Abstract
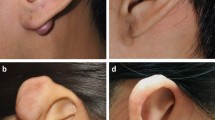
Keloids are abnormal wound reactions of connective tissue. Auricular keloids can develop as a result of, e.g., otoplasty, ear piercing, or skin trauma. A wide variety of therapeutic options exists, including surgery as primary treatment. Furthermore, there are medical, physical, radiotherapeutic and experimental options. The present paper focuses on the different techniques including the therapeutic outcome and quality rating for each chosen pathway. In addition to the experience of the university hospitals, a thorough review of the literature was performed in order to update and compare today’s therapeutic options. Surgical techniques are customized to the lesion’s specific localization and extent. They may include revision of otoplasty. With medical treatment, established modalities such as steroid injection have to be distinguished from experimental methods like interferon, 5-FU, verapamil, imiquimod, or mitomycin C. Radiation is generally accepted to be effective, especially applied accompanying surgery, but needs to be restricted due to possible side effects. Physical therapy, e.g., pressure in a variety of application modalities, has gained a profound position in the therapy of auricular keloids. The success rates of the different treatment modalities vary markedly, and the number of patients per study is considerably low. Resuming the results, a periodic follow-up and good patients’ compliance are mandatory to early realize and treat auricular keloids. However, studies are needed to evaluate accepted and experimental therapies including larger number of patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aköz T, Gideroglu K, Akan M (2002) Combination of different techniques for the treatment of earlobe keloids. Aesthetic Plast Surg 26:184–188
Al-Attar A, Mess S, Thomassen JM, Kauffman CL, Davison SP (2006) Keloid pathogenesis and treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:286–300
Apikian M, Goodman G (2004) Intralesional 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of keloid scars. Australas J Dermatol 45:140–143
Berman B, Flores F (1997) Recurrence rates of excised keloids treated with postoperative triamcinolone acetonide injections or interferon alfa-2b injections. J Am Acad Dermatol 37:755–757
Berman B, Kaufman J (2002) Pilot study of the effect of postoperative imiquimod 5% cream on the recurrence rate of excised keloids. J Am Acad Dermatol 47:S209–S211
Borok TL, Bray M, Sinclair I, Plafker J, Labirth L, Rollins C (1988) Role of ionizing irradiation for 393 keloids. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 15:865–870
Botwood N, Lewanski C, Lowdell C (1999) The risks of treating keloids with radiotherapy. Br J Radiol 72:1222–1224
Brent B (1978) The role of pressure therapy in management of earlobe keloids. Ann Plast Surg 1:579–581
Brown LA, Pierce HE (1986) Keloids: scar revision. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 12:51–56
Buchwald C, Nielsen LH, Rosborg J (1992) Keloids of the external ear. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 54:108–112
Chaudhry MR, Akhtar S, Duvalsaint F, Garner L, Lucente FE (1994) Ear lobe keloids, surgical excision followed by radiation therapy: a 10-year experience. Ear Nose Throat J 73:779–781
Chen T, Kunnavatana SS, Koch RJ (2006) Effects of mitomycin-C on normal dermal fibroblasts. Laryngoscope 116:514–517
Chowdri NA, Masarat M, Mattoo A, Darzi MA (1999) Keloids and hypertrophic scars: results with intraoperative and serial postoperative corticosteroid injection therapy. Aust N Z J Surg 69:655–659
Cohen IK, Diegelmann RF, Johnson ML (1977) Effect of corticosteroids on collagen synthesis. Surgery 82:15–20
Copcu E, Sivrioglu N, Oztan Y (2004) Combination of surgery and intralesional verapamil injection in the treatment of the keloid. J Burn Care Rehabil 25:1–7
D’Andrea F, Brongo S, Ferraro G, Baroni A (2002) Prevention and treatment of keloids with intralesional verapamil. Dermatology 204:60–62
Davison SP, Mess S, Kauffman LC, Al-Attar A (2006) Ineffective treatment of keloids with interferon alpha-2b. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:247–252
de Oliveira GV, Nunes TA, Magna LA, Cintra ML, Kitten GT, Zarpellon S, Raposo Do Amaral CM (2001) Silicone versus nonsilicone gel dressings: a controlled trial. Dermatol Surg 27:721–726
Dinh Q, Veness M, Richards S (2004) Role of adjuvant radiotherapy in recurrent earlobe keloids. Australas J Dermatol 45:162–166
Ehrlich HP, Desmouliere A, Diegelmann RF, Cohen IK, Compton CC, Garner WL, Kapanci Y, Gabbiani G (1994) Morphological and immunochemical differences between keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Pathol 145:105–113
Eishi K, Bae SJ, Ogawa F, Hamasaki Y, Shimizu K, Katayama I (2003) Silicone gel sheets relieve pain and pruritus with clinical improvement of keloid: possible target of mast cells. J Dermatolog Treat 14:248–252
Englisch RS, Shenefelt PD (1999) Keloids and hypertrophic scars. Dermatol Surg 25:631–638
Fikrle T, Pizinger K (2005) Cryosurgery in the treatment of earlobe keloids: report of seven cases. Dermatol Surg 31:1728–1731
Fitzpatrick RE (1999) Treatment of inflamed hypertrophic scars using intralesional 5-FU. Dermatol Surg 25:224–232
Fulton JE (1995) Silicone gel sheeting for the prevention and management of evolving hypertrophic and keloid scars. Dermatol Surg 21:947–951
Funayama E, Chodon T, Oyama A, Sugihara T (2003) Keratinocytes promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of the underlying fibroblasts: an important role in the pathogenesis of keloid. J Invest Dermatol 121:1326–1331
Giugliano G, Pasquali D, Notaro A, Brongo S, Nicoletti G, D’Andrea F, Bellastella A, Sinisi AA (2003) Verapamil inhibits interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor production in primary cultures of keloid fibroblasts. Br J Plast Surg 56:804–809
Granstein RD, Rook A, Flotte TJ, Haas A (1990) A controlled trial of intralesional recombinant interferon-γ in the treatment of keloidal scarring. Arch Dermatol 126:1295–1301
Grimes PE, Hunt SG (1993) Considerations for cosmetic surgery in the black population. Clin Plast Surg 20:27–34
Gupta S, Kalra A (2002) Effiacy and safety of intralesional 5-flourouracil in the treatment of keloids. Dermatology 204:130–132
Hackert I, Aschoff R, Sebastian G (2003) Keloide und ihre Therapie. Hautarzt 54:1003–1015
Hatoko M, Kuwahara M, Shiba A, Tada H, Okazaki T, Muramatsu T, Shirai T (1998) Earlobe reconstruction using a subcutaneous island pedicle flap after resection of “earlobe keloid”. Dermatol Surg 24:257–261
Jemec B, Linge C, Grobbelaar AO, Smith PJ, Sanders R, McGrouther DA (2000) The effect of 5-fluorouracil on Dupuytren fibroblast proliferation and differentiation. Chir Main 19:15–22
Kelly AP (2004) Medical and surgical therapies for keloids. Dermatol Ther 17:212–218
Kim JY, Stewart CE (2004) Application of Mitomycin-C for head and neck keloids. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131(2):P73
Kim DY, Kim ES, Eo SR, Kim KS, Lee SY, Cho BH (2004) A surgical approach for earlobe keloid: keloid fillet flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:1668–1674
Lawrence WT (1996) Treatment of earlobe keloids with surgery plus adjuvant intralesional verapamil and pressure earrings. Ann Plast Surg 37:167–169
Lee RC, Ping JA (1990) Calcium antagonists retard extracellular matrix production in connective tissue equivalent. J Surg Res 49:463–466
Lee J, Yang CC, Chao SC, Wong TW (2004) Histopathological differential diagnosis of keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Dermatopathol 26:379–384
Mall JW, Pollmann C, Müller JM, Buttemeyer R (2002) Keloidbildung des Ohrläppchens nach Ohrlochstechen. Chirurg 73:514–516
Martin-García RF, Busquets AC (2005) Postsurgical use of imiquimod 5% cream in the prevention of earlobe keloid recurrences: results of an open-label, pilot study. Dermatol Surg 31:1394–1398
Mizuno H, Cagri Uysal A, Koike S, Hyakusoku H (2006) Squamous cell carcinoma of the auricle arising from keloid after radium needle therapy. J Craniofac Surg 17:360–362
Mustoe TA, Cooter RD, Gold MH, Hobbs FD, Ramelet AA, Shakespeare PG, Stella M, Teot L, Wood FM, Ziegler UE (2002) International clinical recommendations on scar management. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:560–571
Nanda S, Reddy BS (2004) Intralesional 5-fluorouracil as a treatment modality of keloids. Dermatol Surg 30:54–57
Nason KH (1942) Keloids and their treatment. N Engl J Med 226:883–886
Ragoowansi R, Cornes PG, Glees JP, Powell BW, Moss AL (2001) Ear-lobe keloids: treatment by a protocol of surgical excision and immediate postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy. Br J Plast Surg 54:504–508
Ragoowansi R, Cornes PG, Moss AL, Glees JP (2003) Treatment of keloids by surgical excision and immediate postoperative single-fraction radiotherapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:1853–1859
Rusciani L, Paradisi A, Alfano C, Chiummariello S, Rusciani A (2006) Cryotherapy in the treatment of keloids. J Drugs Dermatol 5:591–595
Saha SS, Kumar V, Khazanchi RK, Aggarwal A, Garg S (2004) Primary skin grafting in ear lobule keloid. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:1204–1207
Sanders KW, Gage-White L, Stucker FJ (2005) Topical mitomycin C in the prevention of keloid scar recurrence. Arch Facial Plast Surg 7:172–175
Saray Y, Gulec AT (2005) Treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars with dermojet injections of bleomycin: a preliminary study. Int J Dermatol 44:777–784
Sclafani AP, Gordon L, Chadha M, Romo T III (1996) Prevention of earlobe keloid recurrence with postoperative corticosteroid injections versus radiation therapy: a randomized, prospective study and review of the literature. Dermatol Surg 22:569–574
Shons AR, Press BH (1983) The treatment of earlobe keloids by surgical excision and postoperative triamcinolone injection. Ann Plast Surg 10:480–482
Simman R, Alani H, Williams F (2003) Effect of mitomycin C on keloid fibroblasts: an in vitro study. Ann Plast Surg 50:71–76
Stashower ME (2006) Successful treatment of earlobe keloids with imiquimod after tangential shave excision. Dermatol Surg 32:380–386
Stewart CE IV, Kim JY (2006) Application of mitomycin-C for head and neck keloids. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:946–950
Talmi YP, Orenstein A, Wolf M, Kronenberg J (2005) Use of mitomycin C for treatment of keloid: a preliminary report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:598–601
Worret WI, Vogt HJ (2004) Narbentherapie in der Dermatologie. Dtsch Arztebl 101:2819–2824
Wu WS, Wang FS, Yang KD, Huang CC, Kuo YR (2006) Dexamethasone induction of keloid regression through effective suppression of VEGF expression and keloid fibroblast proliferation. J Invest Dermatol 126:1264–1271
Xia W, Phan TT, Lim IJ, Longaker MT, Yang GP (2004) Complex epithelial–mesenchymal interactions modulate transforming growth factor-beta expression in keloid-derived cells. Wound Repair Regen 12:546–556
Xia W, Phan TT, Lim IJ, Longaker MT, Yang GP (2006) Differential transcriptional responses of keloid and normal keratinocytes to serum stimulation. J Surg Res 135:156–163
Ziccardi VB, Lamphier J (2000) Use of keloid skin as an autograft for earlobe reconstruction after excision. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 89:674
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Froelich, K., Staudenmaier, R., Kleinsasser, N. et al. Therapy of auricular keloids: review of different treatment modalities and proposal for a therapeutic algorithm. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264, 1497–1508 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0383-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0383-0