Abstract
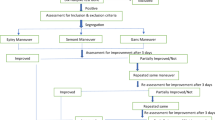
To determine the immediate and short-term efficacies of mastoid oscillation vs. Gufoni maneuver in treating the apogeotropic type of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (HC-BPPV), we designed a randomized, prospective, sham-controlled study. In eight dizziness clinics in Korea, 209 consecutive patients with apogeotropic HC-BPPV were enrolled. The patients were randomly assigned to receive a single application of Gufoni (n = 70), mastoid oscillation (n = 67), or sham maneuver (n = 72). Immediate and second-day responses were determined based on the results within 1 h after a single trial of each maneuver and the following day, respectively. Second-day response was assessed in patients who were non-responders on the first day. The short-term response was determined based on the cumulative response for 2 days. Successful treatment was defined as a resolution of positional nystagmus or as a transition into geotropic horizontal nystagmus (not requires vertigo symptom resolution). The immediate responses of the Gufoni maneuver (33/70, 47.1%) and mastoid oscillation (32/67, 47.8%) were better than the sham maneuver (14/72, 19.4%) (p = 0.00). The second-day results did not differ among the three groups (p = 0.76). The short-term responses showed better efficacies with the Gufoni maneuver (51/70, 76.1%) and mastoid oscillation (46/67, 71.9%) than with the sham maneuver (38/72, 53.5%) (p = 0.02). Therapeutic efficacies did not differ between the Gufoni and mastoid oscillation groups in terms of both immediate and short-term outcomes (p = 0.94, 0.57). Both the Gufoni maneuver and mastoid oscillation are valid methods for treating apogeotropic HC-BPPV, with a success rate of approximately 70% for a single maneuver during the short-term follow-up.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov identifier number: NCT02046980.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Fife TD (1998) Recognition and management of horizontal canal benign positional vertigo. Am J Otol 19:345–351
Baloh RW, Yue Q, Jacobson KM, Honrubia V (1995) Persistent direction-changing positional nystagmus: another variant of benign positional nystagmus? Neurology 45:1297–1301
Appiani GC, Catania G, Gagliardi M, Cuiuli G (2005) Repositioning maneuver for the treatment of the apogeotropic variant of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 26:257–260
Casani AP, Vannucci G, Fattori B, Berrettini S (2002) The treatment of horizontal canal positional vertigo: our experience in 66 cases. Laryngoscope 112:172–178
Nuti D, Agus G, Barbieri MT, Passali D (1998) The management of horizontal-canal paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol 118:455–460
Oh SY, Kim JS, Jeong SH et al (2009) Treatment of apogeotropic benign positional vertigo: comparison of therapeutic head-shaking and modified Semont maneuver. J Neurol 256:1330–1336
Kim JS, Oh SY, Lee SH et al (2012) Randomized clinical trial for apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 78:159–166
Sargent EW, Bankaitis AE, Hollenbeak CS, Currens JW (2001) Mastoid oscillation in canalith repositioning for paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 22:205–209
Epley JM (1992) The canalith repositioning procedure: for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngology 107:399–404
Kim SH, Jo SW, Chung WK, Byeon HK, Lee WS (2012) A cupulolith repositioning maneuver in the treatment of horizontal canal cupulolithiasis. Auris Nasus Larynx 39:163–168
Baloh RW, Honrubia V, Jacobson K (1987) Benign positional vertigo: clinical and oculographic features in 240 cases. Neurology 37:371–378
Lee SH, Choi KD, Jeong SH, Oh YM, Koo JW, Kim JS (2007) Nystagmus during neck flexion in the pitch plane in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo involving the horizontal canal. J Neurol Sci 256:75–80
Han BI, Oh HJ, Kim JS (2006) Nystagmus while recumbent in horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 66:706–710
Koo JW, Moon IJ, Shim WS, Moon SY, Kim JS (2006) Value of lying-down nystagmus in the lateralization of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 27:367–371
Gufoni M, Mastrosimone L, Di Nasso F (1998) Repositioning maneuver in benign paroxysmal vertigo of horizontal semicircular canal. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 18:363–367
Li JC (1995) Mastoid oscillation: a critical factor for success in canalith repositioning procedure. Otolaryngology 112:670–675
Macias JD, Ellensohn A, Massingale S, Gerkin R (2004) Vibration with the canalith repositioning maneuver: a prospective randomized study to determine efficacy. Laryngoscope 114:1011–1014
Motamed M, Osinubi O, Cook JA (2004) Effect of mastoid oscillation on the outcome of the canalith repositioning procedure. Laryngoscope 114:1296–1298
Hain TC, Helminski JO, Reis IL, Uddin MK (2000) Vibration does not improve results of the canalith repositioning procedure. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:617–622
Ruckenstein MJ, Shepard NT (2007) The canalith repositioning procedure with and without mastoid oscillation for the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. ORL 69:295–298
Faralli M, Longari F, Ricci G, Marinetti D, Frenguelli A (2008) Mastoid oscillation in the treatment of the apogeotropic variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of the lateral semicircular canal. Mediterr J Otol 152:156
Imai T, Ito M, Takeda N et al (2005) Natural course of the remission of vertigo in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 64:920–921
Parnes LS, Agrawal SK, Atlas J (2003) Diagnosis and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). CMAJ 169:681–693
Korres S, Balatsouras DG, Ferekidis E (2006) Prognosis of patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo treated with repositioning manoeuvres. J Laryngol Otol 120:528–533
Sakaida M, Takeuchi K, Ishinaga H, Adachi M, Majima Y (2003) Long-term outcome of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 60:1532–1534
Author contributions
Drs. HA Kim and H Lee designed and conceptualized the study, interpreted the data, and drafted and revised the manuscript. Dr. HA Kim wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data. Drs. SW Park, JI Kim, BG Kang, J Lee, BI Han, JI Seok, and EJ Chung contributed to the study concept and design and the revision of the manuscript. Dr. JY Kim contributed to the interpretation of the data and revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Disclosures
Dr. Lee serves on the editorial boards of Research in Vestibular Science, Frontiers in Neuro-otology, and Current Medical Imaging Review. The other authors report no disclosures.
Ethical standards
This study was performed in accordance with the guidelines of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local ethics committee.
Source of Funding
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP) (No. 2014R1A5A2010008).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.A., Park, SW., Kim, J. et al. Efficacy of mastoid oscillation and the Gufoni maneuver for treating apogeotropic horizontal benign positional vertigo: a randomized controlled study. J Neurol 264, 848–855 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8422-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8422-2