Abstract
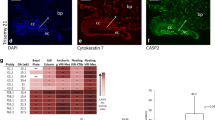
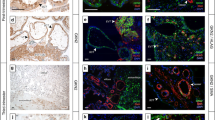
Although placental development and implantation depend on the coordination of trophoblast proliferation, differentiation and invasion, little is known about the cell cycle regulators that govern the control of these events. The hypothesis that the coordinated expression of cell cycle progression and inhibition factors will determine whether cytotrophoblasts proliferate or undergo cell cycle arrest or cell cycle exit allowing subsequent differentiation was tested. The cell cycle promotors cyclin A, cyclin B1, PCNA, Ki67 and the cell cycle inhibitors p21, p27 and p57 were immunolocalized in tissue sections of first trimester pregnancies (weeks 6 and 9–12). Double staining with cytokeratin 7 allowed unambiguous identification of extravillous cytotrophoblast (EVT) in the decidua. Villous cytotrophoblasts were immunolabelled for Ki67 and cyclin A but only few were stained with anti-cyclin B1. The syncytiotrophoblast was devoid of immunoreactivity for any of the cell cycle progression factors. It expressed especially p21, whereas p27 and p57 were predominantly found in villous cytotrophoblasts. PCNA, Ki67, cyclin A and cyclin B1 were immunolocalized in proximal and distal EVTs of anchoring villi and in EVT which had invaded the upper decidual segments. All EVTs strongly expressed p27 and p57, but not p21. These data clearly suggest different functions for p21, p27 and p57 in placental development with distinct roles for p21 and p57 in syncytiotrophoblast and EVT differentiation, respectively. p27 appears to be involved in both the processes. The results may also challenge the concept of differential mitotic activity in the proximal and distal parts of the first trimester cytotrophoblast cell column, but more functional studies are clearly needed. The presence of p27 and p57 in EVT cells, which invade the deciduas deeply, may account for the loss of mitogenic potential of these cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailly E, Pines J, Hunter T, Bornens M (1992) Cytoplasmic accumulation of cyclin B1 in human cells: association with a detergent-resistant compartment and with the centrosome. J Cell Sci 101:529–545
Bamberger A, Sudahl S, Bamberger CM, Schulte HM, Loning T (1999) Expression patterns of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27 and the cell-cycle promoter cyclin E in the human placenta throughout gestation: implications for the control of proliferation. Placenta 20:401–406
Blaschitz A, Weiss U, Dohr G, Desoye G (2000) Antibody reaction patterns in first trimester placenta: implications for trophoblast isolation and purity screening. Placenta 21:733–741
Bulmer JN, Morrison L, Johnson PM (1988) Expression of the proliferation markers Ki67 and transferrin receptor by human trophoblast populations. J Reprod Immunol 14:291–302
Cervar M, Blaschitz A, Dohr G, Desoye G (1999) Paracrine regulation of distinct trophoblast functions in vitro by placental macrophages. Cell Tissue Res 295:297–305
Chang BD, Broude EV, Fang J, Kalinichenko TV, Abdryashitov R, Poole JC, Roninson IB (2000) p21Waf/Cip1/Sdi1-induced growth arrest is associated with depletion of mitosis-control proteins and leads to abnormal mitosis and endoreduplication in recovering cells. Oncogene 19:2165–2170
De Falco M, Fedele V, Cobellis L, Mastrogiacomo A, Giraldi D, Leone S, De Luca L, Laforgia V, De Luca A (2004) Pattern of expression of cyclin D1/CDK4 complex in human placenta during gestation. Cell Tissue Res 317:187–194
DeLoia JA, Burlingame JM, Krasnow JA (1997) Differential expression of G1 cyclins during human placentogenesis. Placenta 18:9–16
Dulic V, Stein GH, Far DF, Reed SI (1998) Nuclear accumulation of p21Cip1 at the onset of mitosis: a role at the G2/M-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 18:546–557
Endl E, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: fascinating forms and an unknown function. Exp Cell Res 257:231–237
Engel FB, Hauck L, Boehm M, Nabel EG, Dietz R, von Harsdorf R (2003) p21(CIP1) controls proliferating cell nuclear antigen level in adult cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biol 23:555–565
Genbacev O, McMaster MT, Fisher SJ (2000) A repertoire of cell cycle regulators whose expression is coordinated with human cytotrophoblast differentiation. Am J Pathol 157:1337–1351
Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1996) Cdk inhibitors in development and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6:56–64
Hattori N, Davies TC, Anson-Cartwright L, Cross JC (2000) Periodic expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57 (Kip2) in trophoblast giant cells defines a G2-like gap phase of the endocycle. Mol Biol Cell 11:1037–1045
Hayashi S (1996) A Cdc2 dependent checkpoint maintains diploidy in Drosophila. Development 122:1051–1058
Hunter T, Pines J (1994) Cyclins and cancer. II Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell 79:573–582
Ichikawa N, Zhai YL, Shiozawa T, Toki T, Noguchi H, Nikaido T, Fujii S (1998) Immunohistochemical analysis of cell cycle regulatory gene products in normal trophoblast and placental site trophoblastic tumor. Int J Gynecol Pathol 17:235–240
Kaufmann P, Castelluci M (1997) Extravillous trophoblast in the human placenta. Trophoblast Res 10:21–65
Lee MH, Reynisdottir I, Massague J (1995) Cloning of p57KIP2, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with unique domain structure and tissue distribution. Genes Dev 9:639–649
Lew DJ, Dulic V, Reed SI (1991) Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell 66:1197–1206
MacAuley A, Cross JC, Werb Z (1998) Reprogramming the cell cycle for endoreduplication in rodent trophoblast cells. Mol Biol Cell 9:795–807
Maga G, Hubscher U (2003) Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): a dancer with many partners. J Cell Sci 116:3051–3060
Nakayama K, Nakayama K (1998) Cip/Kip cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: brakes of the cell cycle engine during development. Bioessays 20:1020–1029
Niculescu AB, Chen X, Smeets M, Hengst L, Prives C, Reed SI (1998) Effects of p21(Cip1/Waf1) at both the G1/S and the G2/M cell cycle transitions: pRb is a critical determinant in blocking DNA replication and in preventing endoreduplication. Mol Cell Biol 18:629–664
Ogryzko VV, Wong P, Howard BH (1997) WAF1 retards S-phase progression primarily by inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases. Mol Cell Biol 17:4877–4882
Olvera M, Harris S, Amezcua CA, McCourty A, Rezk S, Koo C, Felix JC, Brynes RK (2001) Immunohistochemical expression of cell cycle proteins E2F-1, Cdk-2, cyclin E, p27 (kip1), and Ki-67 in normal placenta and gestational trophoblastic disease. Mod Pathol 14:1036–1042
Parker SB, Eichele G, Zhang P, Rawls A, Sands AT, Bradley A, Olson EN, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1995) p53-independent expression of p21Cip1 in muscle and other terminally differentiating cells. Science 267:1024–1027
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1995) Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 9:1149–1163
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1 phase progression. Genes Dev 13:1501–1512
Takahashi T, Caviness VS (1993) PCNA-binding to DNA at the G1/S transition in proliferating cells of the developing cerebral wall. J Neurocytol 22:1096–1102
Xiong Y (1996) Why are there so many CDK inhibitors? Biochim Biophys Acta 1288:1–5
Yan Y, Frise´n J, Lee MH, Massague´ J, Barbacid M (1997) Ablation of the CDK inhibitor p57Kip2 results in increased apoptosis and delayed differentiation during mouse development. Genes Dev 11:973–983
Zybina TG, Kaufmann P, Frank HG, Freed J, Kadyrov M, Biesterfeld S (2002) Genome multiplication of extravillous trophoblast cells in human placenta in the course of differentiation and invasion into endometrium and myometrium. I. Dynamics of polyplodization. Tsitologia 44:1058–1067
Zybina TG, Frank HG, Biesterfeld S, Kaufmann P (2004) Genome multiplication of extravillous trophoblast cells in human placenta in the course of differentiation and invasion into endometrium and myometrium. II. Mechanisms of polyplodization. Tsitologia 46:640–648
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the Research Fund of Akdeniz University (21.01.0122.02), Antalya, Turkey
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korgun, E.T., Celik-Ozenci, C., Acar, N. et al. Location of cell cycle regulators cyclin B1, cyclin A, PCNA, Ki67 and cell cycle inhibitors p21, p27 and p57 in human first trimester placenta and deciduas. Histochem Cell Biol 125, 615–624 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-006-0160-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-006-0160-y