Abstract
The transfer of fluid and elements from subducting crust to the overlying mantle wedge is a fundamental process affecting arc magmatism and the chemical differentiation of the Earth. While the production of fluid by breakdown of hydrous minerals is well understood, the liberation of trace elements remains generally unconstrained. In this paper, we evaluate the behaviour of trace elements during prograde metamorphism and dehydration using samples of high-pressure, low-temperature metamorphic rocks from New Caledonia. Samples examined include mafic and pelitic rock-types that range in grade from lawsonite blueschist to eclogite facies, and represent typical lithologies of subducting crust. Under lawsonite blueschist facies conditions, the low temperatures of metamorphism inhibit equilibrium partitioning between metamorphic minerals and allow for the persistence of igneous and detrital minerals. Despite this, the most important hosts for trace-elements include lawsonite, (REE, Pb, Sr), titanite (REE, Nb, Ta), allanite (LREE, U, Th), phengite (LILE) and zircon (Zr, Hf). At epidote blueschist to eclogite facies conditions, trace-element equilibrium may be attained and epidote (REE, Sr, Th, U, Pb), garnet (HREE), rutile (Nb, Ta), phengite (LILE) and zircon (Zr, Hf) are the major trace-element hosts. Chlorite, albite, amphibole and omphacite contain very low concentrations of the investigated trace elements. The comparison of mineral trace-element data and bulk-rock data at different metamorphic grades indicates that trace elements are not liberated in significant quantities by prograde metamorphism up to eclogite facies. Combining our mineral trace-element data with established phase equilibria, we show that the trace elements considered are retained by newly-formed major and accessory minerals during mineral breakdown reactions to depths of up to 150 km. In contrast, significant volumes of fluid are released by dehydration reactions. Therefore, there is a decoupling of fluid release and trace element release in subducting slabs. We suggest that the flux of trace elements from the slab is not simply linked to mineral breakdown, but results from complex fluid-rock interactions and fluid-assisted partial melting in the slab.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abers GA (2000) Hydrated subducted crust at 100–250 km depth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 176:323–330
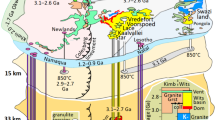
Aitchison J, Clarke GL, Meffre S, Cluzel D (1995) Eocene arc-continent collision in New Caledonia and implications for regional Southwest Pacific tectonic evolution. Geology 23:161–164
Arculus RJ, Lapierre H, Jaillard E (1999) Geochemical window into subduction and accretion processes: Raspas metamorphic complex, Ecuador. Geology 27:547–550
Bebout GE, Barton MD (1989) Fluid flow and measomatism in a subduction zone hydrothermal system: Catalina Schist terrane, California. Geology 17:976–980
Becker H, Jochum KP, Carlson RW (1999) Constraints from high-pressure veins in eclogites on the composition of hydrous fluids in subduction zones. Chem Geol 160:291–308
Becker H, Jochum KP, Carlson RW (2000) Trace element fractionation during dehydration of eclogites from high-pressure terranes and the implications for element fluxes in subduction zones. Chem Geol 163:65–99
Belousova EA, Walters S, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY (2001). Trace-element signatures of apatites in granitoids from the Mt Isa Inlier, northwestern Queensland. Australian J Earth Sci vol. 48, pg 603-619
Black PM (1974) Oxygen isotope study of metamorphic rocks from the Ouegoa District, New Caledonia. Contrib Mineral Petrol 47:197–206
Black PM (1977) Regional high-pressure metamorphism in New Caledonia; phase equilibria in the Ouegoa District. Tectonophysics 43:89–107
Brenan JM, Shaw HF, Ryerson FJ, Phinney DL (1995) Mineral-aqueous fluid partitioning of trace elements at 900 degrees C and 2.0 GPa; constraints on the trace element chemistry of mantle and deep crustal fluids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:3331–3350
Briggs RM, Kobe HW, Black PM (1977) High-pressure metamorphism of stratiform sulphide deposits from the Diahot region, New Caledonia. Miner Deposita 12:263–279
Brothers RN, (1985) Regional mid-Tertiary blueschist-eclogite metamorphism in northern New Caledonia. Geol Fr 1985:37–44
Carson CJ, Powell R, Clarke GL, (1999) Calculated mineral equilibria for eclogites in CaO-Na2O-FeO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O; application to the Pouebo Terrane, Pam Peninsula, New Caledonia. J Metamorph Geol 17:9–24
Carswell DA, Wilson RN, Zhai M (1996) Ultra-high pressure aluminous titantites in carbonate-bearing eclogites at Shuanghe in Dabieshan, central China. Mineral Mag 60:461–471
Clarke GL, Aitchison JC, Cluzel D (1997) Eclogites and blueschists of the Pam Peninsula, NE New Caledonia; a reappraisal. J Petrol 38: 843–876
Connolly JAD, Kerrick DM (2002) Metamorphic controls on seismic velocity of subducted oceanic crust at 100–250 km depth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 204:61–74
Davies JH (1999) The role of hydraulic fractures and intermediate-depth earthquakes in generating subduction-zone magmatism. Nature 398:142–145
Domanik KJ, Hervig RL, Peacock SM (1993) Beryllium and Boron in subduction zone minerals - an ion microprobe study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:4997–5010
Domanik KJ, Holloway JR (1996) The stability and composition of phengitic muscovite and associated phases from 5.5 to 11 GPa; implications for deeply subducted sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:4133–4150
Ellis DJ, Green DH (1979) An experimental study of the effect of Ca upon garnet-clinopyroxene Fe-Mg exchange equilibria. Contrib Mineral Petrol 71:13–22
Evans BW (1990) Phase relations of epidote-blueschists. Lithos 25:3–23
Fitzherbert JA, Clarke GL, Marmo BA, Powell R (2001) Metabasites from the Pam Peninsula, NE New Caledonia: development of regional blueschist to eclogite facies zonation. 6th Int Eclog Conf, 39 pp
Frost BR, Chamberlain KR, Schumacher JC (2001) Sphene (titanite); phase relations and role as a geochronometer. Chem Geol 172:131–148
Getty SR, Selverstone J (1994) Stable isotopic and trace element evidence for restricted fluid migration in 2 GPa eclogites. J Metamorph Geol 12:747–760
Graham CM, Powell R (1984) A garnet-hornblende geothermometer; calibration, testing, and application to the Pelona Schist, Southern California. J Metamorph Geol 2:13–31
Green TH, Hellman PL (1982) Fe-Mg partitioning between coexisting garnet and phengite at high pressure, and comments on a garnet-phengite geothermometer. Lithos 15:253–266
Hawkesworth CJ, Gallagher K, Hergt JM, and McDermott F (1993) Mantle and slab contributions in arc magmas. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 21:175–204
Hermann J (2002) Allanite: thorium and light rare earth element carrier in subducted crust. Chem Geol 192:289–306
Hermann J, Green DH (2001) Experimental constraints on high pressure melting in subducted crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 188:149–168
Itaya T, Brothers RN, Black PM (1985) Sulfides, oxides and sphene in high-pressure schists from New Caledonia. Contrib Mineral Petrol 91:151–162
Kincaid C, Sacks IS (1997) Thermal and dynamical evolution of the upper mantle in subduction zones. J Geophys Res 102:12,295–12,315
Kirby SH, Engdahl ER, Denlinger RP (1996) Intermediate-depth intraslab earthquakes and arc volcanism as physical expressions of crustal and uppermost mantle metamorphism in subducting slabs. In: Bebout BE, Scholl DW, Kirby SH, Platt JP (eds) Subduction: top to bottom. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, pp. 195–214
Kogiso T, Tatsumi Y, Nakano S (1997) Trace element transport during dehydration processes in the subducted oceanic crust; 1, Experiments and implications for the origin of ocean island basalts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 148:193–205
Lin CH, Huang BS, Rau RJ (1999) Seismological evidence for a low-velocity layer within the subducted slab of southern Taiwan. Earth Planet Sci Lett 174:231–240
Liu J, Bohlen SR, Ernst WG (1996) Stability of hydrous phases in subducting oceanic crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 143:161–171
Maurizot P, Eberle J-M, Habault C, Tessarollo C (1989) Notice explicative Sur La Feuille Pam-Ouegoa. BurRech Geol Mini Noumea
Messiga B, Tribuzio R, Bottazzi P, Ottolini L (1995) An ion microprobe study on trace element composition of clinopyroxenes from blueschist and eclogitized Fe-Ti-gabbros, Ligurian Alps, northwestern Italy; some petrologic considerations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:59–75
Nagasaki A, Enami M (1998) Sr-bearing zoisite and epidote in ultra-high pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks from the Su-Lu province, eastern China; an important Sr reservoir under UHP conditions. Am Mineral 83:240–247
Nishiyama T (1989) Kinetics of hydrofracturing and metamorphic veining. Geology 17:1068–1071
Okamoto K, Maruyama S (1999) The high-pressure synthesis of lawsonite in the MORB+H2O system. Am Mineral 84 362–373
Ono S (1998) Stability limits of hydrous minerals in sediment and mid-ocean ridge basalt compositions; implications for water transport in subduction zones. J Geophys Res 103:18253–18267
Pawley AR, Holloway JR (1993) Water sources for subduction zone volcanism; new experimental constraints. Science 260:664–667
Peacock SM (1993) The importance of blueschist→eclogite dehydration reactions in subducting oceanic crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 105:684–694
Peacock SM (1996) Thermal and petrologic structure of subduction zones. In: Bebout BE, Scholl DW, Kirby SH, Platt JP (eds) Subduction: top to bottom. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, pp 119–133
Pearce JA, Peate DW (1995) Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 23:251–285
Perfit MR, Gust DA, Bence AE, Arculus RJ, Taylor SR (1980) Chemical characteristics of island-arc basalts; implications for mantle sources. Chem Geol 30:227–256
Philippot P, Selverstone J (1991) Trace-element-rich brines in eclogitic veins: implications for fluid composition and transport during subduction. Contrib Mineral Petrol 106:417–430
Plank T, Langmuir CH (1998) The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chem Geol 145:325–394
Poli S, Schmidt MW (1995) H2O transport and release in subduction zones - experimental constraints on basaltic and andesitic systems. J Geophys Res 100:22299–22314
Poli S, Schmidt MW (2002) Petrology of subducted slabs. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 30:207–235
Rawling TJ, Lister GS (1999) Oscillating modes of orogeny in the Southwest Pacific and the tectonic evolution of New Caledonia. In: Ring TU, Brandon MS, Lister G, Willett SD (eds) Exhumation processes; normal faulting, ductile flow and erosion. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 154:109–127
Rawling TJ, Lister GS (2002) Large-scale structure of the eclogite-blueschist belt of New Caledonia. J Struct Geol 24:1239–1258
Rollinson H (1993) Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation. Longman, London
Rubatto D (2002) Zircon trace element geochemistry; partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism. Chem Geol 184:123–138
Rubatto D, Hermann J (2003) Zircon formation during fluid circulation in eclogites (Monviso, Western Alps): implications for Zr and Hf budgets in subduction zones. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:2173–2187
Sakai C, Higashino T, Enami M (1984) REE-bearing epidote from Sanbagawa pelitic schists, central Shikoku, Japan. Geochem J 18:45–53
Sassi P, Harte B, Carswell DA, Yujing H (2000) Trace element distribution in central Dabie eclogites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 139:298–315
Scambelluri M, Philippot P (2001) Deep fluids in subduction zones. Lithos 55:213–227
Schmidt MW, Poli S (1998) Experimentally based water budgets for dehydrating slabs and consequences for arc magma generation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 163:361–379
Shatsky VS, Kozmenko OA, Sobolev NV (1990) Behaviour of rare-earth elements during high-pressure metamorphism. Lithos 25:219–226
Sorensen SS (1991) Petrogenetic significance of zoned allanite in garnet amphibolites from a paleosubduction zone—Catalina Schist, southern California. Am Mineral 76: 589–601
Sorensen SS, Grossman JN (1989) Enrichment of trace elements in garnet amphibolites from a paleo-subduction zone; Catalina Schist, Southern California. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53: 3155–3177
Sorensen SS, Grossman JN, Perfit MR (1997) Phengite-hosted LILE enrichment in eclogite and related rocks; implications for fluid-mediated mass transfer in subduction zones and arc magma genesis. J Petrol 38: 3–34
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts; implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in the ocean basins. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 42:313–345
Tatsumi Y, Hamilton DL, Nesbitt RW (1986) Chemical characteristics of fluid phase released from a subducted lithosphere and origin of arc magmas; evidence from high-pressure experiments and natural rocks. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 29:293–309
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford
Tera F, Brown L, Morris J, Sacks IS, Klein J, Middleton R (1986) Sediment incorporation in island-arc magmas; inferences from Be-10. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50:535–550
Thöni M, Jagoutz E (1992) Some new aspects of dating eclogites in orogenic belts: Sm-Nd, Rb-Sr, and Pb-Pb isotopic results from the austoalpine Saualpe and Koralpe type-locality (Carinthia/Styria, southeastern Austria). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:347–368
Tribuzio R, Messiga B, Vannucci R, Bottazzi P (1996) Rare earth element redistribution during high-pressure-low-temperature metamorphism in ophiolitic Fe-gabbros (Liguria, northwestern Italy); implications for light REE mobility in subduction zones. Geology 24:711–714
Tribuzio R, Tiepolo M, Thirlwall MF (2000) Origin of titanian pargasite in gabbroic rocks from the Northern Apennine ophiolites (Italy): insights into the late- magmatic evolution of a MOR-type intrusive sequence. Earth Planet Sci Lett 176:281–293
Troitzsch U, Ellis DJ (2002) Thermodynamic properties and stability of AlF-bearing titanite CaTiOSiO4–Ca-AlFSiO4. Contrib Mineral Petrol 142:543–563
Ueno T (1999) REE-bearing sector-zoned lawsonite in the Sanbagawa pelitic schists of the eastern Kii Peninsula, central Japan. Euro J Mineral 11:993–998
Ulmer P, Trommsdorff V (1995) Serpentine stability to mantle depths and subduction-related magmatism. Science, 268:858–861
White WM (2001). Geochemistry. http://www.geo.cornell.edu/geology/classes/geo455/Chapters.HTML
Wilson M (1989) Igneous petrogenesis; a global tectonic approach. Unwin Hyman, London
Xiao Y, Hoefs J, van den Kerkhof AM, Fiebig J, Zheng Y (2000) Fluid history of UHP metamorphism in Dabie Shan, China: a fluid inclusion and oxygen isotope study on the coesite-bearing eclogite from Bixiling. Contrib Mineral Petrol 139:1–16
Yokoyama K, Brothers RN, Black PM (1986) Regional eclogite facies in the high-pressure metamorphic belt of New Caledonia. In: Evans BW, Brown EH (eds) Blueschists and eclogites. Geol Soc Am Mem 164:407–423
Zack T, Foley SF, Rivers T (2002) Equilibrium and disequilibrium trace element partitioning in hydrous eclogites (Trescolmen, Central Alps). J Petrol 43: 1947–1974
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Australian Research Council and the Australian National University. The authors wish to thank Geoff Clarke for guidance during fieldwork and Frank Brink and Nick Ware for analytical assistance. Critical reviews by Thomas Zack and Harry Becker have greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: J. Hoefs
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spandler, C., Hermann, J., Arculus, R. et al. Redistribution of trace elements during prograde metamorphism from lawsonite blueschist to eclogite facies; implications for deep subduction-zone processes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 146, 205–222 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-003-0495-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-003-0495-5