Abstract
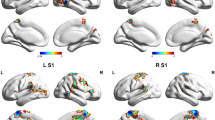
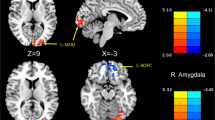
Resting state (RS) functional connectivity (FC) abnormalities of brain networks involved in pain- and multisensory processing have been disclosed in adult-migraine patients. We explored RS FC of large-scale brain networks in pediatric-migraine patients and their correlation with patients’ clinical characteristics. RS functional MRI data was acquired from 13 pediatric-migraine patients and 14 age- and sex-matched controls. Intra- and inter-network RS FC differences between patients and controls were evaluated. Correlations between RS FC abnormalities and patients’ clinical characteristics were also assessed. Compared to controls, pediatric-migraine patients had a decreased RS FC of the left parieto-occipital junction of the default mode network (DMN) and left-dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the executive control network (ECN). They also experienced an increased RS FC of the right frontopolar cortex of the right frontoparietal network (FPN) and the right-middle occipital gyrus of the secondary visual network. A significant stronger connectivity between the ECN and primary visual network and between the right FPN and primary sensorimotor, primary visual and auditory networks were found in migraine patients compared to controls. A significant weaker connectivity between the DMN and right FPN was revealed in migraineurs compared to controls. No correlation was found between intra- and inter-network RS FC abnormalities and patients’ clinical characteristics. Pediatric-migraine patients harbor significant RS FC abnormalities in brain networks involved in multisensory processing and in the cognitive control of pain. An early dysregulation of multisensory processing, including pain, might represent a phenotypic biomarker of the disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.B.D. Collaborators (2016) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388(10053):1545–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6
Puledda F, Messina R, Goadsby PJ (2017) An update on migraine: current understanding and future directions. J Neurol 264(9):2031–2039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8434-y
Messina R, Filippi M, Goadsby PJ (2018) Recent advances in headache neuroimaging. Curr Opin Neurol 31(4):379–385. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000573
Rocca MA, Messina R, Colombo B, Falini A, Comi G, Filippi M (2013) Structural brain MRI abnormalities in pediatric patients with migraine. J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7201-y
Faria V, Erpelding N, Lebel A, Johnson A, Wolff R, Fair D, Burstein R, Becerra L, Borsook D (2015) The migraine brain in transition: girls vs boys. Pain 156(11):2212–2221. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000292
Messina R, Rocca MA, Colombo B, Pagani E, Falini A, Comi G, Filippi M (2015) White matter microstructure abnormalities in pediatric migraine patients. Cephalalgia. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102415578428
Santoro JD, Forkert ND, Yang QZ, Pavitt S, MacEachern SJ, Moseley ME, Yeom KW (2018) Brain diffusion abnormalities in children with tension-type and migraine-type headaches. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 39(5):935–941. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5582
Youssef AM, Ludwick A, Wilcox SL, Lebel A, Peng K, Colon E, Danehy A, Burstein R, Becerra L, Borsook D (2017) In child and adult migraineurs the somatosensory cortex stands out … again: an arterial spin labeling investigation. Hum Brain Mapp 38(8):4078–4087. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23649
Chong CD, Schwedt TJ, Hougaard A (2017) Brain functional connectivity in headache disorders: A narrative review of MRI investigations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17740794
Zhang J, Su J, Wang M, Zhao Y, Zhang QT, Yao Q, Lu H, Zhang H, Li GF, Wu YL, Liu YS, Liu FD, Zhuang MT, Shi YH, Hou TY, Zhao R, Qiao Y, Li J, Liu JR, Du X (2017) The sensorimotor network dysfunction in migraineurs without aura: a resting-state fMRI study. J Neurol 264(4):654–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8404-4
Xue T, Yuan K, Zhao L, Yu D, Zhao L, Dong T, Cheng P, von Deneen KM, Qin W, Tian J (2012) Intrinsic brain network abnormalities in migraines without aura revealed in resting-state fMRI. PLoS ONE 7(12):e52927. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052927
Chong CD, Gaw N, Fu Y, Li J, Wu T, Schwedt TJ (2016) Migraine classification using magnetic resonance imaging resting-state functional connectivity data. Cephalalgia. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102416652091
Schulte LH, May A (2017) Of generators, networks and migraine attacks. Curr Opin Neurol 30(3):241–245. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000441
Maleki N, Gollub RL (2016) What have we learned from brain functional connectivity studies in migraine headache? Headache 56(3):453–461. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12756
Allen EA, Erhardt EB, Damaraju E, Gruner W, Segall JM, Silva RF, Havlicek M, Rachakonda S, Fries J, Kalyanam R, Michael AM, Caprihan A, Turner JA, Eichele T, Adelsheim S, Bryan AD, Bustillo J, Clark VP, Feldstein Ewing SW, Filbey F, Ford CC, Hutchison K, Jung RE, Kiehl KA, Kodituwakku P, Komesu YM, Mayer AR, Pearlson GD, Phillips JP, Sadek JR, Stevens M, Teuscher U, Thoma RJ, Calhoun VD (2011) A baseline for the multivariate comparison of resting-state networks. Front Syst Neurosci 5:2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2011.00002
(IHS) HCCotIHS (2013) The International Classification of Headache Disorders edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 33 (9):629–808. 10.1177/0333102413485658
Coppola G, Di Renzo A, Tinelli E, Di Lorenzo C, Scapeccia M, Parisi V, Serrao M, Evangelista M, Ambrosini A, Colonnese C, Schoenen J, Pierelli F (2017) Resting state connectivity between default mode network and insula encodes acute migraine headache. Cephalalgia. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102417715230
Amin FM, Hougaard A, Magon S, Asghar MS, Ahmad NN, Rostrup E, Sprenger T, Ashina M (2016) Change in brain network connectivity during PACAP38-induced migraine attacks: a resting-state functional MRI study. Neurology 86(2):180–187. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002261
Calhoun VD, Adali T, Pearlson GD, Pekar JJ (2001) A method for making group inferences from functional MRI data using independent component analysis. Hum Brain Mapp 14(3):140–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.1048
Himberg J, Hyvarinen A, Esposito F (2004) Validating the independent components of neuroimaging time series via clustering and visualization. Neuroimage 22(3):1214–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.027
Rocca MA, Savoldi F, Valsasina P, Radaelli M, Preziosa P, Comi G, Falini A, Filippi M (2018) Cross-modal plasticity among sensory networks in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Mult Scler. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458518778008
Jafri MJ, Pearlson GD, Stevens M, Calhoun VD (2008) A method for functional network connectivity among spatially independent resting-state components in schizophrenia. Neuroimage 39(4):1666–1681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.11.001
May A (2013) Pearls and pitfalls: neuroimaging in headache. Cephalalgia 33(8):554–565. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102412467513
Murphy K, Birn RM, Handwerker DA, Jones TB, Bandettini PA (2009) The impact of global signal regression on resting state correlations: are anti-correlated networks introduced? Neuroimage 44(3):893–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.09.036
Goadsby PJ, Holland PR, Martins-Oliveira M, Hoffmann J, Schankin C, Akerman S (2017) Pathophysiology of migraine: a disorder of sensory processing. Physiol Rev 97(2):553–622. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00034.2015
Martin H, Sanchez del Rio M, de Silanes CL, Alvarez-Linera J, Hernandez JA, Pareja JA (2011) Photoreactivity of the occipital cortex measured by functional magnetic resonance imaging-blood oxygenation level dependent in migraine patients and healthy volunteers: pathophysiological implications. Headache 51(10):1520–1528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.02013.x
Tedeschi G, Russo A, Conte F, Corbo D, Caiazzo G, Giordano A, Conforti R, Esposito F, Tessitore A (2016) Increased interictal visual network connectivity in patients with migraine with aura. Cephalalgia 36(2):139–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102415584360
Rocca MA, Messina R, Colombo B, Falini A, Comi G, Filippi M (2014) Structural brain MRI abnormalities in pediatric patients with migraine. J Neurol 261(2):350–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7201-y
Tessitore A, Russo A, Giordano A, Conte F, Corbo D, De Stefano M, Cirillo S, Cirillo M, Esposito F, Tedeschi G (2013) Disrupted default mode network connectivity in migraine without aura. J Headache Pain 14(1):89. https://doi.org/10.1186/1129-2377-14-89
Macaluso E (2010) Orienting of spatial attention and the interplay between the senses. Cortex J dDevot Study of the Nervous Syst Behav 46(3):282–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2009.05.010
Buckner RL, Andrews-Hanna JR, Schacter DL (2008) The brain's default network: anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 1124:1–38. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1440.011
Karsan N, Goadsby PJ (2018) Biological insights from the premonitory symptoms of migraine. Nat Rev Neurol 14(12):699–710. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0098-4
Martins IP, Gil-Gouveia R, Silva C, Maruta C, Oliveira AG (2012) Migraine, headaches, and cognition. Headache 52(10):1471–1482. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02218.x
Rocca MA, Valsasina P, Martinelli V, Misci P, Falini A, Comi G, Filippi M (2012) Large-scale neuronal network dysfunction in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 79(14):1449–1457. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31826d5f10
Tessitore A, Russo A, Conte F, Giordano A, De Stefano M, Lavorgna L, Corbo D, Caiazzo G, Esposito F, Tedeschi G (2015) Abnormal connectivity within executive resting-state network in migraine with aura. Headache 55(6):794–805. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12587
Russo A, Tessitore A, Giordano A, Corbo D, Marcuccio L, De Stefano M, Salemi F, Conforti R, Esposito F, Tedeschi G (2012) Executive resting-state network connectivity in migraine without aura. Cephalalgia 32(14):1041–1048. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102412457089
Mouraux A, Iannetti GD (2018) The search for pain biomarkers in the human brain. Brain 141(12):3290–3307. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy281
Peng K, Steele SC, Becerra L, Borsook D (2018) Brodmann area 10: Collating, integrating and high level processing of nociception and pain. Prog Neurobiol 161:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.11.004
Lorenz J, Minoshima S, Casey KL (2003) Keeping pain out of mind: the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in pain modulation. Brain 126(Pt 5):1079–1091
Rea M, Kullmann S, Veit R, Casile A, Braun C, Belardinelli MO, Birbaumer N, Caria A (2011) Effects of aversive stimuli on prospective memory. An event-related fMRI study. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26290. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026290
Li Z, Lan L, Zeng F, Makris N, Hwang J, Guo T, Wu F, Gao Y, Dong M, Liu M, Yang J, Li Y, Gong Q, Sun S, Liang F, Kong J (2017) The altered right frontoparietal network functional connectivity in migraine and the modulation effect of treatment. Cephalalgia 37(2):161–176. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102416641665
Smallwood J, Brown K, Baird B, Schooler JW (2012) Cooperation between the default mode network and the frontal-parietal network in the production of an internal train of thought. Brain Res 1428:60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.03.072
Godwin CA, Hunter MA, Bezdek MA, Lieberman G, Elkin-Frankston S, Romero VL, Witkiewitz K, Clark VP, Schumacher EH (2017) Functional connectivity within and between intrinsic brain networks correlates with trait mind wandering. Neuropsychologia 103:140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.07.006
Corbetta M, Shulman GL (2002) Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(3):201–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn755
Demarquay G, Mauguiere F (2016) Central nervous system underpinnings of sensory hypersensitivity in migraine: insights from neuroimaging and electrophysiological studies. Headache 56(9):1418–1438. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12651
de Tommaso M, Ambrosini A, Brighina F, Coppola G, Perrotta A, Pierelli F, Sandrini G, Valeriani M, Marinazzo D, Stramaglia S, Schoenen J (2014) Altered processing of sensory stimuli in patients with migraine. Nat Rev Neurol 10(3):144–155. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2014.14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Local Ethical Committees on human studies and has therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
All subjects’ parents provided written informed consent prior to study participation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Messina, R., Rocca, M.A., Colombo, B. et al. Dysregulation of multisensory processing stands out from an early stage of migraine: a study in pediatric patients. J Neurol 267, 760–769 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09639-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09639-9