 182:647–656
Stockinger B, Veldhoen M, Martin B (2007) Th17 T cells: linking innate and adaptive immunity. Semin Immunol 19:353–361
Suen WE, Bergman CM, Hjelmstrom P, Ruddle NH (1997) A critical role for lymphotoxin in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med 186:1233–1240
Swanborg RH (1995) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rodents as a model for human demyelinating disease. Clinical Immunol Immunopathol 77:4–13
Traugott U, Shevach E, Chiba J, Stone SH, Raine CS (1982) Chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: identification and dynamics of T and B cells within the central nervous system. Cell Immunol 68:261–275
von Vietinghoff S, Ley K (2008) Homeostatic regulation of blood neutrophil counts. J Immunol 181:5183–5188
Wang Z, Hong J, Sun W, Xu G, Li N, Chen X, Liu A, Xu L, Sun B, Zhang JZ (2006) Role of IFN-gamma in induction of Foxp3 and conversion of CD4+ CD25− T cells to CD4+ Tregs. J Clin Invest 116:2434–2441
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (30671926) and Shanghai Commission of Science and Technology (06ZR14164). The authors would like to thank Taylor Guo for critical reading of the manuscript. We are grateful to Qi Zhang for help with excellent technical support on the EAE induction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Wu and W. Cao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Cao, W., Yang, Y. et al. Extensive infiltration of neutrophils in the acute phase of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice. Histochem Cell Biol 133, 313–322 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-009-0673-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-009-0673-2