Abstract
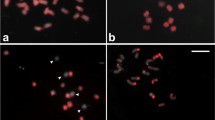
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) has been widely used in the physical mapping of genes and chromosome landmarks in plants and animals. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) contain large inserts making them amenable for FISH mapping. We used BAC-FISH to study genome organization and evolution in hexaploid wheat and its relatives. We selected 56 restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) locus-specific BAC clones from libraries of Aegilops tauschii (the D-genome donor of hexaploid wheat) and A-genome diploid Triticum monococcum. Different types of repetitive sequences were identified using BAC-FISH. Two BAC clones gave FISH patterns similar to the repetitive DNA family pSc119; one BAC clone gave a FISH pattern similar to the repetitive DNA family pAs1. In addition, we identified several novel classes of repetitive sequences: one BAC clone hybridized to the centromeric regions of wheat and other cereal species, except rice; one BAC clone hybridized to all subtelomeric chromosome regions in wheat, rye, barley and oat; one BAC clone contained a localized tandem repeat and hybridized to five D-genome chromosome pairs in wheat; and four BAC clones hybridized only to a proximal region in the long arm of chromosome 4A of hexaploid wheat. These repeats are valuable markers for defined chromosome regions and can also be used for chromosome identification. Sequencing results revealed that all these repeats are transposable elements (TEs), indicating the important role of TEs, especially retrotransposons, in genome evolution of wheat.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albini SM, Schwarzacher T (1992) In situ localization of two repetitive DNA sequences to surface-spread pachytene chromosomes of rye. Genome 35:551–559
Anamthawat-Jonsson K, Heslop-Harrison JS (1993) Isolation and characterization of genome-specific DNA sequences in Triticeae species. Mol Gen Genet 240:151–158
Appels R, Moran LB (1984) Molecular analysis of alien chromatin introduced into wheat. Stadler Genet Symp 16:529–557
Appels R, Dennis ES, Smyth DR, Peacock WJ (1981) Two repeated DNA sequences from the heterochromatic regions of rye (Secale cereale) chromosomes. Chromosoma 84:265–277
Aragon-Alcaide L, Miller T, Schwarzacher T, Reader S, Moore G (1996) A cereal centromeric sequence. Chromosoma 105:261–268
Bedbrook JR, Jones J, O’Dell M, Thompson R, Flavell RB (1980) A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin in Secale species. Cell 19:545–560
Belostotsky DA, Ananiev EV (1990) Characterization of relic DNA from barley genome. Theor Appl Genet 80:374–380
Bennett MD, Leitch IJ (1995) Nuclear DNA amount in angiosperms. Ann Bot 76:113–176
Bennett MD, Smith JB (1976) Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 274:227–274
Bennetzen JL, Freeling M (1997) The unified grass genome: synergy in synteny. Genome Res 7:301–306
Brooks SA, Huang L, Gill BS, Fellers JP (2002) Analysis of 106 kb of contiguous DNA sequence from the D genome of wheat reveals high gene density and a complex arrangement of genes related to disease resistance. Genome 45:963–972
Cheng Z-J, Murata M (2003) A centromeric tandem repeat family originating from a part of Ty3/ gypsy -retroelement in wheat and its relatives. Genetics 164:665–672
Cheng Z, Presting GG, Buell CR, Wing RA, Jiang J (2001) High resolution pachytene chromosome mapping of bacterial artificial chromosomes anchored by genetic markers reveals the centromere location and the distribution of genetic recombination along chromosome 10 of rice. Genetics 157:1749–1757
Cheng Z, Buell CR, Wing RA, Jiang J (2002) Resolution of fluorescence in-situ hybridization mapping on rice mitotic prometaphase chromosomes, meiotic pachytene chromosomes and extended DNA fibers. Chromosome Res 10:379–387
Dong F, Miller T, Jackson SA, Wang GL, Ronald PC, Jiang J (1998) Rice (Oryza sativa) centromeric regions consist of complex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:8135–8140
Dong F, Song J, Naess SK, Helgeson JP, Gebhardt C, Jiang J (2000) Development and applications of a set of chromosome-specific cytogenetic DNA markers in potato. Theor Appl Genet 101:1001–1007
Dvorák J, Zhang HB (1992) Reconstruction of the phylogeny of the genus Triticum from variation in repeated nucleotide sequences. Theor Appl Genet 84:419–429
Faris JD, Haen KM, Gill BS (2000) Saturation mapping of a gene-rich recombinant hot spot region in wheat. Genetics 154:823–835
Flavell RB (1986) Repetitive DNA and chromosome evolution in plants. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 312:227–242
Francki MG (2001) Identification of Bilby, a diverged centromeric Ty1- copia retrotransposon family from cereal rye (Secale cereale L.). Genome 44:266–274
Fransz PF, Armstrong S, de Jong JH, Parnell LD, van Drunen C, Dean C, Zabel P, Bisseling T, Jones GH (2000) Integrated cytogenetic map of chromosome arm 4S of A. thaliana: structural organization of heterochromatic knob and centromere region. Cell 100:367–376
Gomez MI, Islam-Faridi MN, Woo S-S, Schertz KF, Czeschin D, Zwick MS, Wing RA, Stelly DM, Price HJ (1997) FISH of a maize sh2 -selected sorghum BAC to chromosomes of Sorghum bicolor. Genome 40:475–478
Hanson RE, Zwick MS, Choi S, Islam-Faridi MN, McKnight TD, Wing RA, Price HJ, Stelly DM (1995) Fluorescent in situ hybridization of a bacterial artificial chromosome. Genome 38:646–651
Huang S, Sirikhachornkit A, Su X, Faris J, Gill B, Haselkorn R, Gornicki P (2002) Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum / Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8133–8138
Hudakova S, Michalek W, Presting GG, ten Hoopen R, dos Santos K, Jasencakova Z, Schubert I (2001) Sequence organization of barley centromeres. Nucleic Acids Res 29:5029–5035
Hutchinson J, Lonsdale DM (1982) The chromosomal distribution of cloned highly repetitive sequences from hexaploid wheat. Heredity 48:371–376
Jackson SA, Cheng Z, Wang ML, Goodman HM, Jiang J (2000) Comparative fluorescence in situ hybridization mapping of a 431-kb Arabidopsis thaliana bacterial artificial chromosome contig reveals the role of chromosomal duplications in the expansion of the Brassica rapa genome. Genetics 1156:833–838
Jiang J, Gill BS (1994) Different species-specific chromosome translocations in Triticum timopheevii and T. turgidum support the diphyletic origin of polyploid wheats. Chromosome Res 2:59–64
Jiang J, Gill BS, Wang G-L, Ronald PC, Ward D (1995) Metaphase and interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization mapping of the rice genome with bacterial artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:4487–4491
Jiang J, Nasuda S, Dong F, Scherrer CW, Woo SS, Wing RA, Gill BS, Ward DC (1996) A conserved repetitive DNA element located in the centromeres of cereal chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:14210–14213
Johnston PA, Pickering RA (2002) PCR detection of Hordeum bulbosum introgressions in an H. vulgare background using a retrotransposon-like sequence. Theor Appl Genet 104:720–726
Jones JDG, Flavell RB (1982) The structure, amount and chromosomal localization of defined repeated DNA sequences in species of the genus Secale. Chromosoma 86:613–641
Kim J-S, Childs KL, Islam-Faridi MN, Menz MA, Klein RR, Klein PE, Price HJ, Mullet JE, Stelly DM (2002) Integrated karyotyping of sorghum by in situ hybridization of landed BACs. Genome 45:402–412
Kipling D, Warburton PE (1997) Centromeres, CENP-B and Tigger too. Trends Genet 13:141–145
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Li WL, Gill BS (2002) The colinearity of the Sh2/A1 orthologous region in rice, sorghum and maize is interrupted and accompanied by genome expansion in the Triticeae. Genetics 160:1153–1162
Lijavetzky D, Muzzi G, Wicker T, Keller B, Wing R, Dubcovsky J (1999) Construction and characterization of a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library for the A genome of wheat. Genome 42:1176–1182
Lucas H, Moore G, Murphy G, Flavell RB (1992) Inverted repeats in the long-terminal repeats of the wheat retrotransposon Wis 2–1A. Mol Biol Evol 9:716–728
Manninen I, Schulman AH (1993) BARE-1, a copia -like retroelement in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Mol Biol 22:829–846
May CE, Appels R (1987) The molecular genetics of wheat: toward an understanding of 16 billion base pairs of DNA. In: Heyne EG (ed) Wheat and wheat improvement, vol 13, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wis., pp 165–198
McIntyre CL, Pereira S, Moran LB, Appels R (1990) New Secale cereale (rye) DNA derivatives for the detection of rye chromosome segments in wheat. Genome 33:635–640
Mefford HC, Trask BJ (2002) The complex structure and dynamic evolution of human subtelomeres. Nat Rev Genet 3:91–102
Miller JT, Dong F, Jackson SA, Song J, Jiang J (1998) Retrotransposon-related DNA sequences in the centromeres of grass chromosomes. Genetics 150:1615–1623
Moullet O, Lagudah ES (1998) Construction of a wheat D genome bacterial artificial chromosome library. In: Slinkard AE (ed) Proceedings of the 9th International Wheat Genetics Symposium. University Extension Press, Saskatoon, Canada, pp 31–32
Moullet O, Zhang HB, Lagudah ES (1999) Construction and characterization of a large DNA insert library from the D genome of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 99:305–313
Mukai Y, Friebe B, Gill BS (1992) Comparison of C-banding patterns and in situ hybridization sites using highly repetitive and total genomic rye DNA probes of ‘Imperial’ rye chromosomes added to ‘Chinese Spring’ wheat. Jpn J Genet 67:71–83
Mukai Y, Nakahara Y, Yamamoto M (1993) Simultaneous discrimination of the three genomes in hexaploid wheat by multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization using total genomic and highly repeated DNA probes. Genome 36:489–494
Nagaki K, Tsujimoto H, Sasakuma T (1998) Dynamics of tandem repetitive Afa -family sequence in Triticeae, wheat-related species. J Mol Evol 47:183–189
Naranjo T, Roca A, Goicoechea PG, Giraldez R (1987) Arm homoeology of wheat and rye chromosomes. Genome 29:873–882
Pedersen C, Langridge P (1997) Identification of the entire chromosome complement of bread wheat by two-color FISH. Genome 40:589–593
Pedersen C, Rasmussen SK, Linde-Laursen I (1996) Genome and chromosome identification in cultivated barley and related species of the Triticeae (Poaceae) by in situ hybridization with the GAA-satellite sequence. Genome 39:93–104
Pologe LG, Ravetch JV (1988) Large deletions result from breakage and healing of P. falciparum chromosomes. Cell 55:869–874
Presting GG, Malysheva L, Fuchs J, Schubert I (1998) A Ty3/ gypsy retrotransposon-like sequence localizes to the centromeric regions of cereal chromosomes. Plant J 16:721–728
Pryde FE, Louis EJ (1997) Saccharomyces cerevisiae telomeres. A review. Biochemistry (Mosk) 62:1232–1241
Pryde FE, Gorham HC, Louis EJ (1997) Chromosome ends: all the same under their caps. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7:822–828
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1986a) Isolation of a D-genome specific repeated DNA sequence from Aegilops squarrosa. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:102–109
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1986b) Molecular identification of the D-genome chromosomes of wheat. J Hered 77:253–255
Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1996) High resolution mapping of repetitive DNA by in situ hybridization: molecular and chromosomal features of prominent dispersed and discretely localized DNA families from the wild beet species Beta procumbens. Plant Mol Biol 30:1099–1114
Schubert I, Shi F, Fuchs J, Endo TR (1998) An efficient screening for terminal deletions and translocations of barley chromosomes added to common wheat. Plant J 14:489–495
Shirasu K, Schulman AH, Lahaye T, Schulze-Lefert P (2000) A contiguous 66-kb barley DNA sequence provides evidence for reversible genome expansion. Genome Res 10:908–915
Shizuya HB, Birren B, Kim UJ, Mancino V, Slepak T, Tachiiri Y, Simon M (1992) Cloning and stable maintenance of a 300-kilobase-pair fragment of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:8794–8797
Smith DB, Flavell RB (1975) Characterization of the wheat genome by renaturation kinetics. Chromosoma 50:223–242
Spielmeyer W, Moullet O, Laroche A, Lagudah ES (2000) Highly recombinogenic regions at seed storage protein loci on chromosome 1DS of Aegilops tauschii, the D-genome donor of wheat. Genetics 155:361–367
Suzuki G, Ura A, Saito N, Do GS, Seo BB, Yamamoto M, Mukai Y (2001) BAC FISH analysis in Allium cepa. Genes Genet Syst 76:251–256
The Arabidopsis Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Ueng PP, Hang A, Tsang H, Vega JM, Wang L, Burton CS, He FT, Liu B (2000) Molecular analyses of a repetitive DNA sequence in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 43:556–563
van Slageren MW (1994) Wild wheats: a monograph of Aegilops L. and Amblyopurum (Jaub. & Spach) Eig (Poaceae). Wageningen Agricultural University Papers, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Vergnaud G (1999) Structure and evolution of human subtelomeric regions. J Soc Biol 193:35–40 (In French)
Vershinin A, Svitashev S, Gummesson PO, Salomon B, von Bothmer R, Bryngelsson T (1994) Characterization of a family of tandemly repeated DNA sequences in Triticeae. Theor Appl Genet 89:217–225
Vershinin AV, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) The large-scale genomic organization of repetitive DNA families at the telomeres of rye chromosomes. Plant Cell 7:1823–1833
Wicker T, Yahiaoui N, Guyot R, Schlagenhauf E, Liu Z-D, Dubcovsky J, Keller B (2003a) Rapid genome divergence at orthologous low molecular weight glutenin loci of the A and Am genomes of wheat. Plant Cell 15:1186–1197
Wicker T, Guyot R, Yahiaoui N, Keller B (2003b) CACTA transposons in Triticeae. A diverse family of high-copy repetitive elements. Plant Physiol 132:52–63
Wicky C, Villeneuve AM, Lauper N, Codourey L, Tobler H, Müller F (1996) Telomeric repeats (TTAGGC)n are sufficient for chromosome capping function in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:8983–8988
Yan L, Echenique V, Busso C, SanMiguel P, Ramakrishna W, Bennetzen JL, Harrington S, Dubcovsky J (2002) Cereal genes similar to Snf2 define a new subfamily that includes human and mouse genes. Mol Genet Genomics 268:488–499
Zhang P (2002) Analysis of the wheat genome by BAC-FISH. PhD thesis, Department of Plant Pathology, Kansas State University, Manhattan, USA
Zhang P, Friebe B, Lukaszewski AJ, Gill BS (2001) The centromere structure in Robertsonian wheat-rye translocation chromosomes indicates that centric breakage-fusion can occur at different positions within the primary constriction. Chromosoma 110:335–344
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Kansas Wheat Commission and a special USDA grant to the Wheat Genetics Resource Center. We also thank W. John Raupp and Duane Wilson for their excellent assistance, Drs. Li Huang, Lili Qi, and Steven Brooks for beneficial discussions, and Angie Matthews for DNA sequencing. This paper is contribution number 04-062-J from the Kansas Agricultural Experimental Station, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS 66506-5502, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P.B. Moens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Li, W., Fellers, J. et al. BAC-FISH in wheat identifies chromosome landmarks consisting of different types of transposable elements. Chromosoma 112, 288–299 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0273-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0273-9