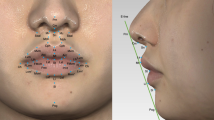
Abstract
Purpose
Non-invasive three-dimensional (3D) stereophotogrammetry is becoming increasingly popular in many fields. However, few studies have focused on its periocular application. We aimed to provide evidence for the periocular application of a novel anthropometric procedure using 3D stereophotogrammetry by evaluating its reliability.
Methods
Fifty-one Caucasians were recruited (102 eyes; mean age, 31.9 ± 13.6 years). Two sets of 3D images were acquired for each subject, and two measurement sessions were performed on each image by two raters. Fifty-two periocular landmarks were identified, and then 49 corresponding linear, curvilinear, and angular measurements were evaluated for intrarater, interrater, and intramethod reliability.
Results
Our findings showed highly reliable results for mean absolute difference (0.59 and 0.68 unit), relative error measurement (2.66% and 3.08%), technical error of measurement (0.59 and 0.66 unit), relative technical error of measurement (2.71% and 2.96%), and intraclass correlation coefficient (0.98) for intrarater 1 and intrarater 2 reliability; respectively 0.94 unit, 4.06%, 0.89 unit, and 3.94%, as well as 0.97 for interrater reliability; and respectively 0.98 unit, 4.66%, 0.96 unit, and 4.64%, as well as 0.96 for intramethod reliability.
Conclusions
This imaging system and the landmark identification protocol are highly reliable. The collected measurements and their errors can be applied for the comparison of reliability among various 3D imaging systems and populations. It could be utilized for planning surgeries and evaluating treatment outcomes for physicians in ophthalmology, plastic and esthetic surgery, and in the maxillofacial field where periocular morphology alterations are made.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wesselius TS, Verhulst AC, Vreeken RD, Xi T, Maal TJJ, Ulrich DJO (2018) Accuracy of three software applications for breast volume calculations from three-dimensional surface images. Plast Reconstr Surg 142:858–865. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000004728
Dindaroglu F, Kutlu P, Duran GS, Gorgulu S, Aslan E (2016) Accuracy and reliability of 3D stereophotogrammetry: a comparison to direct anthropometry and 2D photogrammetry. Angle Orthod 86:487–494. https://doi.org/10.2319/041415-244.1
Metzler P, Sun Y, Zemann W, Bartella A, Lehner M, Obwegeser JA, Kruse-Gujer AL, Lubbers HT (2014) Validity of the 3D VECTRA photogrammetric surface imaging system for cranio-maxillofacial anthropometric measurements. Oral Maxillofac Surg 18:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-013-0404-7
Modabber A, Peters F, Kniha K, Goloborodko E, Ghassemi A, Lethaus B, Holzle F, Mohlhenrich SC (2016) Evaluation of the accuracy of a mobile and a stationary system for three-dimensional facial scanning. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 44:1719–1724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2016.08.008
Verhulst A, Hol M, Vreeken R, Becking A, Ulrich D, Maal T (2018) Three-dimensional imaging of the face: a comparison between three different imaging modalities. Aesthet Surg J 38:579–585. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx227
Guo Y, Schaub F, Mor JM, Jia R, Koch KR, Heindl LM (2019) A simple standardized three-dimensional anthropometry for the periocular region in a European population. Plast Reconstr Surg
Heike CL, Cunningham ML, Hing AV, Stuhaug E, Starr JR (2009) Picture perfect? Reliability of craniofacial anthropometry using three-dimensional digital stereophotogrammetry. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:1261–1272. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181b454bd
Ulijaszek SJ, Kerr DA (1999) Anthropometric measurement error and the assessment of nutritional status. Br J Nutr 82:165–177
Andrade LM, Rodrigues da Silva AMB, Magri LV, Rodrigues da Silva MAM (2017) Repeatability study of angular and linear measurements on facial morphology analysis by means of stereophotogrammetry. J Craniofac Surg 28:1107–1111. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000003554
Camison L, Bykowski M, Lee WW, Carlson JC, Roosenboom J, Goldstein JA, Losee JE, Weinberg SM (2018) Validation of the Vectra H1 portable three-dimensional photogrammetry system for facial imaging. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 47:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2017.08.008
Schaaf H, Pons-Kuehnemann J, Malik CY, Streckbein P, Preuss M, Howaldt HP, Wilbrand JF (2010) Accuracy of three-dimensional photogrammetric images in non-synostotic cranial deformities. Neuropediatrics 41:24–29. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1255060
Lubbers HT, Medinger L, Kruse AL, Gratz KW, Obwegeser JA, Matthews F (2012) The influence of involuntary facial movements on craniofacial anthropometry: a survey using a three-dimensional photographic system. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50:171–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2010.12.002
de Menezes M, Rosati R, Ferrario VF, Sforza C (2010) Accuracy and reproducibility of a 3-dimensional stereophotogrammetric imaging system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:2129–2135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2009.09.036
Geeta A, Jamaiyah H, Safiza MN, Khor GL, Kee CC, Ahmad AZ, Suzana S, Rahmah R, Faudzi A (2009) Reliability, technical error of measurements and validity of instruments for nutritional status assessment of adults in Malaysia. Singap Med J 50:1013–1018
Gibelli D, Pucciarelli V, Poppa P, Cummaudo M, Dolci C, Cattaneo C, Sforza C (2018) Three-dimensional facial anatomy evaluation: reliability of laser scanner consecutive scans procedure in comparison with stereophotogrammetry. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2018.07.008
Weinberg SM, Naidoo S, Govier DP, Martin RA, Kane AA, Marazita ML (2006) Anthropometric precision and accuracy of digital three-dimensional photogrammetry: comparing the Genex and 3dMD imaging systems with one another and with direct anthropometry. J Craniofac Surg 17:477–483
Weinberg SM, Scott NM, Neiswanger K, Brandon CA, Marazita ML (2004) Digital three-dimensional photogrammetry: evaluation of anthropometric precision and accuracy using a Genex 3D camera system. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 41:507–518. https://doi.org/10.1597/03-066.1
Baik HS, Kim SY (2010) Facial soft-tissue changes in skeletal class III orthognathic surgery patients analyzed with 3-dimensional laser scanning. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 138:167–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2010.02.022
Plooij JM, Swennen GR, Rangel FA, Maal TJ, Schutyser FA, Bronkhorst EM, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM, Berge SJ (2009) Evaluation of reproducibility and reliability of 3D soft tissue analysis using 3D stereophotogrammetry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2008.12.009
Ozsoy U, Demirel BM, Yildirim FB, Tosun O, Sarikcioglu L (2009) Method selection in craniofacial measurements: advantages and disadvantages of 3D digitization method. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 37:285–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2008.12.005
Aldridge K, Boyadjiev SA, Capone GT, DeLeon VB, Richtsmeier JT (2005) Precision and error of three-dimensional phenotypic measures acquired from 3dMD photogrammetric images. Am J Med Genet A 138A:247–253. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.30959
Metzger TE, Kula KS, Eckert GJ, Ghoneima AA (2013) Orthodontic soft-tissue parameters: a comparison of cone-beam computed tomography and the 3dMD imaging system. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 144:672–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2013.07.007
Khambay B, Nairn N, Bell A, Miller J, Bowman A, Ayoub AF (2008) Validation and reproducibility of a high-resolution three-dimensional facial imaging system. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2007.04.017
Winder RJ, Darvann TA, McKnight W, Magee JD, Ramsay-Baggs P (2008) Technical validation of the Di3D stereophotogrammetry surface imaging system. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2007.09.005
Funding
This study receives a funding support by the Koeln Fortune Program/Faculty of Medicine, University of Cologne, Germany (Nr. 2680148101) and State Scholarship Fund from China Scholarship Council (Nr. 201708080141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
Intrarater, interrater and intramethod reliability estimates of MAD, TEM, REM, %TEM, total EM, and %total TEM across all measurement categories (XLSX 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Rokohl, A.C., Schaub, F. et al. Reliability of periocular anthropometry using three-dimensional digital stereophotogrammetry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 257, 2517–2531 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-019-04428-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-019-04428-6