Abstract
Background
The low-numbered 14-chromosome karyotype of marsupials has falsified the fusion hypothesis claiming ancestrality from a 22-chromosome karyotype. Since the 14-chromosome condition of the relict Dromiciops gliroides is reminecent of ancestrality, its interstitial traces of past putative fusions and heterochromatin banding patterns were studied and added to available marsupials’ cytogenetic data. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and self-genomic in situ hybridization (self-GISH) were used to detect telomeric and repetitive sequences, respectively. These were complemented with C-, fluorescent banding, and centromere immunodetection over mitotic spreads. The presence of interstitial telomeric sequences (ITS) and diploid numbers were reconstructed and mapped onto the marsupial phylogenetic tree.
Results
No interstitial, fluorescent signals, but clearly stained telomeric regions were detected by FISH and self-GISH. Heterochromatin distribution was sparse in the telomeric/subtelomeric regions of large submetacentric chromosomes. Large AT-rich blocks were detected in the long arm of four submetacentrics and CG-rich block in the telomeric regions of all chromosomes. The ancestral reconstructions both ITS presence and diploid numbers suggested that ITS are unrelated to fusion events.
Conclusion
Although the lack of interstitial signals in D. gliroides’ karyotype does not prove absence of past fusions, our data suggests its non-rearranged plesiomorphic condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Chromosome numbers among marsupials ranges from 2n = 10 to 32, with a modal 14-chromosome number (followed by 2n = 22) for the Australian and South American radiation [1–3]. These karyotypes share extensive resemblance in chromosome morphology [4, 5] and G-banding patterns [6], leading to the hypothesis that 2n = 14 is ancestral for marsupials [6, 7]. Thus, larger diploid numbers are assumed to be derived by fissions, as suggested strongly by cytogenetic and phylogenetic comparisons [8–10]. An opposing view on the hybridization patterns of telomeric sequences claimed ancestrality for the 22-chromosome karyotypes and propose subsequent fusions to explain lower numbers [11]. In fact, the 22-chromosome species exhibit only telomeric signals whereas additional centromeric and interstitial telomeric sequences (ITS) suggesting fusion events were detected in 14- and 18-chromosome species [12, 13]. Nevertheless, the colocalization of ITS in heterochromatic pericentromeric regions has been considered to be part of the satellite DNA rather than true telomeric sequences [14–16]. Consequently, interstitial signals outside pericentromeric regions have turned karyotypic ancestrality of American marsupials into an open question [17]. Based on the early divergence of the didelphid Glironia ventusa (2n = 18) and by ensuing at least four centric fission/fusion events, a bidirectional trend of karyotypic evolution has been proposed [18, 19]. Nevertheless, the phylogenetic information demands an explanation for the convergence to 2n = 18 in the Monodelphis clade [19].
Recent comparative metatherian and eutherian genome assemblies have falsified the fusion hypothesis, thus supporting the ancestrality of the 14-chromosome karyotype [20]. This putative ancestral karyotype is shared by microbiotherians, caenolestids, peramelemorphians, vombatids, and pygmy possums [10]. It includes six large, six medium-sized, and two small sex chromosomes, as inferred from extensive G-banding studies [2, 4, 6] including Dromiciops gliroides (2n = 14) [21].
The Microbiotheria is one of the three orders of American marsupials, comprising 12 extinct species and the sole surviving, D. gliroides [22, 23]. To inquire whether traces of past fusions could still be detected in D. gliroides, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) using telomeric probes on mitotic plates were assayed. Since major structural chromosomal rearrangements are associated with cytogenetically detectable heterochromatic regions and repetitive sequences [24–27], we explored both issues by C-banding and self-genomic in situ hybridization (self-GISH) [28, 29]. This heterochromatic characterization was complemented with AT and CG-rich banding procedures and centromere identification. To further explore the relationships between fusion events and ITS, their ancestral presence using the phylogenetic tree of Mitchell et al. [30] was reconstructed.
Material and methods
Chromosomes
Mitotic plates of two males and one female D. gliroides collected in San Martín experimental station of Universidad Austral de Chile (39°38′S, 73°07′W) were used in this study. Chromosomal material was obtained from primary fibroblast cultures derived from ear tissue stored at −196 °C following Verma and Babu [31]. Metaphase spreads for immunofluorescense were prepared according to Zakharova et al. [32]. The ear cell material was collected and cultured previously to this work according to the protocol of the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of the Universidad Austral de Chile (UACH) No. 11/09. Cells cultured were cryopreserved for six years in mammal tissue collection of the UACH from where it was thawed and recovered [31].
FISH, Self-GISH, and immunofluorescence
Telomeric sequence detection by FISH on metaphase chromosomes was performed with the universal telomeric probe (TTAGGG)n, generated by PCR and labeled with fluorescein 12-dUTP (Roche Applied Science) [33, 34]. Three different posthybridization washed times (5, 2, and 1 min) with formamide 50 % were used to increase the sensitivity for telomere detection. Unspecific repetitive sequences were detected by self-GISH through hybridization of total genomic DNA probes of D. gliroides over its own mitotic plates [29]. Both FISH and self-GISH chromosomes were counterstained with DAPI (4′, 6-diamino-2-phenylindole) and mounted with Vectashield antifade. Mitotic plates were digitally captured at 100x with adequate filters using an Axiolab epifluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss) equipped with an Axiocam camera.
Centromeres were detected with anti-centromere of polyclonal human antibody (ACA; Cat. No. 15–235, Antibodies Incorporated). Goat anti-human IgG conjugated with Texas Red (Cat. No.23773-2, Bioscience) was used as secondary antibody. Both antibodies were diluted in 1:100 PBS and applied on mitotic plates [32]. Mitotic plates were mounted and captured as described previously.
Chromosome banding
C-banding was conducted using the Ba(OH)2 treatment at 46 °C for 3–4 min [35]. Given that AT and CG staining denote chromatin’s nucleotide composition, blocks of AT-rich sequences were detected with methyl-green/DAPI [36] whereas CG-rich regions were identified through chromomycin [37]. C-bands were observed under the microscope with a halogen lamp whereas a mercury lamp with adequate filters was used for chromomycin and methyl-green/DAPI staining. Banding images were captured as described above.
Ancestral state reconstruction
To inquire onto the ancestrality of diploid numbers and ITS presence in American marsupials, Bayesian trait reconstruction onto the phylogeny of Mitchel et al. [30] was performed using BayesTraits v2.0 [38]. This phylogeny includes the largest number of characters and marsupial species. The MCMC multistate module was implemented using a compilation of cytogenetic data listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. The analysis was run for 106 iterations, sampling every 103. The stationary phase was checked using Tracer version 1.6 [39] and sample points prior to the plateau phase were discarded as burn-in. To test significance, Bayes Factor (BF), was estimated as the difference in the log’s marginal likelihood between the data and the theoretical model containing restricted transition rates. Marginal likelihoods were estimated using stepping stone sampler [38, 40].
Results
FISH, Self-GISH, and immunofluorescence
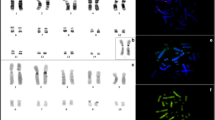
Telomeric, but no centromeric or interstitial signals were detected on all chromosomes of D. gliroides (Fig. 1a), regardless of stringency conditions (Additional file 2: Figure S1).
Molecular cytogenetic analyses on D. gliroides chromosomes. a FISH over a male mitotic plate, using the telomeric probe. Note the absence of interstitial signals in all chromosomes. b Self-GISH on a female mitotic plate. Note the strong fluorescent signals in some telomeric regions and a dot-like fluorescent pattern in all chromosomes, except pair 3. c Immunoassay over male mitotic plates using the anti-centromere of polyclonal human antibody. Colocalization of red fluorescent signals with the primary constriction is observed
Intensive signals of high repetitive sequences in telomeric/subtelomeric regions together with dot-like fluorescent patterns in all chromosomes (except in pair 3) were detected by Self-GISH. Signals were also observed in the short arms of X-chromosomes and on the long arm of chromosomes 5 and 6 (Fig. 1b).
As expected, immunoassays allowed the detection of D. gliroides’ centromeres in primary constrictions devoid of heterochromatin (compare Figs. 1c and 2a).
Banding patterns of Dromiciops gliroides. a C-banding of a female mitotic plate. Note the sparse distribution pattern and absence of pericentromeric heterochromatin. b CG- fluorescent banding of a male mitotic plate. Note the intensively stained blocks of CG-rich sequences in telomeric/subtelomeric regions. c AT- fluorescent banding of a male mitotic plate. Note that AT-rich sequences are the inverse of the CG- banding pattern
Chromosome banding
No centromeric/pericentromeric, but sparse distribution of heterochromatin along all chromosomes resulted from the C-banding procedure (Fig. 2a). Nevertheless, weak heterochromatic areas were observed in telomeric/subtelomeric regions of chromosomes 1–3, and in both arms of chromosome 4 (Fig. 2a).
Large AT-rich blocks were detected in the interstitial regions of chromosomes 1, 2, 4, and 6. Stronger signals were observed in the long arm of chromosomes 1 and 2, and in both arms of chromosomes 3 and 4 (Fig. 2b). GC signals were restricted to telomeric/subtelomeric regions of all chromosomes (Fig. 2c). As reported previously, the Y chromosome was not detected in any of the 150 metaphase plates of each adult male analysed [41].
Ancestral state reconstruction
Both ITS presence and ancestral chromosome number for the American marsupials are shown in Fig. 3. Thus, 2n = 14 probably represents the ancestral diploid number of all marsupials including Paucituberculata, Didelphimorphia, and Australidelphia (Fig. 3, green branches). The transition from 14 to 22 chromosomes occurs in clades A and B, at about ∼ 24 and ∼ 18 Mya, respectively (Fig. 3, purple branches). The transition from 14 to 18 chromosomes would occur about ∼ 36 Mya in the Glironia venusta’s lineage and about ∼ 26 Mya in the Monodelphis clade (Fig. 3, orange branches). Considering the distribution of telomeric sequences in only 17 American species, low confidence (log BF <2) was obtained by ITS reconstruction. Nevertheless, the probability for each ancestor having ITSs is given, such that their highest probabilities would indicate ITS’ ancestral presence (Fig. 3, derived lineages within A and C clades).
Phylogenetic tree of American marsupials [30] depicting ancestral diploid number and ITS presence reconstruction. Branch colors indicate diploid number reconstructed with BayesTraits. Numbers above branches represent probability for each ancestor having ITSs. Cytogenetic data depicted at right follows: 1 = Sousa et al. [56]; 2 = Carvalho and Mattevi [12]; 3 = Svartman and Vianna-Morgante [13]; 4 = Pagnozzi et al. [15]; 5 = this study. Additional information is listed and coded in Additional file 1: Table S1
Discussion
Sparse heterochromatin distribution and few dispersed repetitive sequences on interstitial and centromeric regions characterize the karyotype of D. gliroides (Figs. 1b and 2a). This features are coherent with DNA annealing data depicting few repetitive DNA and higher effective concentration of single-copy sequences in D. gliroides relative to other marsupials [42]. The sparse labeling pattern detected by self-GISH along some chromosomes suggests a correspondence with specific genomic repetitive sequences (e.g. interspersed transposons and dispersed repetitive sequences; Fig. 1b). In fact, a dot-like fluorescent pattern is associated with the enrichment of retroelements on some chromosomes of the rodent Octomys mimax [43], Chionomys nivalis [44], and several Microtus species [45]. The lack of both repetitive sequences and pericentromeric heterochromatin has been associated with centromeric shifts and neocentromerization in cattle and in the marsupial genus Petrogale [46, 47]. This pattern is intriguing considering its role as substrates and as possible stabilizer for centromere formation and function [48]. Further satellite DNA studies, the analyses of centromere DNA-binding proteins, and the epigenetic studies of centromeric chromatin will shed light on the factors that have shaped this peculiar heterochromatic pattern.
GC-rich telomeric sequences detected in all D. gliroides’ chromosomes colocalize with most repetitive sequences detected by FISH and self-GISH (Figs. 1a, b and 2c). Since neither centromeric nor interstitial signals were detected by any technique applied, the lack of ITS is strongly suggested (Figs. 1a, b and 2c). It could be argued that this might be due to either loss or chromatin modification after fusion, as reported in Mus [25]. Assuming fusions, it seems unlikely that all ITS expected in D. gliroides were lost. Thus we hypothesize that ITS have never existed in D. gliroides chromosomes and support the notion that its karyotype does not fit into the fusion model. The undetection of ITS fits well with the cytogenetic/phylogenetic inference and genome assemblage comparison [10, 20]. This hypothesis is further supported by the lack of interstitial C-bands (Fig. 2a), as the opposite is predicted if fusions took place [25–27]. Our results agree with the cytogenetic studies on Australian genera Macropus, Petrogale, and Thylogale [16, 46, 49] that support the ancestrality of the 14-chromosome karyotype. Chromosome painting onto the chromosomes of D. gliroides will clarify its ancestral 14-chromosome condition by showing conserved regions and possible inversions.
Previous and varied phylogenetic studies have indicated that D. gliroides is more related to the Australasian than to the South American radiation [21, 30, 42, 50, 51]. This is consistent with the microbiotherid’s oldest fossil known from the Early Paleocene, when Australia, South America and Antarctica were still connected [52]. These two facts support D. gliroides as a living fossil that links the American and the Australian radiations. Consequently, its cytogenetic features might well be supporting data for the marsupial ancestral state reconstruction. In fact, the shared 14-chromosome karyotypes of Dromiciops, Caenolestes, Rhyncholestes, and Caluromys allow us to confidently (>90 %) support their ancestrality, also extended to the Didelphidae and Caenolestidae, as previously advanced [10, 20].
The lack of ITS in Dromiciops and Caluromys makes improbable their existence in the basal nodes of marsupial phylogeny (Fig. 3). Assuming their absence (P < 0.5), its onset would have been after the divergence of Glironia venusta from the remaining didelphids, more recent than ∼ 36 Mya (Fig. 3). Given the small probability for ITS presence, the transition from 14 to 18 chromosomes would be unrelated to fusion events (Fig. 3, orange branches). In the same line, the onset of marsupial ITS would be traced after the dispersion from South America to Australia, during the Paleocene [53, 54], falsifying the predictions derived from the fusion hypothesis [11–13].
The 14-chromosome ancestors of Gracilanus and Marmosops have a high probability of having ITS while the 14-chromosome ancestor between them and Metachirus has a low corresponding probability (Fig. 3). A similar situation is observed in the ancestor of the Micoureus clade with respect to Marmosa murina. Both instances illustrate the conservation of 14 chromosomes, indicating that ITS acquisition was unrelated to the fusion events. ITS presence might well represent signals of satellite DNA associated to constitutive heterochromatin, as advanced [14–16, 55]. Since ITS presence colocalizes with the constitutive heterochromatin, and its presence occurs in derived 14- and 18-chromosome species depicted in the phylogenetic tree, the fusion hypothesis rendered highly improbable.
Conclusions
Neither centromeric nor interstitial signals reflecting fusions were detected in the “living fossil” D. gliroides by either classical or molecular cytogenetics. The ancestral reconstruction of diploid number as well as the ITS absence suggested their decoupling from past fusion events. Therefore, our data give additional support to the notion that fission events from an ancestral 14-chromosome condition explain the high chromosome numbers in the karyotypic radiation of American marsupials.
Abbreviations
- BF:
-
Bayes factor
- DAPI:
-
4′, 6-diamino-2-phenylindole
- dUTP:
-
deoxyuridine Triphosphate
- FISH:
-
fluorescent in situ hybridization
- IgG:
-
immunoglobulin G
- ITS:
-
interstitial telomeric sequences
- MCMC:
-
Markov chain Monte Carlo
- min:
-
minute
- Mya:
-
million years ago
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffer solution
- self-GISH:
-
self-genomic in situ hybridization
- UACH:
-
Universidad Austral de Chile
References
Carvalho BA, Oliveira LFB, Nunes AP, Mattevi MS. Karyotypes of nineteen marsupial species from Brazil. J Mammal. 2002;83:58–70.
Hayman DL. Marsupial cytogenetics. Aust J Zool. 1989;37:331–49.
Palma RE, Yates TL. The chromosomes of bolivian didelphid marsupials. Occas Pap Mus Texas Tech Univ. 1996;162:1–20.
Hayman D, Martin P, Mammalia I. In: John B, editor. Monotremata and marsupialia, chordata 4. Berlin: Gebrüder Borntraeger; 1974. p. 110.
Martin PG, Hayman DL. Quantitative comparisons between the karyotypes of Australian marsupials from three different superfamilies. Chromosoma. 1967;20:290–310.
Rofe R, Hayman D. G-banding evidence for a conserved complement in the Marsupialia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39:40–50.
Hayman D, Martin P. Cytogenetics of marsupials. In: Benirschke K, editor. Comparative mammalian cytogenetics. New York: Springer; 1969. p. 191–217.
Rens W, O’Brien PC, Fairclough H, Harman L, Graves JA, Ferguson-Smith MA. Reversal and convergence in marsupial chromosome evolution. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2003;102:282–90.
Rens W, O’Brien PCM, Yang F, Graves JAM, Ferguson-Smith MA. Karyotype relationships between four distantly related marsupials revealed by reciprocal chromosome painting. Chromosome Res. 1999;7:461–74.
Westerman M, Meredith RW, Springer MS. Cytogenetics meets phylogenetics: a review of karyotype evolution in diprotodontian marsupials. J Hered. 2010;101:690–702.
Sharman G. The chromosomes of non-eutherian mammals. In: Chiarelli A, Capanna E, editors. Cytotaxonomy and vertebrate evolution. New York: Academic; 1973. p. 485–530.
Carvalho BD, Mattevi MS. (T2AG3)n telomeric sequence hybridization suggestive of centric fusion in karyotype marsupials evolution. Genetica. 2000;108:205–10.
Svartman M, Vianna-Morgante AM. Karyotype evolution of marsupials: from higher to lower diploid numbers. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1998;82:263–6.
Pagnozzi JM, Silva MJJ, Yonenaga-Yassuda Y. Intraspecific variation in the distribution of the interstitial telomeric (TTAGGG)n sequences in Micoureus demerarae (Marsupialia: Didelphidae). Chromosome Res. 2000;8:585–91.
Pagnozzi JM, Ditchfield AD, Yonenaga-Yassuda Y. Mapping the distribution of the interstitial telomeric (TTAGGG)n sequences in eight species of Brazilian marsupials (Didelphidae) by FISH and the correlation with constitutive heterochromatin. Do ITS represent evidence for fusion events in American marsupials? Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002;98:278–84.
Metcalfe CJ, Eldridge MD, Johnston PG. Mapping the distribution of the telomeric sequence (T2AG3)n in the 2n = 14 ancestral marsupial complement and in the macropodines (Marsupialia: Macropodidae) by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Chromosome Res. 2004;12:405–14.
Svartman M. American marsupials chromosomes: Why study them? Genet Mol Biol. 2009;32:675–87.
Voss RS, Jansa SA. Phylogenetic relationships and classification of didelphid marsupials, an extant radiation of New World metatherian mammals. Bull Am Mus Nat Hist. 2009;322:1–177.
Fantin C, Da Silva MNF. The karyotype of a rare South American marsupial. The bushy-tailed opossum genus Glironia (Didelphimorphia: Didelphidae). Mastozoologia Neotropical. 2011;18:125–30.
Deakin JE, Delbridge ML, Koina E, Harley N, Alsop AE, Wang C, Patel VS, Graves JA. Reconstruction of the ancestral marsupial karyotype from comparative gene maps. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:258.
Spotorno A, Marin JC, Yévenes M, Walker L, Fernández-Donoso RA, Pincheira J, Berríos MS, Palma RE. Chromosome divergences among american marsupials and the australian affinities of the american Dromiciops. J Mammal Evol. 1997;4:259–69.
Gardner AL, editor. Mammals of South America: Marsupials, Xenarthrans, Shrews, and Bats. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2008. p. 690.
Hershkovitz P. Dromiciops gliroides Thomas, 1894, last of the Microbiotheria (Marsupialia), with a review of the family Microbiotheriidae. Fieldiana Zool. 1999;93:1–60.
Badaeva ED, Dedkova OS, Gay G, Pukhalskyi VA, Zelenin AV, Bernard S, Bernard M. Chromosomal rearrangements in wheat: their types and distribution. Genome. 2007;50:907–26.
Garagna S, Broccoli D, Redi CA, Searle JB, Cooke HJ, Capanna E. Robertsonian metacentrics of the house mouse lose telomeric sequences but retain some minor satellite DNA in the pericentromeric area. Chromosoma. 1995;103:685–92.
Go Y, Rakotoarisoa G, Kawamoto Y, Randrianjafy A, Koyama N, Hirai H. PRINS analysis of the telomeric sequence in seven lemurs. Chromosome Res. 2000;8:57–65.
Vermeesch JR, De Meurichy W, Van Den Berghe H, Marynen P, Petit P. Differences in the distribution and nature of the interstitial telomeric (TTAGGG)n sequences in the chromosomes of the Giraffidae, okapai (Okapia johnstoni), and giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis): evidence for ancestral telomeres at the okapi polymorphic rob(5;26) fusion site. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1996;72:310–5.
Markova M, Vyskot B. New horizons of genomic in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009;126:368–75.
She C, Liu J, Diao Y, Hu Z, Song Y. The distribution of repetitive DNAs along chromosomes in plants revealed by self-genomic in situ hybridization. J Genet Genomics. 2007;34:437–48.
Mitchell KJ, Pratt RC, Watson LN, Gibb GC, Llamas B, Kasper M, Edson J, Hopwood B, Male D, Armstrong K, et al. Molecular phylogeny, biogeography, and habitat preference evolution of marsupials. Mol Biol Evol. 2014;31:2322–30.
Verma RS, Babu A. Human chromosomes: principles and techniques. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw Hill, Inc.; 1995. p. 419.
Zakharova IS, Shevchenko AI, Shilov AG, Nesterova TB, Vandeberg JL, Zakian SM. Histone H3 trimethylation at lysine 9 marks the inactive metaphase X chromosome in the marsupial Monodelphis domestica. Chromosoma. 2011;120:177–83.
Ijdo JW, Wells RA, Baldini A, Reeders ST. Improved telomere detection using a telomere repeat probe (TTAGGG)n generated by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19:4780.
Baldini A, Ward DC. In situ hybridization banding of human chromosomes with Alu-PCR products: a simultaneous karyotype for gene mapping studies. Genomics. 1991;9:770–4.
Sumner AT. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res. 1972;75:304–6.
Donlon TA, Magenis RE. Methyl green is a substitute for distamycin A in the formation of distamycin A/DAPI C-bands. Hum Genet. 1983;65:144–6.
Schweizer D. Simultaneous fluorescent staining of R bands and specific heterochromatic regions (DA-DAPI bands) in human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27:190–3.
Pagel M, Meade A, Barker D. Bayesian estimation of ancestral character states on phylogenies. Syst Biol. 2004;53:673–84.
Rambaut A, Suchard M, Xie D, Drummond A. Tracer v1.6, Available from http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer. Accessed 28 July 2016.
Xie W, Lewis PO, Fan Y, Kuo L, Chen MH. Improving marginal likelihood estimation for Bayesian phylogenetic model selection. Syst Biol. 2011;60:150–60.
Gallardo MH, Patterson BD. An additional 14-chromosome karyotype and sex-chromosome mosaicism in South American marsupials. Fieldiana Zool. 1987;39:111–5.
Kirsch JA, Dickerman AW, Reig OA, Springer MS. DNA hybridization evidence for the Australasian affinity of the American marsupial Dromiciops australis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:10465–9.
Suárez-Villota EY, Vargas RA, Marchant CL, Torres JE, Kohler N, Nunez JJ, de la Fuente R, Page J, Gallardo MH. Distribution of repetitive DNAs and the hybrid origin of the red vizcacha rat (Octodontidae). Genome. 2012;55:105–17.
Acosta MJ, Marchal JA, Fernandez-Espartero CH, Bullejos M, Sanchez A. Retroelements (LINEs and SINEs) in vole genomes: differential distribution in the constitutive heterochromatin. Chromosome Res. 2008;16:949–59.
Modi W, Serdyukova N, Vorobieva N, Graphodatsky A. Chromosomal localization of six repeated DNA sequences among species of Microtus (Rodentia). Chromosome Res. 2003;11:705–13.
Metcalfe CJ, Eldridge MD, McQuade LR, Johnston PG. Mapping the distribution of the telomeric sequence (T2AG3)n in rock-wallabies, Petrogale (Marsupialia: Macropodidae), by fluorescence in situ hybridization. I. The penicillata complex. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1997;78:74–80.
Sharman G, Close R, Maynes G. Chromosome evolution, phylogeny and speciation of rock wallabies (Petrogale, Macropodidae). Aust J Zool. 1989;37:351–63.
Henikoff S, Ahmad K, Platero JS, van Steensel B. Heterochromatic deposition of centromeric histone H3-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:716–21.
Metcalfe CJ, Eldridge MD, Johnston PG. Mapping the distribution of the telomeric sequence (T2AG3)n in rock wallabies, Petrogale (Marsupialia: Macropodidae), by fluorescence in situ hybridization. II. the lateralis complex. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002;96:169–75.
Meredith RW, Westerman M, Case JA, Springer MS. A phylogeny and timescale for marsupial evolution based on sequences for five nuclear genes. J Mammal Evol. 2008;15:1–36.
Springer M, Westerman M, Kirsch JW. Relationships among orders and families of marsupials based on 12S ribosomal DNA sequences and the timing of the marsupial radiation. J Mammal Evol. 1994;2:85–115.
Gayet M, Marshall LG, Sempere T. The Mesozoic and Paleocene vertebrates of Bolivia and their stratigraphic context: a review. Revista Técnica YPFB. 1991;12:393–433.
Beck RM, Godthelp H, Weisbecker V, Archer M, Hand SJ. Australia’s oldest marsupial fossils and their biogeographical implications. PLoS One. 2008;3:e1858.
Woodburne MO, Case JA. Dispersal, vicariance, and the late Cretaceous to early Tertiary land mammal biogeography from South America to Australia. J Mammal Evol. 1996;3:121–61.
Metcalfe CJ, Eldridge MD, Johnston PG. Mapping the distribution of the telomeric sequence (T2AG3)n in the Macropodoidea (Marsupialia) by fluorescence in situ hybridization. II. The ancestral 2n = 22 macropodid karyotype. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2007;116:212–7.
Souza EM, Silva CEF, Eler ES, Silva MN, Feldberg E. Variations of chromosomal structures in Caluromys philander (Didelphimorphia: Didelphidae) from the Amazon region. Genetica. 2013;141:89–93.
Acknowledgements
We thank to N. Köhler for laboratory assistance and J. J. Nuñez for suggestions regarding to the manuscript. We also appreciate the comments made by three anonymous reviewers and the editor that significantly improved the manuscript. This research was supported by CONICYT, Fondecyt 3160328 to EYS-V and Fondecyt 1070217 to MHG.
Funding
This research was financed by CONICYT, Fondecyt 3160328 to EYS-V and Conicyt, Fondecyt, 1070217 to MHG.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional file (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Authors’ contributions
Research concept and design: EYS-V, MHG. Performed the experiments: EYS-V, REH, RAV. Image and data analysis: EYS-V. Wrote the paper: EYS-V, MHG. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Samples were taken from mammal tissue collection of the Universidad Austral de Chile (UACH). They were collected according to the protocol of the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of the UACH No. 11/09.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional files
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Cytogenetic data used for the reconstructions of ancestral diploid numbers and presence of interstitial telomeric signals (ITS). Multi states codes used in BayesTraits were A: 2n = 14, B: 2n = 18, C: 2n = 22, D: 2n = 10, E: 2n = 12, F: 2n = 16, G: 2n = 18, H: 2n = 20, I: 2n = 24, J: 2n = 32; K: presence of ITS, L: absence of ITS. Missing data code (−) was used for diploid numbers and/or ITS of species without these cytogenetic data. (XLS 44 kb)
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization over D. gliroides mitotic plates using the telomeric probe. Posthybridization washes with formamide 50 % for a: 5 min, b: 2 min, and c: 1 min were tested. Note the absence of interstitial signals in all chromosomes. (JPG 691 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Suárez-Villota, E.Y., Haro, R.E., Vargas, R.A. et al. The ancestral chromosomes of Dromiciops gliroides (Microbiotheridae), and its bearings on the karyotypic evolution of American marsupials. Mol Cytogenet 9, 59 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-016-0270-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-016-0270-8