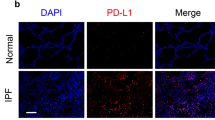
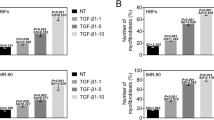
Abstract
Myofibroblasts characterized by alpha smooth muscle actin(α-SMA) expression play a key role in pulmonary fibrosis. Transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) is likely to be involved in the emergence of myofibroblasts, but the intracellular signal pathways for this process have not been well determined. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/activator protein-1 (AP-1) signaling pathways in TGF-β1–induced α-SMA expression in human fetal lung fibroblasts (HLF-02). We found that TGF-β1 treatment activated p38 kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) in HLF-02 cells. The induction of α-SMA by TGF-β1 was suppressed by p38 kinase inhibitor (SB203580) and Erk inhibitor (PD98059). AP-1 inhibitor curcumin also inhibited TGF-β1–induced α-SMA expression. In addition, dominant negative mutant c-Jun (TAM67) downregulated TGF-β1–induced AP-1 transactivation and α-SMA expression. In additional, PD98059 but not SB203580 inhibited the AP-1 DNA binding activity induced by TGF-β1. Based on these findings, we conclude that p38 kinase, Erk, and AP-1 are responsible for the α-SMA expression induced by TGF-β1 in human fetal lung fibroblasts. Erk is involved in inducing α-SMA expression via AP-1 activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahr MJ, Vincent KJ, Arthur MJP, et al. (1999) Control of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 promoter in culture-activated rat hepatic stellate cells: regulation by activator protein-1 DNA binding proteins. Hepatology 29:839–848
Barthelman M, Chen W, Gensler HL, et al. (1998) Inhibitory effects of perillylalcoholon UVB-induced murine skin cancer and AP-1 transactivation. Cancer Res 58:711–716
Brown PH, Chen TK, Birrer MJ (1994) Mechanism of action of a dominant-negative mutant of c-Jun. Oncogene 9:791–799
Brown PH, Alani R, Preis LH, Szabo E, Birrer MJ (1993) Suppression of oncogene-induced transformation by a deletion mutant of c-jun. Oncogene 8:877–886
Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ (1995) How MAP kinases are regulated. J Biol Chem 270:14843–14846
Desmouliere A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F, Gabbiani G (1993) Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 122:103–111
Fitzner B, Sparmann G, Emmrich J, Liebe S, Jaster R (2004) Involvement of AP-1 proteins in pancreatic stellate cell activation in vitro. Int J Colorectal Dis 19:414–420
Hahm ER, Cheon G, Lee J, et al. (2002) New and known symmetrical curcumin derivatives inhibit the formation of Fos-Jun-DNA complex. Cancer Lett 184:89–96
Hanafusa H. Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Masuyama N, et al. (1999) Involvement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in transforming growth factor-beta-induced gene expression. J Biol Chem 274:27161–27167
Hergenhahn M, Soto U, Weninger A, et al. (2002) The chemopreventive compound curcumin is an efficient inhibitor of Epstein–Barr virus BZLF1 transcription in Raji DR-LUC cells. Mol Carcinog 33:137–145
Huang BY, Li M, Wu SH, et al. (2003) Establishment and characteristics of the human diploid cell strain HLF-02. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28:587–590
Hyman KM, Seghezzi G, Pintucci G, et al. (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells by activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Surgery 132:173–179
Jung YD, Fan F, McConkey DJ, et al. (2002) Role of P38 MAPK, AP-1, and NF-kappaB in interleukin-1 beta-induced IL-8 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Cytokine 18:206–213
Karin M (1995) The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem 270:16483–16486
Kida Y, Kobayashi M, Suzuki T, et al. (2005) Interleukin-1 stimulates cytokines, prostaglandin E(2) and matrix metalloproteinase-1 production via activation of MAPK/AP-1 and NF-kappaB in human gingival fibroblasts. Cytokine 29:159–168
Kuhn C, McDonald JA (1991) The roles of the myofibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis :ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features of sites of active extracelluar matrix synthesis. Am J Pathol 138:1257–1265
Li JH, Wang W, Huang XR, et al. (2004) Advanced glycation end products induce tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transition through the RAGE-ERK1/2 MAP kinase signaling pathway. Am J Pathol 164:1389–1397
Lu HT, Yang DD, Wysk M, et al. (1999) Defective IL-12 production in mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase 3 (Mkk3)-deficient mice. EMBO J 18:1845–1857
Massague J (2000) How cells read TGF-beta signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:169–178
Pache JC, Christakos PG, Gannon DE, et al. (1998) Myofibroblasts in diffuse alveolar damage of the lung. Mod Pathol 11:1064–1070
Phan SH (2002) The myofibroblast in pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 122:286S–289S
Punithavathi D, Venkatesan N, Babu M (2000) Curcumin inhibition of bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Br J Pharmacol 131:169–172
Ravanti L, Hakkinen L, Larjava H, et al. (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta induces collagenase-3 expression by human gingival fibroblasts via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 274:37292–37300
Roberts AB, Derynck R (2001) Meeting report: signaling schemes for TGF-beta. Sci STKE 113:43
Roy SG, Nozaki Y, Phan SH (2001) Regulation of a-smooth muscle actin gene expression in myofibroblast differentiation from rat lung fibroblasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33:723–734
Serini G, Gabbiani G (1999) Mechanism of myoflbroblast activity and phenotype modulation. Exp Cell Res 250:273–283
Shaulian E, Karin M (2001) AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 20:2390–2400
Sime PJ, Xing Z, Graham FL, Csaky KG, Gauldie J (1997) Adenovector-mediated gene transfer of active transforming growth factor-beta1 induces prolonged severe fibrosis in rat lung. J Clin Invest 100:768–776
Skalli O, Schurch W, Seemayer T, et al. (1989) Myofibroblasts from diverse pathologic settings are heterogeneous in their content of actin isoforms and intermediate filament proteins. Lab Invest 60:275–285
Swantek JL, Cobb MH, Geppert TD (1997) Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK) is required for lipopolysaccharide stimulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) translation: glucocorticoids inhibit TNF-alpha translation by blocking JNK/SAPK. Mol Cell Biol 17:6274–6282
Vitiello M, D’Isanto M, Galdiero M, et al. (2004) Interleukin-8 production by THP-1 cells stimulated by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium porins is mediated by AP-1, NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways. Cytokine 27:15–24
Wang J, Chen H, Seth A, McCulloch CA (2003) Mechanical force regulation of myofibroblast differentiation in cardiac fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H1871–H1881
Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ (1996) Transcription factor AP-1 regulation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways. J Mol Med 74:589–607
Woo CH, Lim JH, Kim JH (2004) Lipopolysaccharide induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via a mitochondrial reactive oxygen species-p38 kinase-activator protein-1 pathway in Raw 264.7 cells. J Immunol 173:6973–6980
Yoon YD, Kang JS, Han SB, et al. (2004) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and AP-1 by polysaccharide isolated from the radix of Platycodon grandiflorum in RAW 264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol 4:1477–1487
Zhang W, Liu HT (2002) MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res 12:9–18
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Wen Ji-Fang for his expert technical support and valuable discussions. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30170399).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Peng, J., Feng, D. et al. Role of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase, p38 Kinase, and Activator Protein-1 in Transforming Growth Factor-β1–Induced Alpha Smooth Muscle Actin Expression in Human Fetal Lung Fibroblasts In Vitro. Lung 184, 33–42 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-005-2560-5
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-005-2560-5