Abstract
The hallmarks of cancer were updated by Hanahan and Weinberg in 2011. Here we discuss the updated hallmarks in relation to what is known of the molecular and cellular processes underlying the development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Several mechanisms are described, and recent surveys of HNSCC suggest a limited number of mutations, from which more mechanisms may emerge. There are also epigenetic changes to the control of normal processes. More than one mechanism underlies each hallmark. Processes essential to the development of HNSCC need not be essential to the proliferation of the fully developed tumour. Attention is paid to the emerging hallmarks, deregulation of cellular energy metabolism and evasion of immune destruction, and enabling characteristics, genome instability and mutation and tumour-promoting inflammation. HNSCC may adapt to hypoxia, suppress HLA expression, and express Toll-like receptors to facilitate inflammation, which support the proliferation of the tumour.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Rezende TM, de Souza Freire M, Franco OL (2010) Head and neck cancer: proteomic advances and biomarker achievements. Cancer 116:4914–4925
Marur S, D’Souza G, Westra WH, Forastiere AA (2010) HPV-associated head and neck cancer: a virus-related cancer epidemic. Lancet Oncol 11:781–789
Slaughter DP, Southwick HW, Smejkal W (1953) Field cancerization in oral stratified squamous epithelium; clinical implications of multicentric origin. Cancer 6:963–968
Park BJ, Chiosea SI, Grandis JR (2010) Molecular changes in the multistage pathogenesis of head and neck cancer. Cancer Biomarker 9:325–339
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH (2011) The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 11:9–22
Grandis JR, Chakraborty A, Zeng Q, Melhem MF, Tweardy DJ (1998) Downmodulation of TGF-alpha protein expression with antisense oligonucleotides inhibits proliferation of head and neck squamous carcinoma but not normal mucosal epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem 69:55–62
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2003) Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:2787–2799
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur RK, Raben D, Baselga J, Spencer SA, Zhu J, Youssoufian H, Rowinsky EK, Ang KK (2010) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol 11:21–28
Cripps C, Winquist E, Devries MC, Stys-Norman D, Gilbert R (2010) Epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy in stages III and IV head and neck cancer. Curr Oncol 17:37–48
Stephen JK, Chen KM, Havard S, Harris G, Worsham MJ (2012) Promoter methylation in head and neck tumorigenesis. Method Mol Biol 863:187–206
Youssef EM, Lotan D, Issa JP, Wakasa K, Fan YH, Mao L, Hassan K, Feng L, Lee JJ, Lippman SM, Hong WK, Lotan R (2004) Hypermethylation of the retinoic acid receptor-beta(2) gene in head and neck carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 10:1733–1742
Jones PA, Baylin SB (2007) The epigenomics of cancer. Cell 128:683–692
Childs G, Fazzari M, Kung G, Kawachi N, Brandwein-Gensler M, McLemore M, Chen Q, Burk RD, Smith RV, Prystowsky MB, Belbin TJ, Schlecht NF (2009) Low-level expression of microRNAs let-7d and miR-205 are prognostic markers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol 174:736–745
Ghildiyal M, Zamore PD (2009) Small silencing RNAs: an expanding universe. Nat Rev Genet 10:94–108
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D, Slack FJ (2005) RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 120:635–647
McDonald JS, Jones H, Pavelic ZP, Pavelic LJ, Stambrook PJ, Gluckman JL (1994) Immunohistochemical detection of the H-ras, K-ras, and N-ras oncogenes in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Oral Pathol Med 23:342–346
Lane DP (1992) Cancer p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 358:15–16
Levine AJ, Oren M (2009) The first 30 years of p53: growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer 9:749–758
Shin DM, Charuruks N, Lippman SM, Lee JJ, Ro JY, Hong WK, Hittelman WN (2001) p53 protein accumulation and genomic instability in head and neck multistep tumorigenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarker Prev 10:603–609
Braakhuis BJ, Snijders PJ, Keune WJ, Meijer CJ, Ruijter-Schippers HJ, Leemans CR, Brakenhoff RH (2004) Genetic patterns in head and neck cancers that contain or lack transcriptionally active human papillomavirus. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:998–1006
Valentin-Vega YA, Barboza JA, Chau GP, El-Naggar AK, Lozano G (2007) High levels of the p53 inhibitor MDM4 in head and neck squamous carcinomas. Hum Pathol 38:1553–1562
Saha MN, Jiang H, Mukai A, Chang H (2010) RITA inhibits multiple myeloma cell growth through induction of p53-mediated caspase-dependent apoptosis and synergistically enhances nutlin-induced cytotoxic responses. Mol Cancer Ther 9:3041–3051
Weinberg RA (1995) The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81:323–330
Soni S, Kaur J, Kumar A, Chakravarti N, Mathur M, Bahadur S, Shukla NK, Deo SV, Ralhan R (2005) Alterations of rb pathway components are frequent events in patients with oral epithelial dysplasia and predict clinical outcome in patients with squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology 68:314–325
Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, Weber R, Rosenthal DI, Nguyen-Tan PF, Westra WH, Chung CH, Jordan RC, Lu C, Kim H, Axelrod R, Silverman CC, Redmond KP, Gillison ML (2010) Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med 363:24–35
Smeets SJ, Braakhuis BJ, Abbas S, Snijders PJ, Ylstra B, van de Wiel MA, Meijer GA, Leemans CR, Brakenhoff RH (2006) Genome-wide DNA copy number alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas with or without oncogene-expressing human papillomavirus. Oncogene 25:2558–2564
Lu SL, Herrington H, Reh D, Weber S, Bornstein S, Wang D, Li AG, Tang CF, Siddiqui Y, Nord J, Andersen P, Corless CL, Wang XJ (2006) Loss of transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor promotes metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Dev 20:1331–1342
Kolev V, Mandinova A, Guinea-Viniegra J, Hu B, Lefort K, Lambertini C, Neel V, Dummer R, Wagner EF, Dotto GP (2008) EGFR signalling as a negative regulator of Notch1 gene transcription and function in proliferating keratinocytes and cancer. Nat Cell Biol 10:902–911
Stransky N, Egloff AM, Tward AD, Kostic AD, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, Kryukov GV, Lawrence MS, Sougnez C, McKenna A, Shefler E, Ramos AH, Stojanov P, Carter SL, Voet D, Cortes ML, Auclair D, Berger MF, Saksena G, Guiducci C, Onofrio RC, Parkin M, Romkes M, Weissfeld JL, Seethala RR, Wang L, Rangel-Escareno C, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Melendez-Zajgla J, Winckler W, Ardlie K, Gabriel SB, Meyerson M, Lander ES, Getz G, Golub TR, Garraway LA, Grandis JR (2011) The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science 333:1157–1160
Agrawal N, Frederick MJ, Pickering CR, Bettegowda C, Chang K, Li RJ, Fakhry C, Xie TX, Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang N, El-Naggar AK, Jasser SA, Weinstein JN, Trevino L, Drummond JA, Muzny DM, Wu Y, Wood LD, Hruban RH, Westra WH, Koch WM, Califano JA, Gibbs RA, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE, Papadopoulos N, Wheeler DA, Kinzler KW, Myers JN (2011) Exome sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma reveals inactivating mutations in NOTCH1. Science 333:1154–1157
Fortini ME (2009) Notch signaling: the core pathway and its posttranslational regulation. Dev Cell 16:633–647
Koch U, Radtke F (2007) Notch and cancer: a double-edged sword. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2746–2762
Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Zeng Q, Watkins SC, Melhem MF, Endo S, Johnson DE, Huang L, He Y, Kim JD (2000) Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling abrogates apoptosis in squamous cell carcinogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4227–4232
Vanhaesebroeck B, Stephens L, Hawkins P (2012) PI3 K signalling: the path to discovery and understanding. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:195–203
Pedrero JM, Carracedo DG, Pinto CM, Zapatero AH, Rodrigo JP, Nieto CS, Gonzalez MV (2005) Frequent genetic and biochemical alterations of the PI 3-K/AKT/PTEN pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 114:242–248
Hayflick L (2000) The illusion of cell immortality. Br J Cancer 83:841–846
Patel MM, Parekh LJ, Jha FP, Sainger RN, Patel JB, Patel DD, Shah PM, Patel PS (2002) Clinical usefulness of telomerase activation and telomere length in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 24:1060–1067
Bouck N, Stellmach V, Hsu SC (1996) How tumors become angiogenic. Adv Cancer Res 69:135–174
Caponigro F, Formato R, Caraglia M, Normanno N, Iaffaioli RV (2005) Monoclonal antibodies targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and vascular endothelial growth factor with a focus on head and neck tumors. Curr Opin Oncol 17:212–217
Denhart BC, Guidi AJ, Tognazzi K, Dvorak HF, Brown LF (1997) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in oral and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and dysplasia. Lab Invest 77:659–664
Eisma RJ, Spiro JD, Kreutzer DL (1999) Role of angiogenic factors: coexpression of interleukin-8 and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with head and neck squamous carcinoma. Laryngoscope 109:687–693
Zang J, Li C, Zhao LN, Shi M, Zhou YC, Wang JH, Li X (2012) Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. Head Neck [Epub ahead of print]
Tanaka N, Odajima T, Ogi K, Ikeda T, Satoh M (2003) Expression of E-cadherin, alpha-catenin, and beta-catenin in the process of lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 89:557–563
Shintani S, Li C, Mihara M, Nakashiro K, Hamakawa H (2003) Gefitinib (‘Iressa’), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, mediates the inhibition of lymph node metastasis in oral cancer cells. Cancer Lett 201:149–155
Georgolios AK, Batistatou A, Charalabopoulos K (2005) Integrins in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): a review of the current literature. Cell Commun Adhes 12:1–8
Kawata R, Shimada T, Maruyama S, Hisa Y, Takenaka H, Murakami Y (2002) Enhanced production of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human head and neck carcinomas is correlated with lymph node metastasis. Acta Otolaryngol 122:101–106
Chin D, Boyle GM, Williams RM, Ferguson K, Pandeya N, Pedley J, Campbell CM, Theile DR, Parsons PG, Coman WB (2005) Novel markers for poor prognosis in head and neck cancer. Int J Cancer 113:789–797
Tremble PM, Lane TF, Sage EH, Werb Z (1993) SPARC, a secreted protein associated with morphogenesis and tissue remodeling, induces expression of metalloproteinases in fibroblasts through a novel extracellular matrix-dependent pathway. J Cell Biol 121:1433–1444
Goldblum SE, Ding X, Funk SE, Sage EH (1994) SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine) regulates endothelial cell shape and barrier function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3448–3452
Warburg O (1956) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123:309–314
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324:1029–1033
Tripathi P, Kamarajan P, Somashekar BS, Mackinnon N, Chinnaiyan AM, Kapila YL, Rajendiran TM, Ramamoorthy A (2012) Delineating metabolic signatures of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Phospholipase A(2), a potential therapeutic target. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(11):1852–1861
Reynolds TY, Rockwell S, Glazer PM (1996) Genetic instability induced by the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res 56:5754–5757
Thomlinson RH, Gray LH (1955) The histological structure of some human lung cancers and the possible implications for radiotherapy. Br J Cancer 9:539–549
Teicher BA (1994) Hypoxia and drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev 13:139–168
Janssen HL, Haustermans KM, Balm AJ, Begg AC (2005) Hypoxia in head and neck cancer: how much, how important? Head Neck 27:622–638
Hermans R (2006) Head and neck cancer: how imaging predicts treatment outcome. Cancer Imag 6:S145–S153
Nordsmark M, Bentzen SM, Rudat V, Brizel D, Lartigau E, Stadler P, Becker A, Adam M, Molls M, Dunst J, Terris DJ, Overgaard J (2005) Prognostic value of tumor oxygenation in 397 head and neck tumors after primary radiation therapy. An international multi-center study. Radiother Oncol 77:18–24
Peridis S, Pilgrim G, Athanasopoulos I, Parpounas K (2011) Carbonic anhydrase-9 expression in head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268:661–670
Grandis JR, Falkner DM, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, Drenning SD, Morel PA (2000) Human leukocyte antigen class I allelic and haplotype loss in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: clinical and immunogenetic consequences. Clin Cancer Res 6:2794–2802
Campoli M, Ferrone S (2008) HLA antigen changes in malignant cells: epigenetic mechanisms and biologic significance. Oncogene 27:5869–5885
Lopez-Albaitero A, Nayak JV, Ogino T, Machandia A, Gooding W, DeLeo AB, Ferrone S, Ferris RL (2006) Role of antigen-processing machinery in the in vitro resistance of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cells to recognition by CTL. J Immunol 176:3402–3409
Hoffmann TK, Dworacki G, Tsukihiro T, Meidenbauer N, Gooding W, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (2002) Spontaneous apoptosis of circulating T lymphocytes in patients with head and neck cancer and its clinical importance. Clin Cancer Res 8:2553–2562
Cruz IB, Snijders PJ, Meijer CJ, Braakhuis BJ, Snow GB, Walboomers JM, van der Waal I (1998) p53 expression above the basal cell layer in oral mucosa is an early event of malignant transformation and has predictive value for developing oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol 184:360–368
Dvorak HF (1986) Tumors: wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N Engl J Med 315:1650–1659
Prince ME, Ailles LE (2008) Cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:2871–2875
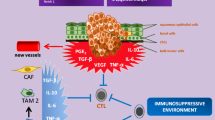
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140:883–899
Gallo O, Masini E, Bianchi B, Bruschini L, Paglierani M, Franchi A (2002) Prognostic significance of cyclooxygenase-2 pathway and angiogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol 33:708–714
Tezal M, Sullivan MA, Hyland A, Marshall JR, Stoler D, Reid ME, Loree TR, Rigual NR, Merzianu M, Hauck L, Lillis C, Wactawski-Wende J, Scannapieco FA (2009) Chronic periodontitis and the incidence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:2406–2412
Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Szajnik M, Harasymczuk M, Boyiadzis M, Kruk-Zagajewska A, Szyfter W, Zeromski J, Whiteside TL (2009) Triggering of Toll-like receptor 4 expressed on human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor development and protects the tumor from immune attack. Cancer Res 69:3105–3113
Balan V, Nangia-Makker P, Raz A (2010) Galectins as cancer biomarkers. Cancers 2:592–610
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernstein, J.M., Bernstein, C.R., West, C.M.L. et al. Molecular and cellular processes underlying the hallmarks of head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 2585–2593 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2323-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2323-x