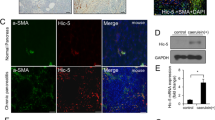
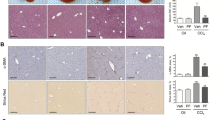
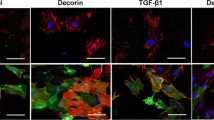
Abstract
Background and aims
Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) play a key role in the development of pancreatic fibrosis. The molecular mechanisms underlying their activation in response to profibrogenic mediators, however, are largely unknown. Extending previous studies on the transcriptional regulation of PSC activation, we have now focused on the involvement of activator protein (AP)-1.
Materials and methods
Using cultured rat PSCs, phenotypic transition of PSCs towards activated myofibroblasts was monitored by an immunoblot analysis of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression. Transcription factor activation profiles were studied by electrophoretic mobility shift assays. DNA synthesis in PSCs was assessed through the quantification of 5-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine incorporation.
Results
Activated AP-1 complexes were detectable already before high levels of α-SMA were expressed. Maximal DNA binding activity of AP-1, as well as of NF-κB, was observed early in the course of PSC culture, while the strongest activation of STAT3 was observed much later. A detailed analysis of AP-1 complex composition revealed that phenotypic transition of PSCs towards myofibroblasts was accompanied by an increase of the JunD content relative to the one of JunB. Studies on the role of JunB and JunD in PSC activation indicated an inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor-induced DNA synthesis by antisense oligonucleotides to JunB but not JunD.
Conclusions
The results of this study implicate AP-1 in PSC activation and suggest distinct roles of individual Jun proteins in the regulation of PSC function. In further studies, it should be analyzed whether signaling pathways involved in PSC activation might be suitable targets for antifibrotic therapies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apte MV, Haber PS, Applegate TL, Norton ID, McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC, Wilson JS (1998) Periacinar stellate shaped cells in rat pancreas: identification, isolation, and culture. Gut 43:128–133
Bachem MG, Schneider E, Groß H, Weidenbach H, Schmid RM, Menke A, Siech M, Beger H, Grünert A, Adler G (1998) Identification, culture, and characterisation of pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology 115:421–432
Ramadori G (1991) The stellate cell (Ito-cell, fat-storing cell, lipocyte, perisinusoidal cell) of the liver. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol 61:147–158
Haber PS, Kegh GW, Apte MV, Moran CS, Stewart NL, Crawford DHG, Pirola RC, McCaughan GW, Ramm GA, Wilson J (1999) Activation of pancreatic stellate cells in human and experimental pancreatic fibrosis. Am J Pathol 155:1087–1095
Longnecker DS (1983) Pathology and pathogenesis of diseases of the pancreas. Am J Pathol 107:103–121
Etemad B, Whitcomb DC (2001) Chronic pancreatitis: diagnosis, classification and new genetic developments. Gastroenterology 120:682–707
Emmrich J, Weber I, Sparmann G, Liebe S (2000) Activation of pancreatic stellate cells in experimental chronic pancreatitis in rats. Gastroenterology 118:A166
Apte MV, Haber PS, Darby SJ, Rodgers SC, McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC, Wilson JS (1999) Pancreatic stellate cells are activated by proinflammatory cytokines: implications for pancreatic fibrogenesis. Gut 44:534–541
Luttenberger T, Schmid-Kotsas A, Menke A, Siech M, Beger H, Adler G, Grünert A, Bachem MG (2000) Platelet-derived growth factors stimulate proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis of pancreatic stellate cells: implications in pathogenesis of pancreas fibrosis. Lab Invest 80:47–55
Apte MV, Phillips PA, Fahmy RG, Darby SJ, Rodgers SC, McCaughan GW, Korsten MA, Pirola RC, Naidoo D, Wilson JS (2000) Does alcohol directly stimulate pancreatic fibrogenesis? Gastroenterology 118:780–794
Mews P, Phillips P, Fahmy R, Korsten M, Pirola R, Wilson J, Apte M (2002) Pancreatic stellate cells respond to inflammatory cytokines: potential role in chronic pancreatitis. Gut 50:535–541
Jaster R, Sparmann G, Emmrich J, Liebe S (2002) Extracellular signal-regulated kinases are key mediators of mitogenic signals in rat pancreatic stellate cells. Gut 51:579–584
Jaster R, Brock P, Sparmann G, Emmrich J, Liebe S (2003) Inhibition of pancreatic stellate cell activation by the hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor lovastatin. Biochem Pharmacol 65:1295–1303
Jaster R, Hilgendorf I, Fitzner B, Brock P, Sparmann G, Emmrich J, Liebe S (2003) Biological and molecular effects of all-trans retinoic acid in pancreatic stellate cells: correlation between cell growth inhibition, diminished collagen synthesis and transrepression of AP-1. Biochem Pharmacol 66:633–641
Karin M, Liu ZG, Zandi E (1997) AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:240–246
Shaulian E, Karin M (2001) AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 20:2390–2400
Halazonetis TD, Georgopoulos K, Greenberg M, Leder P (1988) C-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell 55:917–924
Price MA, Hill C, Treisman R (1996) Integration of growth factor signals at the c-fos serum response element. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 351:551–559
Kyriakis JM (1999) Activation of the AP-1 transcription factor by inflammatory cytokines of the TNF family. Gene Expr 7:217–231
Bittorf T, Büchse T, Sasse T, Jaster R, Brock J (2001) Activation of the transcription factor NF-κB by the erythropoietin receptor: structural requirements and biological significance. Cell Signal 13:673–681
Gressner AM, Bachem MG (1995) Molecular mechanisms of liver fibrogenesis—a homage to the role of activated fat-storing cells. Digestion 56:335–346
Friedman SD (1993) The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. N Engl J Med 328:1828–1835
Kotenko SV, Pestka S (2000) Jak-Stat signal transduction pathway through the eyes of cytokine class II receptor complexes. Oncogene 19:2557–2565
Ihle JN (2001) The Stat family in cytokine signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:211–217
Baud V, Karin M (2001) Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol 11:372–377
Karin M, Delhase M (2000) The I kappa B kinase (IKK) and NF-kappa B: key elements of proinflammatory signalling. Semin Immunol 12:85–98
ten Dijke P, Miyazone K, Heldin C-H (2000) Signaling inputs converge on nuclear effectors in TGF-β signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 25:64–70
Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH (1998) Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell 95:737–740
Bahr MJ, Vincent KJ, Arthur MJP Fowler AV, Smart DE, Wright MC, Clark IM, Benyon RC, Iredale JP, Mann DA (1999) Control of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 promoter in culture-activated rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 29:839–848
Mann DA, Smart DE (2002) Transcriptional regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation. Gut 50:891–896
Passegue E, Wagner EF (2000) JunB suppresses cell proliferation by transcriptional activation of p16(INK4a)expression. EMBO J 19:2969–2979
Passegue E, Jochum W, Schorpp-Kistner M, Mohle-Steinlein U, Wagner EF (2001) Chronic myeloid leukemia with increased granulocyte progenitors in mice lacking junB expression in the myeloid lineage. Cell 104:21–32
Wang H, Xie Z, Scott RE (1996) Differentiation modulates the balance of positive and negative Jun/AP-1 DNA binding activities to regulate cellular proliferative potential: different effects in nontransformed and transformed cells. J Cell Biol 135:1151–1162
Lang A, Schoonhovan R, Tuvia S, Brenner DA, Rippe RA (2000) Nuclear factor kappaB in proliferation, activation and apoptosis in rat hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 33:49–58
Lu G, Shimizu I, Cui X, Itonaga M, Tamaki K, Fukuno H, Inoue H, Honda H, Ito S (2002) Interferon-α enhances biological defense activities against oxidative stress in cultured rat hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells. J Med Invest 49:172–181
Saile B, Eisenbach C, El-Armouche H, Neubauer K, Ramadori G (2003) Antiapoptotic effect of interferon-alpha on hepatic stellate cells (HSC): a novel pathway of IFN-alpha signal transduction via Janus kinase 2. Eur J Cell Biol 82:31–41
Sparmann G, Merkord J, Jäschke A, Nizze H, Jonas L, Lohr M, Liebe S, Emmrich J (1997) Pancreatic fibrosis in experimental pancreatitis induced by dibutyltin dichloride. Gastroenterology 112:1664–1672
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (01ZZ0108). We gratefully acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Mrs. Helga Schulze.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitzner, B., Sparmann, G., Emmrich, J. et al. Involvement of AP-1 proteins in pancreatic stellate cell activation in vitro. Int J Colorectal Dis 19, 414–420 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-003-0565-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-003-0565-1