Abstract
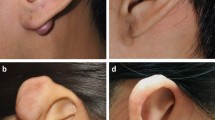
The aim of this study was to present long-term results in patients with auricular keloids after surgical excision and/or medical therapy by corticoid injection. A retrospective study at an academic tertiary referral centre is presented. Seventeen patients after excision, injection of corticoid, full skin grafting (single therapy or combination of interventions) for auricular keloids were followed up. The validated questionnaires SF-36 and patient outcomes of surgery-head/neck were applied to evaluate the quality of life and the patients’ satisfaction after therapy. Photographs of the former keloid site were rated by an experienced facial plastic surgeon being unaware of treatment method and the patient’s own estimation. The best results for retroauricular keloids were reached by excision, skin grafting and triamcinolone injection, and for earlobe keloids by excision, primary wound closure and triamcinolone injection. Both in rating by the patients and in grading by an investigator, the highest scores for aesthetics and satisfaction were found after triamcinolone injection together with or without excision or skin grafting. A size-related resection of keloids with defect reconstruction by full thickness skin grafting for retroauricular keloids and primary wound closure of ear lobe keloids with an additional steroid injection lead to good cosmetic results and high level of satisfaction among patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler PD, Longaker MT, Yang GP (2008) Current progress in keloid research and treatment. J Am Coll Surg 206:731–741. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.12.001
De Lorenzi F, Tielemans HJ, van der Hulst RR, Rhemrev R, Nieman FH, Lutgens LC, Boeckx WD (2007) Is the treatment of keloid scars still a challenge in 2006? Ann Plast Surg 58:186–192. doi:10.1097/01.sap.0000237761.52586.f9
Donkor P (2007) Head and neck keloid: treatment by core excision and delayed intralesional injection of steroid. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:1292–1296. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2006.10.049
Chowdri NA, Masarat M, Mattoo A, Darzi MA (1999) Keloids and hypertrophic scars: results with intraoperative and serial postoperative corticosteroid injection therapy. Aust N Z J Surg 69:655–659. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1622.1999.01658.x
Apikian M, Goodman G (2004) Intralesional 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of keloid scars. Australas J Dermatol 45:140–143. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2004.00072.x
Gupta S, Kalra A (2002) Efficacy and safety of intralesional 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of keloids. Dermatology 204:130–132. doi:10.1159/000051830
Stewart CE, Kim JY (2006) Application of mitomycin-C for head and neck keloids. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:946–950. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2005.07.026
Naeini FF, Najafian J, Ahmadpour K (2006) Bleomycin tattooing as a promising therapeutic modality in large keloids and hypertrophic scars. Dermatol Surg 32:1023–1029. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2006.32225.x
Yamamoto T (2006) Bleomycin and the skin. Br J Dermatol 155:869–875. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07474.x
Savion Y, Sela M (2008) Prefabricated pressure earring for earlobe keloids. J Prosthet Dent 99:406–407. doi:10.1016/S0022-3913(08)60091-8
Saha SS, Kumar V, Khazanchi RK, Aggarwal A, Garg S (2004) Primary skin grafting in ear lobule keloid. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:1204–1207. doi:10.1097/01.PRS.0000135889.48745.E4
Yencha MW, Oberman JP (2006) Combined therapy in the treatment of auricular keloids. Ear Nose Throat J 85:93–97
Shih PY, Chen HH, Chen CH, Hong HS, Yang CH (2008) Rapid recurrence of keloid after pulse dye laser treatment. Dermatol Surg 34:1124–1127. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2008.34225.x
Parikh DA, Ridgway JM, Ge NN (2008) Keloid banding using suture ligature: a novel technique and review of literature. Laryngoscope 118:1960–1965. doi:10.1097/MLG.0b013e3181817b61
Leventhal D, Furr M, Reiter D (2006) Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Arch Facial Plast Surg 8:362–368. doi:10.1001/archfaci.8.6.362
Froelich K, Staudenmaier R, Kleinsasser N, Hagen R (2007) Therapy of auricular keloids: review of different treatment modalities and proposal for a therapeutic algorithm. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264:1497–1508. doi:10.1007/s00405-007-0383-0
Bullinger M (1995) German translation and psychometric testing of the SF-36 health survey: preliminary results from the IQOLA Project. International Quality of Life Assessment. Soc Sci Med 41:1359–1366. doi:10.1016/0277-9536(95)00115-N
Cano SJ, Browne JP, Lamping DL, Roberts AH, McGrouther DA, Black NA (2006) The patient outcomes of surgery-head/neck (POS-head/neck): a new patient-based outcome measure. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:65–73. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2005.04.060
Rosen DJ, Patel MK, Freeman K, Weiss PR (2007) A primary protocol for the management of ear keloids: results of excision combined with intraoperative and postoperative steroid injections. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:1395–1400. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000279373.25099.2a
Sallstrom KO, Larson O, Heden P, Eriksson G, Glas JE, Ringborg U (1989) Treatment of keloids with surgical excision and postoperative X-ray radiation. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 23:211–215. doi:10.3109/02844318909075120
Guix B, Henriquez I, Andres A, Finestres F, Tello JI, Martinez A (2001) Treatment of keloids by high-dose-rate brachytherapy: a seven-year study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50:167–172. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(00)01563-7
Ragoowansi R, Cornes PG, Moss AL, Glees JP (2003) Treatment of keloids by surgical excision and immediate postoperative single-fraction radiotherapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:1853–1859. doi:10.1097/01.PRS.0000056869.31142.DE
Hulsbergen Henning JP, Roskam Y, van Gemert MJ (1986) Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars with an argon laser. Lasers Surg Med 6:72–75. doi:10.1002/lsm.1900060115
Norris JE (1991) The effect of carbon dioxide laser surgery on the recurrence of keloids. Plast Reconstr Surg 87:44–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bermueller, C., Rettinger, G. & Keck, T. Auricular keloids: treatment and results. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267, 575–580 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-1059-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-009-1059-8