Abstract
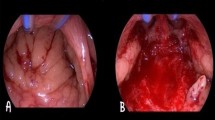
The objective of the study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of temperature-controlled radiofrequency (RF) tonsil ablation in the treatment of halitosis caused by chronic tonsillitis with caseum. The study method was retrospective. The medical records of 58 patients undergoing temperature-controlled RF tonsil ablation due to chronic tonsillitis with caseum between November 1, 2005 and November 30, 2008 were reviewed. Forty-nine (84.4%) of 58 patients reported complete disappearance of bad breath after the first treatment; five patients (8.6%) reported as having insufficient improvement and four (6.9%) patients had no change. Two patients from “insufficient group” and all four patients from “no change” group agreed to a repeat treatment. After the second session, four (6.9%) patients reported complete disappearance of halitosis with the disappearance of caseum formation. But two patients still suffered from halitosis. One of these patients underwent tonsillectomy, other patient is under our follow-up. Overall, complete elimination of halitosis was accomplished with one session in 49 (84.4%) patients, two sessions in four (6.9%) patients, making a total of 53 (91.3%) patients. Postoperative morbidities included one transient mild bleeding, one secondary bleeding and one mild edema. Temperature-controlled RF tonsil ablation is an effective method for treating halitosis which derived from chronic tonsillitis with caseum. This well-tolerated technique avoids the post-procedure morbidities and discomfort of more invasive surgical modalities currently used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nogueira-Filho GR, Duarte PM, Toledo S et al (2002) Effect of triclosan dentifrices on mouth volatile sulphur compounds and dental plaque trypsin-like activity during experimental gingivitis development. J Clin Periodontol 29:1067–1073
van Steenberghe D (1997) Breath malodor. Curr Opin Periodontol 4(9):137–143
Delanghe G, Ghyselen J, Bollen C et al (1999) An inventory of patients’ response to treatment at a multidisciplinary breath odor clinic. Quintessence Int 30(5):307–310
Bosy A, Kulkarni GV, Rosenberg M et al (1994) Relationship of oral malodor to periodontitis: evidence of independence in discrete subpopulations. J Periodontol 65(1):37–46
Krespi YP, Ling EH (1994) Tonsils cryptolysis using CO2 Swift Laser. Oper Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 5:294–297
Krespi YP, Ling EH (1994) Laser assisted serial tonsillectomy. J Otolaryngol 23:325–327
Finkelstein Y, Talmi YP, Ophir D, Berger G (2004) Laser cryptolysis for the treatment of halitosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131(4):372–377
Ansai T, Takehara T (2005) Tonsillolith as a halitosis-inducing factor. Br Dent J 198(5):263–264
Bluestone CD (1992) Current indications for tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 155:58–64
Yoshida A, Okamoto K (1988) Indications of tonsillectomy for recurrent tonsillitis. Acta Otoryngol 454:305–312
Nelson LM (2000) Radiofrequency treatment for obstructive tonsillar hypertrophy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 26:736–740
Friedman M, LoSavio P, Ibrahim H et al (2003) Radiofrequency tonsil reduction: safety, morbidity, and efficacy. Laryngoscope 113(5):882–887
Nelson LM (2001) Temperature-controlled radiofrequency tonsil reduction: extended follow-up. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:456–461
Brook I, Yocum P, Foote PA Jr (1995) Changes in the core tonsillar bacteriology of recurrent tonsillitis: 1977–1993. Clin Infect Dis 21:171–176
Brook I, Foote PA Jr, Slots J, Jackson W (1993) Immune response to Prevotella intermedia in patients with recurrent nonstreptococcal tonsillitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 102(2):113–116
Claesson R, Edlund MB, Persson S et al (1990) Production of volatile sulfur compounds by various Fusobacterium species. Oral Microbiol Immunol 5(3):137–142
Li KK, Powell NB, Riley RW, Guilleminault C (2002) Temperature-controlled radiofrequency tongue base reduction for sleep-disordered breathing: long-term outcomes. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127(3):230–234
Emery BE, Flexon PB (2000) Radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction of the soft palate: a new treatment for snoring. Laryngoscope 110(7):1092–1098
Nease CJ, Krempl GA (2004) Radiofrequency treatment of turbinate hypertrophy: a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130(3):291–299
Wachtel JM, Kuehn DP, Weiss KS (2000) Hypernasality after tonsillectomy without adenoidectomy in an adult. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122:112–113
Auf I, Osborne JE, Sparkes C, Khalil H (1997) Is the KTP laser effective in tonsillectomy? Clin Otolaryngol 22:145–146
Nunez DA, Provan J, Crawford M (2000) Postoperative tonsillectomy pain in pediatric patients. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:837–841
Hoddeson EK, Gourin CG (2009) Adult tonsillectomy: current indications and outcomes. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(1):19–22
Anand A, Vilela RJ, Guarisco JL (2005) Intracapsular versus standard tonsillectomy: review of literature. J La State Med Soc 157(5):259–261
Lassaletta L, Martin G, Villafruela MA et al (1997) Pediatric tonsillectomy: post-operative morbidity comparing microsurgical bipolar dissection versus cold sharp dissection. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 41:307–317
Hultcrantz E, Linder A, Markström A (1999) Tonsillectomy or tonsillotomy? A randomized study comparing postoperative pain and long-term effects. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 51(3):171–176
Ilgen F (2005) Laser-assisted tonsillotomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea and adenotonsillary hyperplasia—experiences as an outpatient procedure. Laryngorhinootologie 84(9):665–670
Berger G, Finkelstein Y, Ophir D (1999) Histopathologic changes of the soft palate after laser-assisted uvulopalatoplasty. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:786–790
Rai MR, Parry TM, Dombrovskis A et al (2008) Remifentanil target-controlled infusion vs propofol target-controlled infusion for conscious sedation for awake fibreoptic intubation: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth 100(1):125–130
Renna M, Chung R, Li W, Maguire C et al (2009) Remifentanil plus low-dose midazolam for outpatient sedation in transesophageal echocardiography. Int J Cardiol 136(3):325–329
Leone M, Albanèse J, Viviand X et al (2004) The effects of remifentanil on endotracheal suctioning-induced increases in intracranial pressure in head-injured patients. Anesth Analg 99(4):1193–1198
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanyeri, H.M., Polat, S. Temperature-controlled radiofrequency tonsil ablation for the treatment of halitosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268, 267–272 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1356-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1356-2