Abstract
Background and purpose
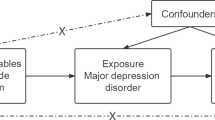
Although observational studies have reported a positive association between depression and ischemic stroke, causality remains inconclusive. We aimed to assess the causal relationship of major depressive disorder (MDD) with ischemic stroke, especially with the small vessel stroke (SVS) subtype.
Methods
We used 72 independent single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with MDD in a genome-wide association study (GWAS) from the Psychiatric Genetics Consortium as instrumental variables. The corresponding data for ischemic stroke and its subtypes of European ancestry were available from the MEGASTROKE consortium of 34,217 ischemic stroke cases and 406,111 controls. Primary Mendelian randomization estimates were calculated with inverse-variance weighted method, and several alternate methods and multiple sensitivity analyses were also performed.
Results
We found that genetic predisposition to higher risk of MDD was associated with higher risk of SVS, with an odds ratio of 1.33 (95% confidence interval, 1.08–1.65; p = 0.009) per log-odds increment in MDD risk, but not with large artery stroke (OR, 1.08; 95% CI 0.83–1.41; p = 0.559), cardioembolic stroke (OR, 0.98; 95% CI 0.80–1.20; p = 0.833), or all ischemic stroke (OR, 1.03; 95% CI 0.92–1.15; p = 0.633). The association of MDD with SVS was overall robust to sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions
We provided evidence for a possible causal effect of MDD on increased risk of SVS. Future researches are required to investigate whether rational intervention on depression may help to reduce societal burden of SVS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mortality GBD, Causes of Death C (2016) Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 388(10053):1459–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1
Hong KS, Yegiaian S, Lee M, Lee J, Saver JL (2011) Declining stroke and vascular event recurrence rates in secondary prevention trials over the past 50 years and consequences for current trial design. Circulation 123(19):2111–2119. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.934786
Wang Y, Rudd AG, Wolfe CD (2013) Trends and survival between ethnic groups after stroke: the South London Stroke Register. Stroke 44(2):380–387. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.680843
Kubo M, Kiyohara Y, Kato I, Tanizaki Y, Arima H, Tanaka K, Nakamura H, Okubo K, Iida M (2003) Trends in the incidence, mortality, and survival rate of cardiovascular disease in a Japanese community: the Hisayama study. Stroke 34(10):2349–2354. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000090348.52943.A2
Rosengren A, Giang KW, Lappas G, Jern C, Toren K, Bjorck L (2013) Twenty-four-year trends in the incidence of ischemic stroke in Sweden from 1987 to 2010. Stroke 44(9):2388–2393. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001170
Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, Chen Z, Wang W, Anderson CS, Sandercock P, Wang Y, Huang Y, Cui L, Pu C, Jia J, Zhang T, Liu X, Zhang S, Xie P, Fan D, Ji X, Wong KL, Wang L, China Stroke Study C (2019) Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol 18(4):394–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30500-3
Bang OY, Ovbiagele B, Kim JS (2015) Nontraditional risk factors for ischemic stroke: an update. Stroke 46(12):3571–3578. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.010954
O'Donnell MJ, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H, Chin SL, Rao-Melacini P, Rangarajan S, Islam S, Pais P, McQueen MJ, Mondo C, Damasceno A, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Hankey GJ, Dans AL, Yusoff K, Truelsen T, Diener HC, Sacco RL, Ryglewicz D, Czlonkowska A, Weimar C, Wang X, Yusuf S, Investigators I (2010) Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): a case-control study. Lancet 376(9735):112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60834-3
Daskalopoulou M, George J, Walters K, Osborn DP, Batty GD, Stogiannis D, Rapsomaniki E, Pujades-Rodriguez M, Denaxas S, Udumyan R, Kivimaki M, Hemingway H (2016) Depression as a risk factor for the initial presentation of twelve cardiac, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial diseases: data linkage Study of 1.9 Million Women and Men. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0153838. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153838
Sun J, Ma H, Yu C, Lv J, Guo Y, Bian Z, Yang L, Chen Y, Shen H, Chen Z, Hu Z, Li L, China Kadoorie Biobank Collaborative G (2016) Association of major depressive episodes with stroke risk in a prospective study of 0.5 million Chinese adults. Stroke 47(9):2203–2208. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013512
Bos MJ, Linden T, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Skoog I, Breteler MM, Tiemeier H (2008) Depressive symptoms and risk of stroke: the Rotterdam Study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(9):997–1001. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2007.134965
Wium-Andersen MK, Wium-Andersen IK, Prescott EIB, Overvad K, Jorgensen MB, Osler M (2019) An attempt to explain the bidirectional association between ischaemic heart disease, stroke and depression: a cohort and meta-analytic approach. Br J Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2019.130
Salaycik KJ, Kelly-Hayes M, Beiser A, Nguyen AH, Brady SM, Kase CS, Wolf PA (2007) Depressive symptoms and risk of stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke 38(1):16–21. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000251695.39877.ca
Wassertheil-Smoller S, Qi Q, Dave T, Mitchell BD, Jackson RD, Liu S, Park K, Salinas J, Dunn EC, Leira EC, Xu H, Ryan K, Smoller JW (2018) Polygenic risk for depression increases risk of ischemic stroke: from the stroke genetics network study. Stroke 49(3):543–548. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018857
Correction to: Polygenic Risk for Depression Increases Risk of Ischemic Stroke From the Stroke Genetics Network Study (2019). Stroke 50 (1):e24-e25. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000182
Malik R, Chauhan G, Traylor M, Sargurupremraj M, Okada Y, Mishra A, Rutten-Jacobs L, Giese AK, van der Laan SW, Gretarsdottir S, Anderson CD, Chong M, Adams HHH, Ago T, Almgren P, Amouyel P, Ay H, Bartz TM, Benavente OR, Bevan S, Boncoraglio GB, Brown RD Jr, Butterworth AS, Carrera C, Carty CL, Chasman DI, Chen WM, Cole JW, Correa A, Cotlarciuc I, Cruchaga C, Danesh J, de Bakker PIW, DeStefano AL, den Hoed M, Duan Q, Engelter ST, Falcone GJ, Gottesman RF, Grewal RP, Gudnason V, Gustafsson S, Haessler J, Harris TB, Hassan A, Havulinna AS, Heckbert SR, Holliday EG, Howard G, Hsu FC, Hyacinth HI, Ikram MA, Ingelsson E, Irvin MR, Jian X, Jimenez-Conde J, Johnson JA, Jukema JW, Kanai M, Keene KL, Kissela BM, Kleindorfer DO, Kooperberg C, Kubo M, Lange LA, Langefeld CD, Langenberg C, Launer LJ, Lee JM, Lemmens R, Leys D, Lewis CM, Lin WY, Lindgren AG, Lorentzen E, Magnusson PK, Maguire J, Manichaikul A, McArdle PF, Meschia JF, Mitchell BD, Mosley TH, Nalls MA, Ninomiya T, O'Donnell MJ, Psaty BM, Pulit SL, Rannikmae K, Reiner AP, Rexrode KM, Rice K, Rich SS, Ridker PM, Rost NS, Rothwell PM, Rotter JI, Rundek T, Sacco RL, Sakaue S, Sale MM, Salomaa V, Sapkota BR, Schmidt R, Schmidt CO, Schminke U, Sharma P, Slowik A, Sudlow CLM, Tanislav C, Tatlisumak T, Taylor KD, Thijs VNS, Thorleifsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Tiedt S, Trompet S, Tzourio C, van Duijn CM, Walters M, Wareham NJ, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Wilson JG, Wiggins KL, Yang Q, Yusuf S, Starnet Bis JC, Pastinen T, Ruusalepp A, Schadt EE, Koplev S, Bjorkegren JLM, Codoni V, Civelek M, Smith NL, Tregouet DA, Christophersen IE, Roselli C, Lubitz SA, Ellinor PT, Tai ES, Kooner JS, Kato N, He J, van der Harst P, Elliott P, Chambers JC, Takeuchi F, Johnson AD, Sanghera DK, Melander O, Jern C, Strbian D, Fernandez-Cadenas I, Longstreth WT Jr, Rolfs A, Hata J, Woo D, Rosand J, Pare G, Hopewell JC, Saleheen D, Stefansson K, Worrall BB, Kittner SJ, Seshadri S, Fornage M, Markus HS, Howson JMM, Kamatani Y, Debette S, Dichgans M, Consortium AF, Cohorts for H, Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology C, International Genomics of Blood Pressure C, Consortium I, BioBank Japan Cooperative Hospital G, Consortium C, Consortium E-C, Consortium EP-I, International Stroke Genetics C, Consortium M, Neurology Working Group of the CC, Network NSG, Study UKYLD, Consortium M (2018) Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat Genet 50(4):524–537. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0058-3
Wray NR, Ripke S, Mattheisen M, Trzaskowski M, Byrne EM, Abdellaoui A, Adams MJ, Agerbo E, Air TM, Andlauer TMF, Bacanu SA, Baekvad-Hansen M, Beekman AFT, Bigdeli TB, Binder EB, Blackwood DRH, Bryois J, Buttenschon HN, Bybjerg-Grauholm J, Cai N, Castelao E, Christensen JH, Clarke TK, Coleman JIR, Colodro-Conde L, Couvy-Duchesne B, Craddock N, Crawford GE, Crowley CA, Dashti HS, Davies G, Deary IJ, Degenhardt F, Derks EM, Direk N, Dolan CV, Dunn EC, Eley TC, Eriksson N, Escott-Price V, Kiadeh FHF, Finucane HK, Forstner AJ, Frank J, Gaspar HA, Gill M, Giusti-Rodriguez P, Goes FS, Gordon SD, Grove J, Hall LS, Hannon E, Hansen CS, Hansen TF, Herms S, Hickie IB, Hoffmann P, Homuth G, Horn C, Hottenga JJ, Hougaard DM, Hu M, Hyde CL, Ising M, Jansen R, Jin F, Jorgenson E, Knowles JA, Kohane IS, Kraft J, Kretzschmar WW, Krogh J, Kutalik Z, Lane JM, Li Y, Li Y, Lind PA, Liu X, Lu L, MacIntyre DJ, MacKinnon DF, Maier RM, Maier W, Marchini J, Mbarek H, McGrath P, McGuffin P, Medland SE, Mehta D, Middeldorp CM, Mihailov E, Milaneschi Y, Milani L, Mill J, Mondimore FM, Montgomery GW, Mostafavi S, Mullins N, Nauck M, Ng B, Nivard MG, Nyholt DR, O'Reilly PF, Oskarsson H, Owen MJ, Painter JN, Pedersen CB, Pedersen MG, Peterson RE, Pettersson E, Peyrot WJ, Pistis G, Posthuma D, Purcell SM, Quiroz JA, Qvist P, Rice JP, Riley BP, Rivera M, Saeed Mirza S, Saxena R, Schoevers R, Schulte EC, Shen L, Shi J, Shyn SI, Sigurdsson E, Sinnamon GBC, Smit JH, Smith DJ, Stefansson H, Steinberg S, Stockmeier CA, Streit F, Strohmaier J, Tansey KE, Teismann H, Teumer A, Thompson W, Thomson PA, Thorgeirsson TE, Tian C, Traylor M, Treutlein J, Trubetskoy V, Uitterlinden AG, Umbricht D, Van der Auwera S, van Hemert AM, Viktorin A, Visscher PM, Wang Y, Webb BT, Weinsheimer SM, Wellmann J, Willemsen G, Witt SH, Wu Y, Xi HS, Yang J, Zhang F, Arolt V, Baune BT, Berger K, Boomsma DI, Cichon S, Dannlowski U, de Geus ECJ, DePaulo JR, Domenici E, Domschke K, Esko T, Grabe HJ, Hamilton SP, Hayward C, Heath AC, Hinds DA, Kendler KS, Kloiber S, Lewis G, Li QS, Lucae S, Madden PFA, Magnusson PK, Martin NG, McIntosh AM, Metspalu A, Mors O, Mortensen PB, Muller-Myhsok B, Nordentoft M, Nothen MM, O'Donovan MC, Paciga SA, Pedersen NL, Penninx B, Perlis RH, Porteous DJ, Potash JB, Preisig M, Rietschel M, Schaefer C, Schulze TG, Smoller JW, Stefansson K, Tiemeier H, Uher R, Volzke H, Weissman MM, Werge T, Winslow AR, Lewis CM, Levinson DF, Breen G, Borglum AD, Sullivan PF, eQtlgen, andMe, Major Depressive Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics C (2018) Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat Genet 50(5):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0090-3
Adams HP Jr., Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke 24(1):35–41
Choi KW, Chen CY, Stein MB, Klimentidis YC, Wang MJ, Koenen KC, Smoller JW, Major Depressive Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics C (2019) Assessment of bidirectional relationships between physical activity and depression among adults: a 2-sample Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.4175
Burgess S, Scott RA, Timpson NJ, Davey Smith G, Thompson SG, Consortium E-I (2015) Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur J Epidemiol 30(7):543–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-015-0011-z
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, Burgess S (2016) Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol 40(4):304–314. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21965
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S (2015) Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol 44(2):512–525. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv080
Zhao Q, Wang J, Bowden J, Small DS (2018) Statistical inference in two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization using robust adjusted profile score. arXiv 1801.09652
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R (2018) Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 50(5):693–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7
Bowden J, Del Greco MF, Minelli C, Davey Smith G, Sheehan NA, Thompson JR (2016) Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol 45(6):1961–1974. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyw220
Hemani G, Tilling K, Davey Smith G (2017) Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet 13(11):e1007081. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007081
Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, Wade KH, Haberland V, Baird D, Laurin C, Burgess S, Bowden J, Langdon R, Tan VY, Yarmolinsky J, Shihab HA, Timpson NJ, Evans DM, Relton C, Martin RM, Davey Smith G, Gaunt TR, Haycock PC (2018) The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34408
Staley JR, Blackshaw J, Kamat MA, Ellis S, Surendran P, Sun BB, Paul DS, Freitag D, Burgess S, Danesh J, Young R, Butterworth AS (2016) PhenoScanner: a database of human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics 32(20):3207–3209. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw373
Rutten-Jacobs LCA, Markus HS, Study UKYLSD (2017) Vascular risk factor profiles differ between magnetic resonance imaging-defined subtypes of younger-onset lacunar stroke. Stroke 48(9):2405–2411. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017813
Larsson SC, Scott RA, Traylor M, Langenberg CC, Hindy G, Melander O, Orho-Melander M, Seshadri S, Wareham NJ, Markus HS, Collaboration, M, Network NSG (2017) Type 2 diabetes, glucose, insulin, BMI, and ischemic stroke subtypes: Mendelian randomization study. Neurology 89(5):454–460. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004173
Hindy G, Engstrom G, Larsson SC, Traylor M, Markus HS, Melander O, Orho-Melander M, Stroke Genetics N (2018) Role of blood lipids in the development of ischemic stroke and its subtypes: a Mendelian Randomization Study. Stroke 49(4):820–827. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.019653
Schilling S, Tzourio C, Dufouil C, Zhu Y, Berr C, Alperovitch A, Crivello F, Mazoyer B, Debette S (2014) Plasma lipids and cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 83(20):1844–1852. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000980
Pratt LA, Druss BG, Manderscheid RW, Walker ER (2016) Excess mortality due to depression and anxiety in the United States: results from a nationally representative survey. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 39:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2015.12.003
Trajkova S, d'Errico A, Soffietti R, Sacerdote C, Ricceri F (2019) Use of antidepressants and risk of incident stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology. https://doi.org/10.1159/000500686
Gill D, James NE, Monori G, Lorentzen E, Fernandez-Cadenas I, Lemmens R, Thijs V, Rost NS, Scott R, Hankey GJ, Lindgren A, Jern C, Maguire JM, International Stroke Genetics C, the GN (2019) Genetically determined risk of depression and functional outcome after ischemic stroke. Stroke. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026089
Meng L, Chen D, Yang Y, Zheng Y, Hui R (2012) Depression increases the risk of hypertension incidence: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Hypertens 30(5):842–851. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32835080b7
Lustman PJ, Clouse RE (2005) Depression in diabetic patients: the relationship between mood and glycemic control. J Diabetes Complications 19(2):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2004.01.002
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Ma L (2018) Depression and cardiovascular disease in elderly: current understanding. J Clin Neurosci 47:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.09.022
Taylor WD, Aizenstein HJ, Alexopoulos GS (2013) The vascular depression hypothesis: mechanisms linking vascular disease with depression. Mol Psychiatry 18(9):963–974. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.20
Hartwig FP, Borges MC, Horta BL, Bowden J, Davey Smith G (2017) Inflammatory biomarkers and risk of schizophrenia: a 2-sample mendelian randomization study. JAMA Psychiatry 74(12):1226–1233. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3191
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank the MEGASTROKE consortium and the PGC for providing summary statistics data. All MEGASTROKE consortium and MDD Working Group of the PGC authors are listed in the online supplementary. The MEGASTROKE project received funding from sources specified at https://www.megastroke.org/acknowledgments.html.
Funding
This study received the support of Social Welfare Science and Technology Research Project of Zhongshan City (2018B1065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The author declares that they have no competing interest.
Ethics approval
All data sources were approved by relevant institutional review boards from original studies (MEGASTROKE and PGC consortia).
Informed consent
All participants were given informed consent from original studies (MEGASTROKE and PGC consortia).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Cai, B., Zhang, H. et al. Major depression and small vessel stroke: a Mendelian randomization analysis. J Neurol 266, 2859–2866 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09511-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09511-w