Abstract
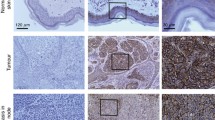
Molecular events underlying the progression of malignant tumors through the surrounding tissue are largely mediated by membrane-bound adhesion molecules. Basal-cell adhesion molecule (B-CAM), a 90-kDa laminin receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is induced in some epithelial malignancies. Its function in these tumors, however, still remains obscure. We demonstrated that expression of B-CAM is very weak, if detectable at all, in normal epidermis but is strongly induced in both basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas of the skin, and most pronounced at the basal surface of the tumor nests. Interestingly, the only known B-CAM ligand, laminin, was markedly upregulated within corresponding microanatomical sites surrounding the tumor nests, suggesting that both molecules may interact there. Consistent with this hypothesis, we were able to directly demonstrate binding of a B-CAM/Fc chimeric molecule to the peritumoral stroma in situ. Finally, in proof-of-principle experiments, human B-CAM was overexpressed both in murine and in human fibroblasts. The haptotactic migration of these novel B-CAM+ cell populations on a laminin matrix was significantly increased (P=0.02) as compared to mock-transfected cells when integrin-mediated adhesion was blocked by chelation of divalent cations. Thus, our findings provide the first direct experimental evidence that interactions of B-CAM and laminin may be involved in progression of epithelial skin tumors.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCC:
-
Basal cell carcinoma
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- mAb:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence activated cell sorter
References
Gallagher RP, Ma B, McLean DI (1990) Trends in basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma of the skin from 1973 through 1987. J Am Acad Dermatol 23:413–421
Giles GG, Marks R, Foley P (1988) The incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer treated in Australia. BMJ 296:13–17
Goldberg LH (1996) Basal cell carcinoma. Lancet 347:663–666
Marks R (1996) Squamous cell carcinoma. Lancet 347:735
Preston DS, Stern RS (1992) Nonmelanoma skin cancers of the skin. N Engl J Med 327:1649–1662
Ziegler A, Jonason AS, Leffell DJ, Simon JA, Sharma HW, Kimmelman J, Remington L, Jacks T, Brash DE (1994) Sunburn and p53 in the onset of skin cancer. Nature 372:773–776
Cleaver JE, Bootsma D (1975) Xeroderma pigmentosum: biochemical and genetic characteristics. Annu Rev Genet 9:19–38
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulos PG (1996) Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 85:841–851
Gailani MR, Stahle-Bäckdahl M, Leffell DJ (1996) The role of the human homologue of Drosophila patched in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Nat Genet 14:78–81
Lear JT, Heagerty AHM, Smith A (1996) Multiple cutaneous basal cell carcinomas: glutathione S-transferase (GSTM1, GSTT1) and cytochrome P450 (CYP2D6, CYP1A1) polymorphisms influence tumor numbers and accrual. Carcinogenesis 17:1891–1896
Walder BK, Robertson MR, Jeremy DR (1971) Skin cancer and immunosuppression. Lancet ii:1282–1283
Kurwa HA, Marks R (1995) Protracted cutaneous disorders in association with low CD4+ lymphocyte counts. Br J Dermatol 133:625–629
Sitz KV, Keppen M, Johnson DF (1987) Metastatic basal cell carcinoma in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related complex. JAMA 257:340–343
Edwards L, Whiting D, Rogers D, Luck K, Smiles KA (1990) The effect of intralesional interferon gamma on basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 22:496–500
Kooy AJW, Tank B, Vuzevski VD, van Joost T, Prens EP (1998) Expression of interferon-gamma receptors and interferon-gamma-induced up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in basal cell carcinoma; decreased expression of IFN-γR and shedding of ICAM-1 as means to escape immune surveillance. J Pathol 184:169–176
Schön MP, Reifenberger J, von Schmiedeberg S, Megahed M, Lang K, Gattermann N, Meckenstock G, Goerz G, Ruzicka T (1999) Multiple basal cell carcinomas associated with hairy cell leukaemia. Br J Dermatol 140:150–153
Woodhouse EC, Chuaqui RF, Liotta LA (1997) General mechanisms of metastasis. Cancer 80:1529–1537
Cavenagh JD, Cahill MR, Kelsey SM (1998) Adhesion molecules in clinical medicine. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 35:415–459
Bernstein LR, Liotta LA (1994) Molecular mediators of interactions with extracellular matrix components in metastasis and angiogenesis. Curr Opin Oncol 6:106–113
Meyer T, Hart IR (1998) Mechanisms of tumour metastasis. Eur J Cancer 34:214–221
Campbell IG, Foulkes WD, Senger G, Trowsdale J, Garin-Chesa P, Rettig WJ (1994) Molecular cloning of the B-CAM cell surface glycoprotein of epithelial cancers: a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer Res 54:5761–5765
Schön M, Klein CE, Hogenkamp V, Kaufmann R, Wienrich BG, Schön MP (2000) Basal-cell adhesion molecule (B-CAM) is induced in epithelial skin tumors and inflammatory epidermis, and is expressed at cell-cell and cell-substrate contact sites. J Invest Dermatol 115:1047–1053
Zen Q, Cottman M, Truskey G, Fraser R, Telen MJ (1999) Critical factors in basal cell adhesion molecule/lutheran-mediated adhesion to laminin. J Biol Chem 274:728–734
Rettig WJ, Garin-Chesa P, Beresford HR, Oettgen HF, Melamed MR, Old LJ (1988) Cell-surface glycoproteins of human sarcomas: differential expression in normal and malignant tissues and cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:3110–3114
Hynes RO (1992) Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69:11–25
Peltonen J, Larjava H, Jaakkola S, Gralnick H, Akiyama SK, Yamada SS, Yamada KM, Uitto J (1989) Localization of integrin receptors for fibronectin, collagen, and laminin in human skin. Variable expression in basal and squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest 84:1916–1923
Ralfkiaer E, Thomsen K, Vejlsgaard GL (1991) Expression of a cell adhesion protein (VLA beta) in normal and diseased skin. Br J Dermatol 124:527–532
Stamp GW, Pignatelli M (1991) Distribution of beta 1, alpha 1, alpha 2 and alpha 3 integrin chains in basal cell carcinomas. J Pathol 163:307–313
Schofield O, Kist D, Lucas A, Wayner E, Carter W, Zachary C (1998) Abnormal expression of epiligrin and alpha 6 beta 4 integrin in basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg 24:555–559
Watt FM (2002) Role of integrins in regulating epidermal adhesion, growth and differentiation. EMBO J 21:3919–3926
Chen CH, Clegg DO, Hansma HG (1998) Structures and dynamic motion of laminin-1 as observed by atomic force microscopy. Biochemistry 37:8262–8267
Moulson CL, Li C, Miner JH (2001) Localization of Lutheran, a novel laminin receptor, in normal, knockout, and transgenic mice suggests an interaction with laminin alpha5 in vivo. Dev Dyn 222:101–114
Engvall E, Wewer UM (1996) Domains of laminin. J Cell Biochem 61:493–501
Kleinman HK, Koblinski J, Lee S, Engbring J (2001) Role of basement membrane in tumor growth and metastasis. Surg Oncol Clin North Am 10:329–338
Terranova VP, Liotta LA, Russo RG, Martin GR (1982) Role of laminin in the attachment and metastasis of murine tumor cells. Cancer Res 42:2265–2269
Mercurio AM, Rabinovitz I, Shaw LM (2001) The alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and epithelial cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:541–545
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Herz, B. Glas and K. Rohrbach for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by a Rudolf-Virchow-Award from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and a grant from the Deutsche Krebshilfe to MPS (10-1765-Schö 1) and a Research grant from Sachsen-Anhalt to M.S. C.D., M.S., R.J.H., H.G. and M.P.S. are members of the Forschungszentrum Immunologie Sachsen-Anhalt (grant BMBF 01ZZ0110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drewniok, C., Wienrich, B.G., Schön, M. et al. Molecular interactions of B-CAM (basal-cell adhesion molecule) and laminin in epithelial skin cancer. Arch Dermatol Res 296, 59–66 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-004-0481-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-004-0481-4