Abstract
Introduction
Few studies evaluated clinical benefits of pre-operative templating in total hip arthroplasty (THA). We investigated whether mismatch between planned and real implant sizes and medio-lateral offsets compromises THA outcomes.
Materials and methods
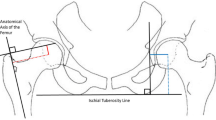
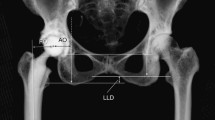
We reviewed records of 184 primary THAs with pre-operative CT scans used for templating. Acetabular offset (AO), femoral offset (FO) and global offset (GO) were measured on pre-operative CT scans, during acetate templating, and post-operative antero-posterior radiographs. Multivariable analyses were performed to determine if Forgotten Joint Score (FJS) and Oxford Hip Score (OHS) at > 2 years were associated with differences between post-operative and planned parameters.
Results
The FJS and OHS were not influenced by mismatch of component sizes nor of FO and GO. The FJS was better when the post-operative AO was greater than planned (p = 0.050). The FJS differed among arthritic types (p = 0.015). Multivariable analyses confirmed that older patients had better OHS (beta − 0.16; p = 0.033) and FJS (beta 0.74; p = 0.002), medialized hips had worse FJS (beta − 20.1; p = 0.041) and hips with greater AO than planned had better FJS (beta 1.71; p = 0.024)
Conclusions
Implanting a component of different size than planned did not compromise THA outcomes, but medialized hips had worse scores, and conservative acetabular reaming improved scores.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Della Valle AG, Padgett DE, Salvati EA (2005) Preoperative planning for primary total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 13(7):455–462
Shemesh SS, Robinson J, Keswani A, Bronson MJ, Moucha CS, Chen D (2017) The Accuracy of digital templating for primary total hip arthroplasty: is there a difference between direct anterior and posterior approaches? J Arthroplasty 32(6):1884–1889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2016.12.032
Shin JK, Son SM, Kim TW, Shin WC, Lee JS, Suh KT (2016) Accuracy and reliability of preoperative on-screen templating using digital radiographs for total hip arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis 28(4):201–207. https://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.201
Schmalzried TP (2005) Preoperative templating and biomechanics in total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics 28(8 Suppl):s849–s851
Gonzalez Della Valle A, Slullitel G, Piccaluga F, Salvati EA (2005) The precision and usefulness of preoperative planning for cemented and hybrid primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20(1):51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2004.04.016
Jolles BM, Zangger P, Leyvraz PF (2002) Factors predisposing to dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty: a multivariate analysis. J Arthroplasty 17(3):282–288
Biedermann R, Tonin A, Krismer M, Rachbauer F, Eibl G, Stockl B (2005) Reducing the risk of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: the effect of orientation of the acetabular component. J Bone Jt Surg Br 87(6):762–769. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.87B6.14745
Fottner A, Woiczinski M, Kistler M, Schroder C, Schmidutz TF, Jansson V, Schmidutz F (2017) Influence of undersized cementless hip stems on primary stability and strain distribution. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137(10):1435–1441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2784-x
Rudiger HA, Guillemin M, Latypova A, Terrier A (2017) Effect of changes of femoral offset on abductor and joint reaction forces in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137(11):1579–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2788-6
Petretta R, Strelzow J, Ohly NE, Misur P, Masri BA (2015) Acetate templating on digital images is more accurate than computer-based templating for total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 473(12):3752–3759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4321-y
Asayama I, Chamnongkich S, Simpson KJ, Kinsey TL, Mahoney OM (2005) Reconstructed hip joint position and abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20(4):414–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2004.01.016
Sakalkale DP, Sharkey PF, Eng K, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH (2001) Effect of femoral component offset on polyethylene wear in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 388:125–134
Liebs TR, Nasser L, Herzberg W, Ruther W, Hassenpflug J (2014) The influence of femoral offset on health-related quality of life after total hip replacement. Bone Jt J 96-B(1):36–42. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.96B1.31530
Cassidy KA, Noticewala MS, Macaulay W, Lee JH, Geller JA (2012) Effect of femoral offset on pain and function after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 27(10):1863–1869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2012.05.001
Hassani H, Cherix S, Ek ET, Rudiger HA (2014) Comparisons of preoperative three-dimensional planning and surgical reconstruction in primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 29(6):1273–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2013.12.033
Dastane M, Dorr LD, Tarwala R, Wan Z (2011) Hip offset in total hip arthroplasty: quantitative measurement with navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(2):429–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1554-7
Kumar PG, Kirmani SJ, Humberg H, Kavarthapu V, Li P (2009) Reproducibility and accuracy of templating uncemented THA with digital radiographic and digital TraumaCad templating software. Orthopedics 32(11):815. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20090922-08
Bertz A, Indrekvam K, Ahmed M, Englund E, Sayed-Noor AS (2012) Validity and reliability of preoperative templating in total hip arthroplasty using a digital templating system. Skeletal Radiol 41(10):1245–1249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-012-1431-4
Bono JV (2004) Digital templating in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am 86-A(Suppl 2):118–122
Crooijmans HJ, Laumen AM, van Pul C, van Mourik JB (2009) A new digital preoperative planning method for total hip arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(4):909–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0486-y
Gamble P, de Beer J, Petruccelli D, Winemaker M (2010) The accuracy of digital templating in uncemented total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 25(4):529–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2009.04.011
Della Valle AG, Comba F, Taveras N, Salvati EA (2008) The utility and precision of analogue and digital preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 32(3):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0317-2
Iorio R, Siegel J, Specht LM, Tilzey JF, Hartman A, Healy WL (2009) A comparison of acetate vs digital templating for preoperative planning of total hip arthroplasty: is digital templating accurate and safe? J Arthroplasty 24(2):175–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.019
Kosashvili Y, Shasha N, Olschewski E, Safir O, White L, Gross A, Backstein D (2009) Digital versus conventional templating techniques in preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Can J Surg 52(1):6–11
The B, Diercks RL, van Ooijen PM, van Horn JR (2005) Comparison of analog and digital preoperative planning in total hip and knee arthroplasties. A prospective study of 173 hips and 65 total knees. Acta Orthop 76(1):78–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016470510030364
Flecher X, Ollivier M, Argenson JN (2016) Lower limb length and offset in total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 102(1 Suppl):S9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2015.11.001
Ollivier M, Parratte S, Lecoz L, Flecher X, Argenson JN (2013) Relation between lower extremity alignment and proximal femur anatomy. Parameters during total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(5):493–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.02.006
Pasquier G, Ducharne G, Ali ES, Giraud F, Mouttet A, Durante E (2010) Total hip arthroplasty offset measurement: is CT scan the most accurate option? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 96(4):367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2010.02.006
Sariali E, Klouche S, Mouttet A, Pascal-Moussellard H (2014) The effect of femoral offset modification on gait after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 85(2):123–127. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453674.2014.889980
Sariali E, Mauprivez R, Khiami F, Pascal-Mousselard H, Catonne Y (2012) Accuracy of the preoperative planning for cementless total hip arthroplasty. A randomised comparison between three-dimensional computerised planning and conventional templating. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 98(2):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2011.09.023
Sariali E, Mouttet A, Pasquier G, Durante E, Catone Y (2009) Accuracy of reconstruction of the hip using computerised three-dimensional pre-operative planning and a cementless modular neck. J Bone Jt Surg Br 91(3):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.91B3.21390
Inoue D, Kabata T, Maeda T, Kajino Y, Fujita K, Hasegawa K, Yamamoto T, Tsuchiya H (2015) Value of computed tomography-based three-dimensional surgical preoperative planning software in total hip arthroplasty with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Orthop Sci 20(2):340–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-014-0683-3
Liu YP, Hao YD (2014) Restoration of femoral offset, rotation centers, limbs length equality of Chinese total hip arthroplasty patients. Pak J Med Sci 30(1):116–121. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.301.3635
Mahmood SS, Mukka SS, Crnalic S, Wretenberg P, Sayed-Noor AS (2016) Association between changes in global femoral offset after total hip arthroplasty and function, quality of life, and abductor muscle strength. A prospective cohort study of 222 patients. Acta Orthop 87(1):36–41. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453674.2015.1091955
Kase M, O'Loughlin PF, Ait-Si-Selmi T, Pagenstert G, Langlois J, Bothorel H, Bonnin MP (2019) Pre-operative templating in THA. Part I: a classification of architectural hip deformities. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 140:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-019-03298-1
Kobayashi H, Cech A, Kase M, Pagenstert G, Carrillon G, O'Loughlin PF, Bothorel H, Ait-Si-Selmi T, Bonnin MP (2019) Pre-operative templating in THA. Part II: a CT-based strategy to correct architectural hip deformities. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 140:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-019-03298-1
Bonnin MP, Neto CC, Aitsiselmi T, Murphy CG, Bossard N, Roche S (2015) Increased incidence of femoral fractures in small femurs and women undergoing uncemented total hip arthroplasty—why? Bone Jt J 97-B(6):741–748. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.97B6.35022
Murphy CG, Bonnin MP, Desbiolles AH, Carrillon Y, Aїt Si Selmi T (2016) Varus will have varus; a radiological study to assess and predict varus stem placement in uncemented femoral stems. Hip Int 26(6):554–560. https://doi.org/10.5301/hipint.5000412
Bonnin MP, Archbold PH, Basiglini L, Fessy MH, Beverland DE (2012) Do we medialise the hip centre of rotation in total hip arthroplasty? Influence of acetabular offset and surgical technique. Hip Int 22(4):371–378. https://doi.org/10.5301/HIP.2012.9350
Meermans G, Doorn JV, Kats JJ (2016) Restoration of the centre of rotation in primary total hip arthroplasty: the influence of acetabular floor depth and reaming technique. Bone Jt J 98-B(12):1597–1603. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B12.BJJ-2016-0345.R1
Khanuja HS, Vakil JJ, Goddard MS, Mont MA (2011) Cementless femoral fixation in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Am 93(5):500–509. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.00774
Behrend H, Giesinger K, Giesinger JM, Kuster MS (2012) The "forgotten joint" as the ultimate goal in joint arthroplasty: validation of a new patient-reported outcome measure. J Arthroplasty 27(3):430–436e431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.06.035
Delaunay C, Epinette JA, Dawson J, Murray D, Jolles BM (2009) Cross-cultural adaptations of the Oxford-12 HIP score to the French speaking population. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 95(2):89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2009.01.003
Baghdadi YM, Larson AN, Sierra RJ (2013) Restoration of the hip center during THA performed for protrusio acetabuli is associated with better implant survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(10):3251–3259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3072-x
Bonnin MP, Archbold PH, Basiglini L, Selmi TA, Beverland DE (2011) Should the acetabular cup be medialised in total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int 21(4):428–435. https://doi.org/10.5301/HIP.2011.8582
Terrier A, Levrero Florencio F, Rudiger HA (2014) Benefit of cup medialization in total hip arthroplasty is associated with femoral anatomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(10):3159–3165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3787-3
Terrier A, Parvex V, Rudiger HA (2016) Impact of individual anatomy on the benefit of cup medialisation in total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int 26(6):537–542. https://doi.org/10.5301/hipint.5000392
Tezuka T, Inaba Y, Kobayashi N, Ike H, Kubota S, Kawamura M, Saito T (2015) Effects of hip joint center location and femoral offset on abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. Mod Rheumatol 25(4):630–636. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2014.988863
Delp SL, Maloney W (1993) Effects of hip center location on the moment-generating capacity of the muscles. J Biomech 26(4–5):485–499
Delp SL, Wixson RL, Komattu AV, Kocmond JH (1996) How superior placement of the joint center in hip arthroplasty affects the abductor muscles. Clin Orthop Relat Res 328:137–146
Doehring TC, Rubash HE, Dore DE (1999) Micromotion measurements with hip center and modular neck length alterations. Clin Orthop Relat Res 362:230–239
Doehring TC, Rubash HE, Shelley FJ, Schwendeman LJ, Donaldson TK, Navalgund YA (1996) Effect of superior and superolateral relocations of the hip center on hip joint forces. An experimental and analytical analysis. J Arthroplasty 11(6):693–703
Miles AW, McNamee PB (1989) Strain gauge and photoelastic evaluation of the load transfer in the pelvis in total hip replacement: the effect of the position of the axis of rotation. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 203(2):103–107. https://doi.org/10.1243/PIME_PROC_1989_203_018_01
Little NJ, Busch CA, Gallagher JA, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB (2009) Acetabular polyethylene wear and acetabular inclination and femoral offset. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(11):2895–2900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-0845-3
Ji HM, Won SH, Han J, Won YY (2017) Does femoral offset recover and affect the functional outcome of patients with displaced femoral neck fracture following hemiarthroplasty? Injury 48(6):1170–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.03.022
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Mr. Mo Saffarini for his assistance with manuscript preparation and illustrations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors AC, MK, HK, YC, PFOL, and HB declare that they have no conflict of interest. TASS receives royalties and or consulting fees from DePuy-Synthes, Symbios, and Corin-Tornier. MPB receives royalties and or consulting fees from DePuy-Synthes, Symbios, Corin-Tornier, Wright-Tornier, and Integra.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board (IRB) who approved this study in advance (COS- RGDS-2019-05-005-BONNIN-M) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cech, A., Kase, M., Kobayashi, H. et al. Pre-operative planning in THA. Part III: do implant size prediction and offset restoration influence functional outcomes after THA?. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 140, 563–573 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03342-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-020-03342-5