Abstract
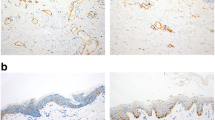
To characterize the vitality and age of skin wounds by means of the ICAM-1 pattern, 157 intravital human skin wounds (time since injury ranging from 5 min to 730 days) were immunohistochemically investigated. ICAM-1 was detected in paraffin sections after autoclaving and using the ABC technique in 86% of the wounds investigated. The correlation between ICAM-1 expression and the degree of wound inflammation is weak. Strong positive staining was observed 1.5 h at the earliest and 3.5 days at the latest after the time of injury. ICAM-1 also appeared at low concentrations in samples of uninjured skin (n = 65), on keratinocytes and the endothelial cells of blood vessels. Moderate to strong ICAM-1 expression is a valuable indication of the vitality of the wound. However, at present the detection of ICAM-1 alone is not sufficient to fix the wound age with the accuracy which is required for forensics applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 July 1996 / Received in revised form: 16 April 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreßler, J., Bachmann, L., Kasper, M. et al. Time dependence of the expression of ICAM-1 (CD 54) in human skin wounds. Int J Leg Med 110, 299–304 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004140050092
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004140050092