Abstract
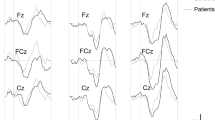
The objective of this study was to evaluate the mismatch negativity (MMN) in patients with first-episode schizophrenia at acute and post-acute phases in order to determine the contribution of trait and/or state features to MMN disturbances in schizophrenia. Subject groups comprised 30 patients with first-episode schizophrenia at the acute phase and 34 healthy controls. Ten patients were neuroleptic-naive during testing at the acute phase. Twenty-one patients were retested at the post-acute phase when their symptoms improved. All patients were taking antipsychotic medication at the post-acute retest session. MMN amplitude of the patients at acute phase did not differ from controls. However, MMN amplitude at post-acute phase was reduced compared to both controls and acute phase. Similar results were obtained when the analyses were confined to neuroleptic-naive patients. The sensory memory functions indexed by MMN seem to be unaffected at the onset of schizophrenia but deteriorated during the post-acute illness phase. MMN reduction at the post-acute phase might be emerged from antipsychotic medication.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alain C, Woods DL (1997) Attention modulates auditory pattern memory as indexed by event-related brain potentials. Psychophysiology 34:534–546
Alho K, Woods DL, Algazi A (1994) Processing of auditory stimuli during auditory and visual attention as revealed by event-related potentials. Psychophysiology 31:469–479
Alho K, Woods DL, Algazi A, Naatanen R (1992) Intermodal selective attention. II. Effects of attentional load on processing of auditory and visual stimuli in central space. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 82:356–368
Andreasen NC (1983) The scale for the assessment of negative symptoms (SANS). University of Iowa, Iowa City
Andreasen NC (1984) The scale for the assessment of positive symptoms (SAPS). University of Iowa, Iowa City
Baldeweg T, Klugman A, Gruzelier J, Hirsch SR (2004) Mismatch negativity potentials and cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 69:203–217
Brockhaus-Dumke A, Tendolkar I, Pukrop R, Schultze-Lutter F, Klosterkotter J, Ruhrmann S (2005) Impaired mismatch negativity generation in prodromal subjects and patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 73:297–310
Catts SV, Shelley AM, Ward PB, Liebert B, McConaghy N, Andrews S, Michie PT (1995) Brain potential evidence for an auditory sensory memory deficit in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 152:213–219
Dittmann-Balcar A, Thienel R, Schall U (1999) Attention-dependent allocation of auditory processing resources as measured by mismatch negativity. Neuroreport 10:3749–3753
Escera C, Yago E, Polo MD, Grau C (2000) The individual replicability of mismatch negativity at short and long inter-stimulus intervals. Clin Neurophysiol 111:546–551
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1997) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders (SCID-I), clinical version. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
Frodl-Bauch T, Kathmann N, Moller HJ, Hegerl U (1997) Dipole localization and test-retest reliability of frequency and duration mismatch negativity generator processes. Brain Topogr 10:3–8
Javitt DC, Doneshka P, Grochowski S, Ritter W (1995) Impaired mismatch negativity generation reflects widespread dysfunction of working memory in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:550–558
Javitt DC, Doneshka P, Zylberman I, Ritter W, Vaughan HG Jr (1993) Impairment of early cortical processing in schizophrenia: an event-related potential confirmation study. Biol Psychiatry 33:513–519
Javitt DC, Grochowski S, Shelley AM, Ritter W (1998) Impaired mismatch negativity (MMN) generation in schizophrenia as a function of stimulus deviance, probability, and interstimulus/interdeviant interval. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 108:143–153
Javitt DC, Shelley AM, Ritter W (2000) Associated deficits in mismatch negativity generation and tone matching in schizophrenia. Clin Neurophysiol 111:1733–1737
Javitt DC, Shelley AM, Silipo G, Lieberman JA (2000) Deficits in auditory and visual context-dependent processing in schizophrenia: defining the pattern. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:1131–1137
Kathmann N, Frodl-Bauch T, Hegerl U (1999) Stability of the mismatch negativity under different stimulus and attention conditions. Clin Neurophysiol 110:317–323
Kathmann N, Wagner M, Rendtorff N, Engel RR (1995) Delayed peak latency of the mismatch negativity in schizophrenics and alcoholics. Biol Psychiatry 37:754–757
Kirino E, Inoue R (1999) The relationship of mismatch negativity to quantitative EEG and morphological findings in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 33:445–456
Kramer AF, Trejo LJ, Humphrey D (1995) Assessment of mental workload with task-irrelevant auditory probes. Biol Psychol 40:83–100
Kujala T, Kallio J, Tervaniemi M, Naatanen R (2001) The mismatch negativity as an index of temporal processing in audition. Clin Neurophysiol 112:1712–1719
Lukoff D, Nuechterlein KH, Ventura J (1986) Manual for the expanded brief psychiatric rating scale. Schizophr Bull 12:594–602
Michie PT, Budd TW, Todd J, Rock D, Wichmann H, Box J, Jablensky AV (2000) Duration and frequency mismatch negativity in schizophrenia. Clin Neurophysiol 111:1054–1065
Michie PT, Innes-Brown H, Todd J, Jablensky AV (2002) Duration mismatch negativity in biological relatives of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Biol Psychiatry 52:749–758
Naatanen R (1990) The role of attention in auditory information processing as revealed by event-related potentials and other brain measures of cognitive function. Behav Brain Sci 13:201–288
Naatanen R, Gaillard AWK, Mantysalo S (1978) Early selective-attention effect on evoked potential reinterpreted. Acta Psychol 42:313–329
Naatanen R, Paavilainen P, Reinikainen K (1989) Do event-related potentials to infrequent decrements in duration of auditory stimuli demonstrate a memory trace in man? Neurosci Lett 107:347–352
Naatanen R, Paavilainen P, Tiitinen H, Jiang D, Alho K (1993) Attention and mismatch negativity. Psychophysiology 30:436–450
O’Donnell BF, Hokama H, McCarley RW, Smith RS, Salisbury DF, Mondrow E, et al. (1994) Auditory ERPs to non-target stimuli in schizophrenia: relationship to probability, task-demands, and target ERPs. Int J Psychophysiol 17:219–231
Otten LJ, Alain C, Picton TW (2000) Effects of visual attentional load on auditory processing. Neuroreport 11:875–880
Paavilainen P, Karlsson ML, Reinikainen K, Naatanen R (1989) Mismatch negativity to change in spatial location of an auditory stimulus. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 73:129–141
Paavilainen P, Tiitinen H, Alho K, Naatanen R (1993) Mismatch negativity to slight pitch changes outside strong attentional focus. Biol Psychol 37:23–41
Ritter W, Paavilainen P, Lavikainen J, Reinikainen K, Alho K, Sams M, Naatanen R (1992) Event-related potentials to repetition and change of auditory stimuli. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 83:306–321
Salisbury DF, Shenton ME, Griggs CB, Bonner-Jackson A, McCarley RW (2002) Mismatch negativity in chronic schizophrenia and first-episode schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:686–694
Schall U, Catts SV, Chaturvedi S, Liebert B, Redenbach J, Karayanidis F, Ward PB (1998) The effect of clozapine therapy on frontal lobe dysfunction in schizophrenia: neuropsychology and event-related potential measures. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 1:19–29
Schall U, Catts SV, Karayanidis F, Ward PB (1999) Auditory event-related potential indices of fronto-temporal information processing in schizophrenia syndromes: valid outcome prediction of clozapine therapy in a three-year follow-up. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2:83–93
Schroger E, Paavilainen P, Naatanen R (1994) Mismatch negativity to changes in a continuous tone with regularly varying frequencies. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 92:140–147
Shelley AM, Silipo G, Javitt DC (1999) Diminished responsiveness of ERPs in schizophrenic subjects to changes in auditory stimulation parameters: implications for theories of cortical dysfunction. Schizophr Res 37:65–79
Shelley AM, Ward PB, Catts SV, Michie PT, Andrews S, McConaghy N (1991) Mismatch negativity: an index of a preattentive processing deficit in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 30:1059–1062
Shinozaki N, Yabe H, Sato Y, Hiruma T, Sutoh T, Nashida T et al (2002) The difference in mismatch negativity between the acute and post-acute phase of schizophrenia. Biol Psychol 59:105–119
Tervaniemi M, Lehtokoski A, Sinkkonen J, Virtanen J, Ilmoniemi RJ, Naatanen R (1999) Test-retest reliability of mismatch negativity for duration, frequency and intensity changes. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1388–1393
Ucok A, Polat A, Cakir S, Genc A, Turan N (2004) Duration of untreated psychosis may predict acute treatment response in first-episode schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 38:163–168
Umbricht DS, Bates JA, Lieberman JA, Kane JM, Javitt DC (2006) Electrophysiological indices of automatic and controlled auditory information processing in first-episode, recent-onset and chronic schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 59:762–772
Umbricht D, Javitt D, Novak G, Bates J, Pollack S, Lieberman J, Kane J (1998) Effects of clozapine on auditory event-related potentials in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 44:716–725
Umbricht D, Javitt D, Novak G, Bates J, Pollack S, Lieberman J, Kane J (1999) Effects of risperidone on auditory event-related potentials in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2:299–304
Umbricht D, Koller R, Schmid L, Skrabo A, Grubel C, Huber T, Stassen H (2003) How specific are deficits in mismatch negativity generation to schizophrenia? Biol Psychiatry 53:1120–1131
Umbricht D, Krljes S (2005) Mismatch negativity in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 76:1–23
Valkonen-Korhonen M, Purhonen M, Tarkka IM, Sipila P, Partanen J, Karhu J, Lehtonen J (2003) Altered auditory processing in acutely psychotic never-medicated first-episode patients. Cogn Brain Res 17:747–758
Youn T, Park HJ, Kim JJ, Kim MS, Kwon JS (2003) Altered hemispheric asymmetry and positive symptoms in schizophrenia: equivalent current dipole of auditory mismatch negativity. Schizophr Res 59:253–260
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Fund of The University of Istanbul. Project numbers: 173/15012004 and UDP-826/19072006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devrim-Üçok, M., Keskin-Ergen, H.Y. & Üçok, A. Mismatch negativity at acute and post-acute phases of first-episode schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosc 258, 179–185 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-007-0772-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-007-0772-9