Abstract
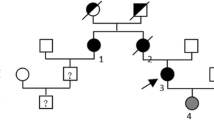
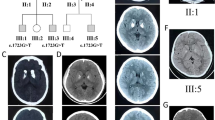
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) mutation has been reported in Alexander disease. We report a 31-year-old woman suffering from Alexander disease with a V87L mutation in GFAP. She showed psychomotor regression and a history of seizures, in addition to pendular nystagmus, dysarthria, spastic gait, and bladder dysfunction. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed atrophy of the medulla oblongata and mild cervical cord atrophy, deep white matter abnormalities, periventricular rim, and signal changes of the medulla oblongata and dentate hilum. Sequence analysis of her GFAP gene showed a heterozygous c.273G>C mutation predictive of a p.V87L amino acid substitution. We concluded that she was actually affected with Alexander disease. Twenty months later she fell down and sustained a head contusion. Urgent head computed tomography (CT) showed calcification in the subcortical and cortical regions, which may relate to the psychomotor regression and history of seizures. Calcification in the subcortical and cortical regions on head CT has not been reported in Alexander disease; this may be associated with a V87L mutation in GFAP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander WS (1949) Progressive fibrinoid degeneration of fibrillary astrocytes associated with mental retardation in a hydrocephalic infant. Brain 72:373–381
Iwaki T, Kume-Iwaki A, Liem RK, Goldman JE (1989) Alpha B-crystallin is expressed in non-lenticular tissues and accumulates in Alexander’s disease brain. Cell 57:71–78
Pareyson D, Fancellu R, Mariotti C, Romano S, Salmaggi A, Carella F, Girotti F, Gattellaro G, Carriero MR, Farina L, Ceccherini I, Savoiardo M (2008) Adult-onset Alexander disease: a series of eleven unrelated cases with review of the literature. Brain 131:2321–2331
Balbi P, Salvini S, Fundarò C, Frazzitta G, Maestri R, Mosah D, Uggetti C, Sechi G (2010) The clinical spectrum of late-onset Alexander disease: a systematic literature review. J Neurol 257:1955–1962
Namekawa M, Takiyama Y, Honda J, Shimazaki H, Sakoe K, Nakano I (2010) Adult-onset Alexander disease with typical “tadpole” brainstem atrophy and unusual bilateral basal ganglia involvement: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Neurol 10:21
Yoshida T, Sasaki M, Yoshida M, Namekawa M, Okamoto Y, Tsujino S, Sasayama H, Mizuta I, Nakagawa M, The Alexander Disease Study Group in Japan (2011) Nationwide survey of Alexander disease in Japan and proposed new guidelines for diagnosis. J Neurol [Epub ahead of print]
Okamoto Y, Mitsuyama H, Jonosono M, Hirata K, Arimura K, Osame M, Nakagawa M (2002) Autosomal dominant palatal myoclonus and spinal cord atrophy. J Neurol Sci 195:71–76
Sreedharan J, Shaw CE, Jarosz J, Samuel M (2007) Alexander disease with hypothermia, microcoria, and psychiatric and endocrine disturbances. Neurology 68:1322–1323
Balbi P, Seri M, Ceccherini I, Uggetti C, Casale R, Fundarò C, Caroli F, Santoro L (2008) Adult-onset Alexander disease: report on a family. J Neurol 255:24–30
Jefferson RJ, Absoud M, Jain R, Livingston JH, van der Knaap MS, Jayawant S (2010) Alexander disease with periventricular calcification: a novel mutation of the GFAP gene. Dev Med Child Neurol 52:1160–1163
Howard RS, Greenwood R, Gawler J, Scaravilli F, Marsden CD, Harding AE (1993) A familial disorder associated with palatal myoclonus, other brainstem signs, tetraparesis, ataxia and Rosenthal fibre formation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56:977–981
Walls TJ, Jones RA, Cartlidge N, Saunders M (1984) Alexander’s disease with Rosenthal fibre formation in an adult. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:399–403
Sawaishi Y (2010) Periventricular calcification added to the phenotypic repertoire of Alexander disease. Dev Med Child Neurol 52:1081–1082
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Alexander disease research grants received from the Intractable Disease Research Grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of the Government of Japan.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, H., Yoshida, T., Kitada, M. et al. Late-onset Alexander disease with a V87L mutation in glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and calcifying lesions in the sub-cortex and cortex. J Neurol 259, 457–461 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6201-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6201-z