Abstract.
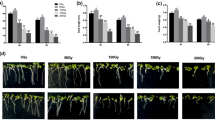
To clarify the effect of heavy ions in plants, dry seeds of Arabidopsis were irradiated with carbon, neon, and argon ions with various linear energy transfer (LET) values. The relative biological effectiveness (RBE) for lethality peaked at LET values over 350 keV/µm for neon and argon ions. This LET giving the peak RBE was higher than the LET of 100–200 keV/µm which was reported to have a maximum RBE for other types of cells, such as mammalian cells. Furthermore, sterility showed a higher RBE at an LET of 354 keV/µm with neon ions than that at an LET of 113 keV/µm with carbon ions. Lethality and sterility are both considered to be caused by damage to DNA. The results indicate that the LET having a maximum of RBE for lethality is higher in Arabidopsis seeds than in other unicellular systems. The most likely explanation for this shift of LET is that the DNA in dry seeds has a different chemical environment and/or hydration state than the DNA in cells in culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shikazono, N., Tanaka, A., Kitayama, S. et al. LET dependence of lethality in Arabidopsis thaliana irradiated by heavy ions. Radiat Environ Biophys 41, 159–162 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-002-0157-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-002-0157-4