Abstract
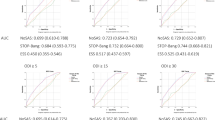
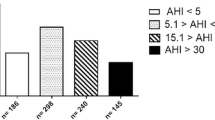
We sought to analyze the predictive value of anthropometric, clinical and epidemiological parameters in the identification of patients with suspected OSA, and their relationship with apnoea/hypopnoea respiratory events during sleep. We studied retrospectively 433 patients with OSA, 361 men (83.37%) and 72 women (16.63%), with an average age of ±47, standard deviation ±11.10 years (range 18–75 years). The study variables for all of the patients were age, sex, spirometry, neck circumference, body mass index (BMI), Epworth sleepiness scale, nasal examination, pharyngeal examination, collapsibility of the pharynx (Müller Manoeuvre), and apnoea-hypopnoea index (AHI). Age, neck circumference, BMI, Epworth sleepiness scale, pharyngeal examination and pharyngeal collapse were the significant variables. Of the patients, 78% were correctly classified, with a sensitivity of 74.6% and a specificity of 66.3%. We found a direct relationship between the variables analysed and AHI. Based on these results, we obtained the following algorithm to calculate the prediction of AHI for a new patient: AHI = −12.04 + 0.36 neck circumference +2.2286 pharyngeal collapses (MM) + 0.1761 Epworth + 0.0017 BMI × age + 1.1949 pharyngeal examinations. The ratio variance in the number of respiratory events explained by the model was 33% (r 2 = 0.33). The variables given in the algorithm are the best ones for predicting the number of respiratory events during sleep in patients studied for suspected OSA. The algorithm proposed may be a good screening method to the identification of patients with OSA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballester E, Badía JR, Hernández L, Carrasco E, de Pablo J, Fornas C, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Montserrat JM (1999) Evidence of the effectiveness of continuous positive airway pressure in the treatment of sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:495–501
Barbé F, Pericás J, Muñoz A, Findley L, Antó JM, Agustí AG (1998) Automobile accidents in patients with sleep apnea syndrome. An epidemiological and mechanistic study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158:18–22
Chaouat A, Weitzenblum E, Krieger J, Ifoundza T, Oswald M, Kessler R (1995) Association of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:82–86
Chervin RD, Guilleminault C (1996) Obstructive sleep apnea and related disorders. Neurol Clin 14:583–609
Chervin RD, Aldrich MS, Pickett R, Guilleminault C (1997) Comparison of the results of the Epworth sleepiness scale and the multiple sleep latency test. J Psychosom Res 42:145–155
Crocker BD, Olson LG, Saunders NA, Hensley MJ, McKeon JL, Allen KM, Gyulay SG (1990) Estimation of the probability of disturbed breathing during sleep before a sleep study. Am Rev Respir Dis 142:14–18
Davies RJ, Ali NJ, Stradling JR (1992) Neck circumference and other clinical features in the diagnosis of the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Thorax 47:101–105
Dealberto MJ, Ferber C, Garma L, Lemoine P, Alperovitch A (1994) Factors related to sleep apnea syndrome in sleep clinic patients. Chest 105:1753–1758
Deegan PC, McNicholas WT (1996) Predictive value of clinical features for the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J 9:117–124
Ferguson KA, Ono T, Lowe AA, Keenan SP, Fleetham JA (1995) The relationship between obesity and craniofacial structure in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 108:375–381
Flemons WW, Whitelaw WA, Brant R, Remmers JE (1994) Likelihood ratios for a sleep apnea clinical prediction rule. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 150:1279–1285
Franceschi M, Zamproni P, Crippa D, Smirne S (1982) Excessive daytime sleepiness: a 1-year study in an unselected inpatient population. Sleep 5:239–247
Gislason T, Almqvist M, Eriksson G, Taube A, Boman G (1988) Prevalence of sleep apnoea syndrome among Swedish men—an epidemiological study. J Clin Epidemiol 41:571–576
Guilleminault C, Stoohs R, Kim YD, Chervin R, Black J, Clerk A (1995) Upper airway sleep-disordered breathing in women. Ann Intern Med 1(122):493–501
Hoffstein V, Szalai JP (1993) Predictive value of clinical features in diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 16:118–122
Haponik EF, Smith PL, Meyers DA, Bleecker ER (1984) Evaluation of sleep-disordered breathing. Is polysomnography necessary? Am J Med 77:671–677
Harding SM (2001) Prediction formulae for sleep-disordered breathing. Curr Opin Pulm Med 7:381–385
He J, Kryger MH, Zorick FJ, Conway W, Roth T (1988) Mortality and apnea index in obstructive sleep apnea. Experience in 385 male patients. Chest 94:9–14
Johns MW (1991) A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14:540–545
Johns MW (1992) Reliability and factor analysis of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 15:376–381
Kiely JL, McNicholas WT (2000) Cardiovascular risk factors in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J 16:128–133
Kirby SD, Eng P, Danter W, George CF, Francovic T, Ruby RR, Ferguson KA (1999) Neural network prediction of obstructive sleep apnea from clinical criteria. Chest 116:409–415
Lavie P (2002) Incidence of sleep apnea in a presumably healthy working population: a significant relationship with excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep 25:312–318
Leung RS, Bradley TD (2001) Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:2147–2165
Maislin G, Pack AI, Kribbs NB, Smith PL, Schwartz AR, Kline LR, Schwab RJ, Dinges DF (1995) A survey screen for prediction of apnea. Sleep 18:158–166
Martinez Garcia MA, Soler Cataluña JJ, Roman Sanchez P, Cabero Salt L, Gimenez Ibañez I, Gastaldo Palop T (2003) Clinical predictors of sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome susceptible to treatment with continuous positive airway pressure. Arch Bronconeumol 39:449–454
Millman RP, Carlisle CC, McGarvey ST, Eveloff SE, Levinson PD (1995) Body fat distribution and sleep apnea severity in women. Chest 107:362–366
Olson LG, King MT, Hensley MJ, Saunders N (1995) A community study of snoring and sleep-disordered breathing. Prevalence. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:711–716
Petri N, Suadicani P, Wildschiodtz G, Bjorn-Jorgensen J (1994) Predictive value of Muller maneuver, cephalometry and clinical features for the outcome of uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Evaluation of predictive factors using discriminant analysis in 30 sleep apnea patients. Acta Otolaryngol 114:565–571
Pradhan PS, Gliklich RE, Winkelman J (1996) Screening for obstructive sleep apnea in patients presenting for snoring surgery. Laryngoscope 106:1393–1397
Rowley JA, Aboussouan LS, Badr MS (2000) The use of clinical prediction formulas in the evaluation of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 1(23):929–938
Scharf SM, Garshick E, Brown R, Tishler PV, Tosteson T, McCarley R (1990) Screening for subclinical sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep 13:344–353
Schmidt-Nowara WW, Coultas DB, Wiggins C, Skipper BE, Samet JM (1990) Snoring in a Hispanic-American population. Risk factors and association with hypertension and other morbidity. Arch Intern Med 150:597–601
Shahar E, Whitney CW, Redline S, Lee ET, Newman AB, Javier Nieto F, O’Connor GT, Boland LL, Schwartz JE, Samet JM (2001) Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: cross-sectional results of the sleep heart health study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:19–25
Sher AE, Thorpy MJ, Shprintzen RJ, Spielman AJ, Burack B, McGregor PA (1985) Predictive value of Muller maneuver in selection of patients for uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Laryngoscope 95:1483–1487
Stradling JR (1995) Sleep-related breathing disorders. Obstructive sleep apnoea: definitions, epidemiology, and natural history. Thorax 50:683–689
Stradling JR, Crosby JH (1991) Predictors and prevalence of obstructive sleep apnoea and snoring in 1001 middle aged men. Thorax 46:85–90
Viner S, Szalai JP, Hoffstein V (1991) Are history and physical examination a good screening test for sleep apnea? Ann Intern Med 1(115):356–359
Ward SL, Marcus CL (1996) Obstructive sleep apnea in infants and young children. J Clin Neurophysiol 13:198–207
Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S (1993) The occurrence of sleep disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 328:1230–1235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santaolalla Montoya, F., Iriondo Bedialauneta, J.R., Aguirre Larracoechea, U. et al. The predictive value of clinical and epidemiological parameters in the identification of patients with obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA): a clinical prediction algorithm in the evaluation of OSA. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264, 637–643 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0241-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0241-5