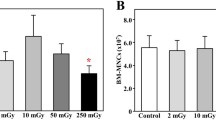
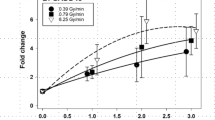
Abstract
It has been well established that the bone marrow (BM) is a radiosensitive tissue, but the radiosensitivity of the heart is poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the comparative effects of 28Silicon (28Si) ions (one type of heavy ion found in space) on tissue from the heart and the BM of exposed mice. We gave adult male CBA/CaJ mice a whole-body exposure to a total dose of 0, 0.1, 0.25, or 0.5 Gy of 300 MeV/nucleon (n) 28Si ions, using a fractionated schedule (two exposures, 15 days apart that totaled each selected dose). The heart and BM were collected from 5 mice per treatment group at various times up to 6 months post-irradiation. In each mouse, we obtained tissue lysates from the heart and from the total population of BM cells for measuring the levels of cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (cleaved PARP, a marker of apoptotic cell death) and the levels of activated nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and selected NF-κB-regulated cytokines known to be involved in inflammatory responses. Our data showed that, up to 6 months post-irradiation, the levels of apoptotic cell death and inflammatory responses in tissues from the heart and BM collected from exposed mice were statistically higher than those in sham controls. Hence, these findings are suggestive of chronic apoptotic cell death and inflammation in both tissues after exposure to 28Si ions. In summary, our data are indicative of a possible association between exposure to 28Si ions during space flight and long-term health risk.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin AS Jr (1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–683
Banerjee I, Fuseler JW, Intwala AR, Baudino TA (2009) IL-6 loss causes ventricular dysfunction, fibrosis, reduced capillary density, and dramatically alters the cell populations of the developing and adult heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296:H1694–H1704
Baudino TA, Carver W, Giles W, Borg TK (2006) Cardiac fibroblasts: friend or foe? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H1015–H1026
Bialik S, Geenen DL, Sasson IE, Cheng R, Horner JW, Evans SM, Lord EM, Koch CJ, Kitsis RN (1997) Myocyte apoptosis during acute myocardial infarction in the mouse localizes to hypoxic regions but occurs independently of p53. J Clin Inv 100:1363–1372
Brown RD, Ambler SK, Mitchell MD, Long CS (2005) The cardiac fibroblast: therapeutic target in myocardial remodeling and failure. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:657–687
Carr ZA, Land CE, Kleinerman RA, Weinstock RW, Stovall M, Griem ML, Mabuchi K (2005) Coronary heart disease after radiotherapy for peptic ulcer disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61:842–850
Cesselli D, Jakoniuk I, Barlucchi L, Beltrami AP, Hintze TH, Nadal-Ginard B, Kajstura J, Leri A, Anversa P (2001) Oxidative stress-mediated cardiac cell death is a major determinant of ventricular dysfunction and failure in dog dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 89:279–286
Cilhers GD, Lochner A (1993) Radiation-induced damage of the Wistar rat heart: biochemistry and function. Radiother Oncol 27:216–222
Cucinotta FA, Nikjoo H, Goodhead DT (1998) The effects of delta rays on the number of particle-track traversals per cell in laboratory and space exposures. Radiat Res 150:115–119
Cucinotta FA, Schimmerling W, Wilson JW, Peterson LE, Badhwar GD, Saganti PB, Dicello JF (2001) Space radiation cancer risks and uncertainties for Mars missions. Radiat Res 156:682–688
Darby SC, Cutter DJ, Boerma M, Constine LS, Fajardo LF, Kodama K, Mabuchi K, Marks LB, Mettler FA, Pierce LJ, Trott KR, Yeh ETH, Shore RE (2010) Radiation-related heart disease: Current knowledge and future prospects. In J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:656–665
Desai N, Davis E, O’Neill P, Durante M, Cucinotta FA, Wu H (2005) Immunofluorescence detection of clustered gamma-H2AX foci induced by HZE-particle radiation. Radiat Res 164:518–522
Frangogiannis NG (2008) The immune system and cardiac repair. Pharmacol Res 58:88–111
Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB (1998) NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 16:225–260
Gordon JW, Shaw JA, Kirshenbaum LA (2011) Multiple facets of NF-κB in the heart. Circ Res 108:1122–1132
Gullestad L, Ueland T, Vinge LE, Finsen A, Yndestad A, Aukrust P (2012) Inflammatory cytokines in heart failure: mediators and markers. Cardiology 122:23–35
Han Z-B, Suzuki H, Suzuki F, Suzuki M, Furusawa Y, Kato T, Ikenaga M (1998) Relative biological effectiveness of accelerated heavy Ions for induction of morphological transformation in Syrian Hamster embryo cells. J Radiat Res 39:193–201
Haudek SB, Taffet GE, Schneider MD, Mann DL (2007) TNF provokes cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac remodeling through activation of multiple cell death pathways. J Clin Invest 117:2692–2701
Hendry J, Akahoshi M, Wang L, Lipshultz S, Stewart F, Trott K (2008) Radiation-induced cardiovascular injury. Radiat Environ Biophys 47:189–193
Kajstura J, Cheng W, Reiss K, Clark WA, Sonnenblick EH, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Olivetti G, Anversa P (1996) Apoptotic and necrotic myocyte cell deaths are independent contributing variables of infarct size in rat. Lab Invest 74:86–107
Kim N-H, Kang PM (2010) Apoptosis in cardiovascular diseases: mechanism and clinical Implications. Korean Circ J 40:299–305
Kumar D, Jugdutt BI (2003) Apoptosis and oxidants in the heart. J Lab Clin Med 142:288–297
Levine B, Kalman J, Mayer L, Fillit HM, Packer M (1990) Elevated circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 323:236–241
Li N, Karin M (1999) Is NF-κB the sensor of oxidative stress? FASEB J 13:1137–1143
Little MP, Gola A, Tzoulaki I (2009) A model of cardiovascular disease giving a plausible mechanism for the effect of fractionated low-dose ionizing radiation exposure. PLoS Comput Biol 5:e1000539
Little MP, Kleinerman RA, Stovall M, Smith SA, Mabuchi K (2012) Analysis of dose response for circulatory disease after radiotherapy for benign disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84(5):1101–1109
Narula J, Haider N, Virmani R, DiSalvo TG, Kolodgie FD, Hajjar RJ, Schmidt U, Semigran MJ, Dec GW, Khaw B-A (1996) Apoptosis in myocytes in end-stage heart failure. N Engl J Med 335:1182–1189
Natarajan M, Aravindan N, Meltz ML, Herman TS (2002) Post-translational modification of I-kappa B alpha activates NF-kappa B in human monocytes exposed to 56Fe ions. Radiat Environ Biophys 41(2):139–144
Oikonomou E, Tousoulis D, Siasos G, Zaromitidou M, Papavassiliou AG, Stefanadis C (2011) The role of inflammation in heart failure: new therapeutic approaches. Hellenic J Cardiol 52(1):30–40
Park M, Shen Y-T, Gaussin V, Heyndrickx GR, Bartunek J, Resuello RRG, Natividad FF, Kitsis RN, Vatner DE, Vatner SF (2009) Apoptosis predominates in nonmyocytes in heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H785–H791
Persoon-Rothert M, van der Wees KGC, van der Laarse A (2002) Mechanical overload-induced apoptosis: a study in cultured neonatal ventricular myocytes and fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem 241:115–124
Ponnaiya B, Suzuki M, Tsuruoka C, Uchihori Y, Wei Y, Hei TK (2011) Detection of chromosomal instability in bystander cells after Si490-ion irradiation. Radiat Res 176:280–290
Preston DL, Shimizu Y, Pierce DA, Suyama A, Mabuchi K (2003) Studies of mortality of atomic bomb survivors. Report 13: solid cancer and noncancer disease mortality: 1950–1997. Radiat Res 160:381–407
Rithidech K, Bond VP, Cronkite EP, Thompson MH, Bullis JE (1995) Hypermutability of mouse chromosome 2 during the development of x-ray-induced murine myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 92:1152–1156
Rithidech K, Tungjai M, Arbab E, Simon SR (2005) Activation of NF-kappa B in bone marrow cells of BALB/cJ mice following exposure in vivo to low doses of 137Cs gamma rays. Radiat Environ Biophys 44:139–143
Rithidech K, Reungpatthanaphong P, Honikel L, Rusek A, Simon S (2010) Dose-rate effects of protons on in vivo activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and cytokines in mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Environ Biophys 49:405–419
Rithidech K, Tungjai M, Reungpatthanaphong P, Honikel L, Sanford SR (2012a) Attenuation of oxidative damage and inflammatory responses by apigenin given to mice after irradiation. Mutat Res 749:29–38
Rithidech KN, Udomtanakunchai C, Honikel LM, Whorton EB (2012b) No evidence for the in vivo induction of genomic instability by low doses of 137Cs gamma rays in bone marrow cells of BALB/CJ and C57BL/6J mice. Dose Response 10:11–36
Shukla J, Khan NM, Thakur VS, Poduval TB (2011) l-arginine mitigates radiation-induced early changes in cardiac dysfunction: the role of inflammatory pathways. Radiat Res 176:158–169
Soucy K, Attarzadeh D, Ramachandran R, Soucy P, Romer L, Shoukas A, Berkowitz D (2010) Single exposure to radiation produces early anti-angiogenic effects in mouse aorta. Radiat Environ Biophys 49:397–404
Soucy KG, Lim HK, Kim JH, Oh Y, Attarzadeh DO, Sevinc B, Kuo MM, Shoukas AA, Vazquez ME, Berkowitz DE (2011) HZE 56Fe-ion irradiation induces endothelial dysfunction in rat aorta: role of xanthine oxidase. Radiat Res 176:474–485
Stewart JR, Fajardo LF, Gillette SM, Constine LS (1995) Radiation injury to the heart. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1205–1211
Suman S, Datta K, Trani D, Laiakis EC, Strawn SJ, Fornace AJJ (2012) Relative biological effectiveness of 12C and 28Si radiation in C57BL/6J mice. Radiat Environ Biophys 51:303–309
Taylor CW, Nisbet A, McGale P, Darby SC (2007) Cardiac exposures in breast cancer radiotherapy: 1950s–1990s. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:1484–1495
Tian B, Liu J, Bitterman PB, Bache RJ (2002) Mechanisms of cytokine induced NO-mediated cardiac fibroblast apoptosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H1958–H1967
Tsuruoka C, Suzuki M, Kanai T, Fujitaka K (2005) LET and ion species dependence for cell killing in normal human skin fibroblasts. Radiat Res 163:494–500
Tukenova M, Guibout C, Oberlin O, Doyon F, Mousannif A, Haddy N, Guérin S, Pacquement H, Aouba A, Hawkins M, Winter D, Bourhis J, Lefkopoulos D, Diallo I, de Vathaire F (2010) Role of cancer treatment in long-term overall and cardiovascular mortality after childhood cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:1308–1315
Wang Y, Meng A, Lang H, Brown SA, Konopa JL, Kindy MS, Schmiedt RA, Thompson JS, Zhou D (2004) Activation of nuclear factor κB in vivo selectively protects the murine small intestine against ionizing radiation-induced damage. Cancer Res 64:6240–6246
Wencker D, Chandra M, Nguyen K, Miao W, Garantziotis S, Factor SM, Shirani J, Armstrong RC, Kitsis RN (2003) A mechanistic role for cardiac myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. J Clin Invest 111:1497–1504
Wu H, Hada M, Meador J, Hu X, Rusek A, Cucinotta FA (2006) Induction of micronuclei in human fibroblasts across the Bragg curve of energetic heavy ions. Radiat Res 166:583–589
Yeung TK, Lauk S, Simmonds RH, Hopewell JW, Trott KR (1989) Morphological and functional changes in the rat heart after X irradiation: strain differences. Radiat Res 119:489–499
Yndestad A, Kristian Damås J, Øie E, Ueland T, Gullestad L, Aukrust P (2006) Systemic inflammation in heart failure—the whys and wherefores. Heart Fail Rev 11:83–92
Yu T, Parks BW, Yu S, Srivastava R, Gupta K, Wu X, Khaled S, Chang PY, Kabarowski JH, Kucik DF (2011) Iron-ion radiation accelerates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Radiat Res 175:766–773
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Grant # NNX11AK91G. We thank Dr. Peter Guida and his team for logistic support, MaryAnn Petry and her BLAF staff for their assistance in animal handling. We also thank Drs. Adam Rusek and Michael Sivertz for dosimetry support. Editorial help from Ms. Louise Honikel and Dr. Marinel M. Ammenheuser is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tungjai, M., Whorton, E.B. & Rithidech, K.N. Persistence of apoptosis and inflammatory responses in the heart and bone marrow of mice following whole-body exposure to 28Silicon (28Si) ions. Radiat Environ Biophys 52, 339–350 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-013-0479-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-013-0479-4