Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of refractive errors and central corneal thickness (CCT) on the measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP) by ICare rebound tonometer (RT), and its agreement with measurements by Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT).
Patients and methods
Two observers measured the IOP by using RT and GAT in four groups of healthy volunteers with emmetropic (n = 78), hyperopic (n = 83), myopic (n = 87) and astigmatic (n = 79) eyes. Refraction was assessed by an autorefractometer. CCT was assessed by ultrasound pachymetry.
Results
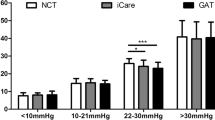
In all groups, no significant interobserver difference was seen in IOP values detected by both tonometers (Wilcoxon signed-rank test not significant). In all groups, IOP values were higher as measured by RT than by GAT (paired t-test p = 0.000): mean RT–GAT difference was higher in myopic eyes (+1.6 ± 1.8 mmHg), and it was less than 1 mmHg in the other groups. RT–GAT difference was correlated to the refraction (p < 0.001), and it was greater when an higher IOP was detected by RT (significant correlation between RT–GAT difference and IOP by RT, p < 0.001). Compared with GAT values, the IOP readings by RT were greater than 2 mmHg in respectively 17.9% (emmetropic), 13.3% (hyperopic), 34.5% (myopic) and 7.6% (astigmatic) of the eyes. With both tonometers, in all groups the IOP values were correlated with CCT (p < 0.05), but the discrepancy between RT and GAT values was not related to CCT.
Conclusions
In all groups of subjects, higher IOP values were detected by RT; the IOP readings exceed the GAT values usually in a range of less than 1 mmHg, except when RT detects IOP >18 mmHg and generally in myopic eyes; RT–GAT discrepancy is related to the refractive error, but not to CCT.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dielemans I, Vingerling JR, Hofman A, Grobbee DE, de Jong PT (1994) Reliability of intraocular pressure measurement with the Goldmann applanation tonometer in epidemiological studies. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 232:141–144
Kaufmann C, Bachmann LM, Thiel MA (2004) Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:3118–3121
Herndon LW (2006) Measuring intraocular pressure-adjustments for corneal thickness and new technologies. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 17:115–119
ElMallah MK, Asrani SG (2008) New ways to measure intraocular pressure. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 19:122–126
Kontiola AI (2000) A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 78:142–145
Kontiola AI, Goldblum D, Mittag T, Danias J (2001) The induction/impact tonometer: a new instrument to measure intraocular pressure in rat. Exp Eye Res 73:781–785
Fernandes P, Diaz-Rey JA, Queiros A, Gonzalez-Meijome JM, Jorge J (2005) Comparison of the ICare(R) rebound tonometer with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:436–440
van der Jagt LH, Jansonius NM (2005) Three portable tonometers, the TGDc-01, the ICARE and the Tonopen XL, compared with each other and with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:429–435
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Castillo A, Garcia-Sanchez J (2005) Reproducibility and clinical evaluation of rebound tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:4578–4580
Iliev ME, Goldblum D, Katsoulis K, Amstutz C, Frueh B (2006) Comparison of rebound tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry and correlation with central corneal thickness. Br J Ophthalmol 90:833–835
Detry-Morel M, Jamart J, Detry MB, Pourjavan S, Charlier L, Dethinne B, Huge L, Ledoux A (2006) Clinical evaluation of the dynamic rebound tonometer Icare. J Fr Ophtalmol 29:1119–1127
Davies LN, Bartlett H, Mallen EA, Wolffsohn JS (2006) Clinical evaluation of rebound tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 84:206–209
Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, Tosoni C, Parisi L (2006) Comparison of ICare tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma 15:213–217
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Vico E, Fernandez-Vidal A, JM Benitez del Castillo, Wasfi M, Garcia-Sanchez J (2006) Effect of corneal thickness on dynamic contour, rebound, and Goldmann tonometry. Ophthalmology 113:2156–2162
Nakamura M, Darhad U, Tatsumi Y, Fujioka M, Kusuhara A, Maeda H, Negi A (2006) Agreement of rebound tonometer in measuring intraocular pressure with three types of applanation tonometers. Am J Ophthalmol 142:332–334
López-Caballero C, Contreras I, Muñoz-Negrete FJ (2007) Rebound tonometry in a clinical setting. Comparison with applanation tonometry. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol 82:273–278
Ruokonen PC, Schwenteck T, Draeger J (2007) Evaluation of the impedance tonometers TGDc-01 and iCare according to the international ocular tonometer standards ISO 8612. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245:1259–1265
Munkwitz S, Elkarmouty A, Hoffmann EM, Pfeiffer N, Thieme H (2008) Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer over a wide IOP range. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246:875–879
Kontiola A, Puska P (2004) Measuring intraocular pressure with the Pulsair 3000 and rebound tonometers in elderly patients without an anesthetic. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:3–7
British Standards Institution (1979) Precision of test methods I: Guide for the determination and reproducibility for a standard test method. BSI, London
Chui WS, Lam A, Chen D, Chiu R (2008) The Influence of corneal croperties on rebound tonometry. Ophthalmology 115:80–84
Pakrou N, Gray T, Mills R, Landers J, Craig J (2008) Clinical comparison of the Icare tonometer and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Glaucoma 17:43–47
Kotecha A, Elsheikh A, Roberts CR, Zhu H, Garway-Heath DF (2006) Corneal thickness- and age-related biomechanical properties of the cornea measured with the ocular response analyzer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:5337–5347
Song Y, Congdon N, Li L, Zhou Z, Choi K, Lam DS, Pang CP, Xie Z, Liu X, Sharma A, Chen W, Zhang M (2008) Corneal hysteresis and axial length among Chinese secondary school children: the Xichang Pediatric Refractive Error Study (X-PRES) Report No. 4. Am J Ophthalmol 145:819–826
Jorge JM, González-Méijome JM, Queirós A, Fernandes P, Parafita MA (2008) Correlations between corneal biomechanical properties measured with the ocular response analyzer and ICare rebound tonometry. J Glaucoma 17:442–448
Acknowledgment
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No financial relationship
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avitabile, T., Longo, A., Rocca, D. et al. The influence of refractive errors on IOP measurement by rebound tonometry (ICare) and Goldmann applanation tonometry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248, 585–591 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-009-1176-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-009-1176-5