Abstract
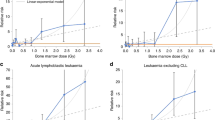
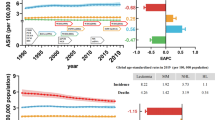
The incidence of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), which is caused by BCR/ABL chimeric oncogene formation in a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell (HSC), increases with age and exposure to ionizing radiation. CML is a comparatively well-characterized neoplasm, important for its own sake and useful for insights into other neoplasms. Here, Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) CML data are analyzed after considering possible misclassification of chronic myelo-monocytic leukemia as CML. For people older than 25 years, plots of male and female CML log incidences versus age at diagnosis are approximately parallel straight lines with males either above or to the left of females. This is consistent with males having a higher risk of developing CML or a shorter latency from initiation to diagnosis of CML. These distinct mechanisms cannot be distinguished using SEER data alone. Therefore, CML risks among male and female Japanese A-bomb survivors are also analyzed. The present analyses suggest that sex differences in CML incidence more likely result from differences in risk than in latency. The simplest but not the sole interpretation of this is that males have more target cells at risk to develop CML. Comprehensive mathematical models of CML could lead to a better understanding of the role of HSCs in CML and other preleukemias that can progress to acute leukemia.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19:716–723
Beheshti A, Sachs RK, Peluso M, Rietman E, Hahnfeldt P, Hlatky L (2013) Age and space irradiation modulate tumor progression: implications for carcinogenesis risk. Radiat Res 179(2):208–220
Bjorkholm M, Ohm L, Eloranta S, Derolf A, Hultcrantz M, Sjoberg J, Andersson T, Hoglund M, Richter J, Landgren O, Kristinsson SY, Dickman PW (2011) Success story of targeted therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia: a population-based study of patients diagnosed in Sweden from 1973 to 2008. J Clin Oncol 29(18):2514–2520
Braun WJ, Murdoch DJ (2007) A first course in statistical programming with R. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Chen Y, Wang H, Kantarjian H, Cortes J (2013) Trends in chronic myeloid leukemia incidence and survival in the United States from 1975 to 2009. Leuk Lymph 54(7):1411–1417
Hsu WL, Preston DL, Soda M, Sugiyama H, Funamoto S, Kodama K, Kimura A, Kamada N, Dohy H, Tomonaga M, Iwanaga M, Miyazaki Y, Cullings HM, Suyama A, Ozasa K, Shore RE, Mabuchi K (2013) The incidence of leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma among atomic bomb survivors: 1950–2001. Radiat Res 179(3):361–382
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Gr Stat 5:299–314
Inskip PD, Kleinerman RA, Stovall M, Cookfair DL, Hadjimichael O, Moloney WC, Monson RR, Thompson WD, Wactawski-Wende J, Wagoner JK (1993) Leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma after pelvic radiotherapy for benign disease. Radiat Res 135(1):108–124
Kozubek S, Lukasova E, Mareckova A, Skalnikova M, Kozubek M, Bartova E, Kroha V, Krahulcova E, Slotova J (1999) The topological organization of chromosomes 9 and 22 in cell nuclei has a determinative role in the induction of t(9,22) translocations and in the pathogenesis of t(9,22) leukemias. Chromosoma 108(7):426–435
Lieberman-Aiden E, van Berkum NL, Williams L, Imakaev M, Ragoczy T, Telling A, Amit I, Lajoie BR, Sabo PJ, Dorschner MO, Sandstrom R, Bernstein B, Bender MA, Groudine M, Gnirke A, Stamatoyannopoulos J, Mirny LA, Lander ES, Dekker J (2009) Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science 326(5950):289–293
Little MP, Heidenreich WF, Moolgavkar SH, Schöllnberger H, Thomas DC (2008) Systems biological and mechanistic modelling of radiation-induced cancer. Radiat Environ Biophys 47(1):39–47
Melo JV, Barnes DJ (2007) Chronic myeloid leukaemia as a model of disease evolution in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(6):441–453
Moolgavkar SH, Luebeck EG (2003) Multistage carcinogenesis and the incidence of human cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer 38(4):302–306
Preston DL, Kusumi S, Tomonaga M, Izumi S, Ron E, Kuramoto A, Kamada N, Dohy H, Matsuo T, Matsui T (1994) Cancer incidence in atomic bomb survivors. Part III. Leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma, 1950–1987. Radiat Res 137(2 Suppl):S68–S97
Radivoyevitch T, Hoel DG (2000) Biologically-based risk estimation for radiation-induced chronic myeloid leukemia. Radiat Environ Biophys 39(3):153–159
Radivoyevitch T, Kozubek S, Sachs RK (2001) Biologically based risk estimation for radiation-induced CML. Inferences from BCR and ABL geometric distributions. Radiat Environ Biophys 40(1):1–9
Radivoyevitch T, Hlatky L, Landaw J, Sachs RK (2012) Quantitative modeling of chronic myeloid leukemia: insights from radiobiology. Blood 119(19):4363–4371
SEER (2013) Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program (www.seer.cancer.gov) Public-Use Data (1973–2010), National Cancer Institute, DCCPS, Surveillance Research Program, Cancer Statistics Branch, released April 2013, based on the November 2012 submission
Shuryak I, Sachs RK, Brenner DJ (2011) A new view of radiation-induced cancer. Radiat Prot Dosim 143(2–4):358–364
Sigurdson AJ, Ha M, Hauptmann M, Bhatti P, Sram RJ, Beskid O, Tawn EJ, Whitehouse CA, Lindholm C, Nakano M, Kodama Y, Nakamura N, Vorobtsova I, Oestreicher U, Stephan G, Yong LC, Bauchinger M, Schmid E, Chung HW, Darroudi F, Roy L, Voisin P, Barquinero JF, Livingston G, Blakey D, Hayata I, Zhang W, Wang C, Bennett LM, Littlefield LG, Edwards AA, Kleinerman RA, Tucker JD (2008) International study of factors affecting human chromosome translocations. Mutat Res 652(2):112–121
Sloma I, Jiang X, Eaves AC, Eaves CJ (2010) Insights into the stem cells of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 24(11):1823–1833
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to anonymous reviewers of the current and an earlier version of the manuscript for their thoughtful comments. TR, RKS and LH were supported by NCI ICBP U54CA149233. RKS was also supported by DOE DE-SC0001434 Office of Science (BER) US Department of Energy. TR and YS were supported by RO1CA138858. RPG acknowledges support from the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre funding scheme. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute or the National Institutes of Health. GJ was supported by Grant # 41004 (Ministry of Science and Education, Republic of Serbia). RVT was supported by the Scott Hamilton CARES grant, Cleveland Clinic Seed Support and an ACS pilot grant. This report makes use of data obtained from the Radiation Effects Research Foundation (RERF), Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan. RERF is a public interest foundation funded by the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) and the US Department of Energy (DOE), the latter in part through DOE award DE-HS0000031 to the National Academy of Sciences. The conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the scientific judgment of RERF or its funding agencies.
Conflict of interest
RPG is a part-time employee of Celgene Corp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radivoyevitch, T., Jankovic, G.M., Tiu, R.V. et al. Sex differences in the incidence of chronic myeloid leukemia. Radiat Environ Biophys 53, 55–63 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-013-0507-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-013-0507-4