Abstract
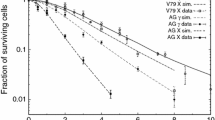
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) produced by densely ionizing radiation are not located randomly in the genome: recent data indicate DSB clustering along chromosomes. Stochastic DSB clustering at large scales, from >100 Mbp down to <0.01 Mbp, is modeled using computer simulations and analytic equations. A random-walk, coarse-grained polymer model for chromatin is combined with a simple track structure model in Monte Carlo software called DNAbreak and is applied to data on alpha-particle irradiation of V-79 cells. The chromatin model neglects molecular details but systematically incorporates an increase in average spatial separation between two DNA loci as the number of base-pairs between the loci increases. Fragment-size distributions obtained using DNAbreak match data on large fragments about as well as distributions previously obtained with a less mechanistic approach. Dose-response relations, linear at small doses of high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation, are obtained. They are found to be non-linear when the dose becomes so large that there is a significant probability of overlapping or close juxtaposition, along one chromosome, for different DSB clusters from different tracks. The non-linearity is more evident for large fragments than for small. The DNAbreak results furnish an example of the RLC (randomly located clusters) analytic formalism, which generalizes the broken-stick fragment-size distribution of the random-breakage model that is often applied to low-LET data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 July 1999 / Accepted in revised form: 10 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponomarev, A., Brenner, D., Hlatky, L. et al. A polymer, random walk model for the size-distribution of large DNA fragments after high linear energy transfer radiation. Radiat Environ Biophys 39, 111–120 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004119900040
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004119900040