Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the insertion characteristics and trauma of a new slim lateral wall electrode (SlimJ) in human temporal bones (TB).
Methods
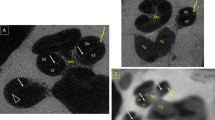
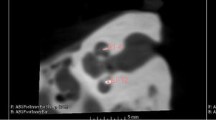
Pre- and postoperative assessment was performed using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and image fusion in 11 human TB. The position of the array in each cochlea was analyzed and described using a vertical scaling factor, calculated by dividing the distance of the scala tympani floor to the centre of the electrode by the duct height. Insertion trauma was scaled according to the presumed localization of the basilar membrane, which was modeled from histologic sections of 20 TBs. The insertion trauma was described by the adaptation of the Eshragi trauma grading.
Results
A full electrode insertion, via the round window, was achieved in all TBs. Surgical handling was good, with a favorable compromise between high flexibility but sufficient stiffness to facilitate smooth insertions. The median angular insertion depth was 368° (range 330°–430°). Scala tympani placement was achieved in ten out of eleven TBs; in one TB a scala translocation was observed, occurring at approximately 180°.
Conclusions
The SlimJ showed atraumatic insertion characteristics. The CBCT fusion technique provides an accurate and reliable assessment of the electrode position and allows for grading insertion trauma without histology. The SlimJ true potential for structure and hearing preservation needs to be further assessed in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blamey P, Artieres F et al (2013) Factors affecting auditory performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants: an update with 2251 patients. Audiol Neurotol 18(1):36–47
Lazard D, Vincent C, Venail F, Van de Heyning P, Truy E, Sterkers O et al (2012) Pre-, per- and postoperative factors affecting performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants: a new conceptual model over time. PLoS One 7(11):e48739
Aschendorff A, Kromeier J, Klenzner T, Laszig R (2007) Quality control after insertion of the nucleus contour and contour advance electrode in adults. Ear Hear 28(2 Suppl):75S–79S
Finley CC, Holden TA, Holden LK et al (2008) Role of electrode placement as a contributor to variability in cochlear implant outcomes. Otol Neurotol 29:920–928
Carlson ML, Driscoll CL, Gifford RH, Service GJ, Tombers NM, Hughes-Borst BJ, Neff BA, Beatty CW (2011) Implications of minimizing trauma during conventional cochlear implantation. Otol Neurotol 32(6):962–968
Gifford RH, Dorman MF, Skarzynski H, Lorens A, Polak M, Driscoll CL, Roland P, Buchman CA (2013) Cochlear implantation with hearing preservation yields significant benefit for speech recognition in complex listening environments. Ear Hear 34(4):413–425
Holden L, Finley C, Firszt J, Holden T, Brenner C, Potts L, Gotter B, Vanderhoof S, Mispagel K, Heydebrand G, Skinner M (2013). Factors affecting open-set word recognition in adults with cochlear implants. Ear Hear 34(3):342–360
Boyle PJ (2016) The rational for a mid-scala electrode array. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 133(Suppl 1):S61–S62
O’Connell BP1, Hunter JB, Gifford RH, Rivas A, Haynes DS, Noble JH, Wanna GB (2016) Electrode location and audiologic performance after cochlear implantation: a comparative study between nucleus CI422 and CI512 electrode arrays. Otol Neurotol 37(8):1032–1035
Svrakic M, Roland JT Jr, McMenomey SO, Svirsky MA (2016) initial operative experience and short-term hearing preservation results with a mid-scala cochlear implant electrode array. Otol Neurotol 37(10):1549–1554
Cohen LT, Saunders E, Knight MR, Cowan RS (2006). Psychophysical measures in patients fitted with Contour and straight Nucleus electrode arrays. Hear Res 212(1–2):160–175
Lim YS, Park SI, Kim YH, Oh SH, Kim SJ (2005) Three-dimensional analysis of electrode behavior in a human cochlear model. Med Eng Phys 27(8):695–703
Drouillard M, Torres R, Mamelle E, De Seta D, Sterkers O, Ferrary E, Nguyen Y (2017). Influence of electrode array stiffness and diameter on hearing in cochlear implanted guinea pig PLoS One 12(8):e0183674
Todt I, Mittmann M, Ernst A, Mittmann P (2017) Comparison of the effects of four different cochlear implant electrodes on intra-cochlear pressure in a model. Acta Otolaryngol 137(3):235–241
Briggs RJ, Tykocinski M, Saunders E, Hellier W, Dahm M, Pyman B, Clark GM (2001). Surgical implications of perimodiolar cochlear implant electrode design: avoiding intracochlear damage and scala vestibuli insertion. Cochlear Implants Int 2(2):135–149
Boyer E, Karkas A, Attye A, Lefournier V, Escude B, Schmerber S (2015) Scalar localization by cone-beam computed tomography of cochlear implant carriers: a comparative study between straight and perimodiolar precurved electrode arrays. Otol Neurotol 36(3):422–429
Connor SE, Holland NJ, Agger A, Leong AC, Varghese RA, Jiang D, Fitzgerald O’Connor A (2012) Round window electrode insertion potentiates retention in the scala tympani. Acta Otolaryngol 132(9):932–937
Wanna GB, Noble JH, Carlson ML, Gifford RH, Dietrich MS, Haynes DS, Dawant BM. Labadie RF (2014). Impact of electrode design and surgical approach on scalar location and cochlear implant outcomes. Laryngoscope 124(Suppl 6):S1–S7
Jeyakumar A, Peña SF, Brickman TM (2014) Round window insertion of precurved electrodes is traumatic. Otol Neurotol 35(1):52–57
Cushing SL, Daly MJ, Treaba CG, Chan H, Irish JC, Blaser S, Gordon KA, Papsin BC (2012) High-resolution cone-beam computed tomography: a potential tool to improve atraumatic electrode design and position. Acta Otolaryngol 132(4):361–368
Saeed SR, Selvadurai D, Beale T, Biggs N, Murray B, Gibson P, Risi F, Boyd P (2014) The use of cone-beam computed tomography to determine cochlear implant electrode position in human temporal bones. Otol Neurotol 35(8):1338–44
Marx M, Risi F, Escudé B, Durmo I, James C, Lauwers F, Deguine O, Fraysse B (2014) Reliability of cone beam computed tomography in scalar localization of the electrode array: a radio histological study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(4):673–679
Güldner C, Wiegand S, Weiss R, Bien S, Sesterhenn A, Teymoortash A, Diogo I.(2012). Artifacts of the electrode in cochlea implantation and limits in analysis of deep insertion in cone beam tomography (CBT). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(3):767–772
Husstedt HW, Aschendorff A, Richter B, Laszig R, Schumacher M (2002) Nondestructive three-dimensional analysis of electrode to modiolus proximity. Otol Neurotol 23(1):49–52
Kurzweg T, Dalchow CV, Bremke M, Majdani O, Kureck I, Knecht R, Werner JA, Teymoortash A (2010) The value of digital volume tomography in assessing the position of cochlear implant arrays in temporal bone specimens. Ear Hear 31(3):413–419
Iso-Mustajärvi M, Matikka H, Risi F, Sipari S, Koski T, Willberg T, Lehtimäki A, Tervaniemi J, Löppönen H, Dietz AA (2017) New slim modiolar electrode array for cochlear implantation: a radiological and histological study. Otol Neurotol 38(9):e327–e334
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Finet J, Fillion-Robin J-C, Pujol S, Bauer C, Jennings D, Fennessy F, Sonka M, Buatti J, Aylward SR, Miller JV, Pieper S, Kikinis R (2012) 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the quantitative imaging network. Magn Reson Imaging 30(9):1323–1341
Johnson HJ, Harris G, Williams K (2007) BRAINSFit: mutual information registrations of whole-brain 3D images, using the insight toolkit. Insight J
Xu J, Xu SA, Cohen LT, Clark GM (2000) Cochlear view: postoperative radiography for cochlear implantation. Am J Otol 21(1):49–56
Eshraghi AA, Yang NW, Balkany TJ (2003) Comparative study of cochlear damage with three perimodiolar electrode designs. Laryngoscope 113:415–419
Dietz A, Gazibegovic D, Tervaniemi J, Vartiainen VM, Löppönen H (2016) Insertion characteristics and placement of the Mid-Scala electrode array in human temporal bones using detailed cone beam computed tomography. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(12):4135–4143
Skarzynski H, Podskarbi-Fayette R (2010) A new cochlear implant electrode design for preservation of residual hearing: a temporal bone study. Acta Otolaryngol 130(4):435–442
Helbig S, Settevendemie C, Mack M, Baumann U, Helbig M, Stöver T.(2011). Evaluation of an electrode prototype for atraumatic cochlear implantation in hearing preservation candidates: preliminary results from a temporal bone study. Otol Neurotol 32(3):419–423
Rebscher SJ, Hetherington A, Bonham B, Wardrop P, Whinney D, Leake PA (2008) Considerations for design of future cochlear implant electrode arrays: electrode array stiffness, size, and depth of insertion. J Rehab Res Dev 45(5):731–748
Avci E, Nauwelaers T, Lenarz T, Hamacher V, Kral A (2014). Variations in microanatomy of the human cochlea. J Comp Neurol 522(14):3245–3261
Aschendorff A, Kubalek R, Turowski B, Zanella F, Hochmuth A, Schumacher M, Klenzner T, Laszig R (2005) Quality control after cochlear implant surgery by means of rotational tomography. Otol Neurotol 26(1):34–37
Diogo I, Franke N, Steinbach-Hundt S, Mandapathil M, Weiss R, Werner JA, Güldner C (2014) Differences of radiological artefacts in cochlear implantation in temporal bone and complete head. Cochlear Implants Int 15(2):112–117
Acknowledgements
The electrode arrays were provided by Advanced Bionics AG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Dzemal Gazibegovic is an employee of Advanced Bionics Clinical Research Department. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The study had institutional authorization as well as the approval from the Finnish National Supervisory Authority for Welfare and Health and fulfilled the requirements of the Helsinki Declaration for ethical use of human material.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dietz, A., Iso-Mustajärvi, M., Sipari, S. et al. Evaluation of a new slim lateral wall electrode for cochlear implantation: an imaging study in human temporal bones. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 1723–1729 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5004-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5004-6