Abstract
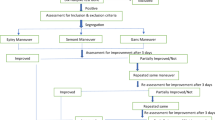
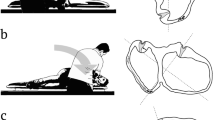
Several methods of physiotherapy have been advanced for apogeotropic type benign positional vertigo involving the horizontal semicircular canal (HC-BPV). The aim of this study was to determine the therapeutic efficacies of the proposed maneuvers in apogeotropic HC-BPV. Using a prospective randomized trial involving seven nationwide dizziness clinics in Korea, we compared the immediate efficacies of head-shaking and modified Semont maneuvers in 103 consecutive patients with apogeotropic HC-BPV. We also determined an additional therapeutic benefit of mastoid oscillation while the patients without response to both maneuvers were performing the Brandt–Daroff exercise. Successful treatment was defined as resolution of positional vertigo and nystagmus, or as transition into geotropic HC-BPV. Results showed that head shaking was more effective than the modified Semont maneuver (37.3 vs. 17.3%, P = 0.02). However, therapeutic efficacy did not differ between the maneuvers after the initial non-responders switched over to the other maneuver (23.3 vs. 25.0%, P = 0.861). Mastoid oscillation provided no additional benefit while the patients without response to both maneuvers were performing the Brandt–Daroff exercise. Most positional vertigos resolved within a week (89.4%) irrespective of the treatment modalities applied and all showed resolution within 28 days. The head-shaking maneuver described here proved more effective than the modified Semont maneuver in treating apogeotropic HC-BPV. Mastoid vibration conferred no additional benefit during the Brandt–Daroff exercise.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appiani GC, Catania G, Gagliardi M, Cuiuli G (2005) Repositioning maneuver for the treatment of the apogeotropic variant of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 26:257–260
Baloh RW, Honrubia V, Jacobson K (1987) Benign positional vertigo: clinical and oculographic features in 240 cases. Neurology 37:371–378
Baloh RW, Jacobson K, Honrubia V (1993) Horizontal semicircular canal variant of benign positional vertigo. Neurology 43:2542–2549
Baloh RW, Yue Q, Jacobson KM, Honrubia V (1995) Persistent direction-changing positional nystagmus: another variant of benign positional nystagmus? Neurology 45:1297–1301
Brandt T, Daroff RB (1980) Physical therapy for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol 106:484–485
Cakir BO, Ercan I, Cakir ZA, Civelek S, Sayin I, Turgut S (2006) What is the true incidence of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:451–454
Casani A, Giovanni V, Bruno F, Luigi GP (1997) Positional vertigo and ageotropic bidirectional nystagmus. Laryngoscope 107:807–813
Casani AP, Vannucci G, Fattori B, Berrettini S (2002) The treatment of horizontal canal positional vertigo: our experience in 66 cases. Laryngoscope 112:172–178
Fife TD (1998) Recognition and management of horizontal canal benign positional vertigo. Am J Otol 19:345–351
Fife TD, Iverson DJ, Lempert T, Furman JM, Baloh RW, Tusa RJ, Hain TC, Herdman S, Morrow MJ, Gronseth GS (2008) Practice parameter: therapies for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 70:2067–2074
Han BI, Oh HJ, Kim JS (2006) Nystagmus while recumbent in horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 66:706–710
Hornibrook J (2004) Horizontal canal benign positional vertigo. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 113:721–725
Imai T, Ito M, Takeda N, Uno A, Matsunaga T, Sekine K, Kubo T (2005) Natural course of the remission of vertigo in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 64:920–921
Koo JW, Moon IJ, Shim WS, Moon SY, Kim JS (2006) Value of lying-down nystagmus in the lateralization of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 27:367–371
Korres SG, Balatsouras DG (2004) Diagnostic, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic aspects of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:438–444
Lee SH, Choi KD, Jeong SH, Oh YM, Koo JW, Kim JS (2007) Nystagmus during neck flexion in the pitch plane in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo involving the horizontal canal. J Neurol Sci 256:75–80
Lempert T (1994) Horizontal benign positional vertigo. Neurology 44:2213–2214
Lempert T, Tiel-Wilck K (1996) A positional maneuver for treatment of horizontal-canal benign positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 106:476–478
Li JC (1995) Mastoid oscillation: a critical factor for success in canalith repositioning procedure. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112:670–672
McClure JA (1985) Horizontal canal BPV. J Otolaryngol 14:30–35
Moon SY, Kim JS, Kim BK, Kim JI, Lee H, Son SI, Kim KS, Rhee CK, Han GC, Lee WS (2006) Clinical characteristics of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in Korea: a multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci 21:539–543
Mosca F, Morano M (2001) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, incidence and treatment. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 118:95–101
Motamed M, Osinubi O, Cook JA (2004) Effect of mastoid oscillation on the outcome of the canalith repositioning procedure. Laryngoscope 114:1296–1298
Nuti D, Agus G, Barbieri MT, Passali D (1998) The management of horizontal-canal paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol 118:455–460
Nuti D, Vannucchi P, Pagnini P (1996) Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of the horizontal canal: a form of canalolithiasis with variable clinical features. J Vestib Res 6:173–184
Sargent EW, Bankaitis AE, Hollenbeak CS, Currens JW (2001) Mastoid oscillation in canalith repositioning for paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 22:205–209
Sherman D, Massoud EA (2001) Treatment outcomes of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Otolaryngol 30:295–299
Steddin S, Ing D, Brandt T (1996) Horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo (h-BPPV): transition of canalolithiasis to cupulolithiasis. Ann Neurol 40:918–922
Vannucchi P, Giannoni B, Nuti D (1992) La cupololitiasi del canale semicircolare orizzontale: aspetti clinici. In: Pagnini P (ed) La cupololitiasi. Formenti-Puropharma, Milan, pp 81–91
Vannucchi P, Giannoni B, Pagnini P (1997) Treatment of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Vestib Res 7:1–6
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant no 03-2007-002 from the SNUBH Research Fund.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S.-Y. Oh (Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Chonbuk National University) conducted the statistical analyses.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, SY., Kim, JS., Jeong, SH. et al. Treatment of apogeotropic benign positional vertigo: comparison of therapeutic head-shaking and modified Semont maneuver. J Neurol 256, 1330–1336 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5122-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5122-6