Abstract
Purpose
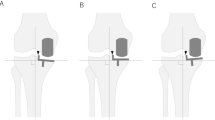
The medial border of the tibial tubercle (MBTT) is one of the fixed anatomic landmarks for tibial component setting during total knee arthroplasty (TKA). In mobile-bearing TKA using a tibial cut first technique, the final tibial component rotation can be guided by the position it achieves following several flexion–extension cycles. In this study, tibial component angle (TCA) and tibial rotational angle (TRA) were determined in dependence of retention or resection of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Methods
The TCA and TRA were examined in 206 patients who underwent primary TKA (PCL retaining: 104 knees, PCL substituting: 102 knees). The tibial component rotation was intraoperatively setting between the parallel to the axis of the most medial aspect of the tibial tubercle as the anterior anatomic landmark and the center of the tibial component as the posterior landmark at the maximum coverage with the osteotomized tibial plateau with its adjustment after several knee flexion–extension exercises. A postoperative quantitative three-dimensional computed tomography technique was used for measurements by a single observer.
Results
The TCA showed a divergence of 0.21° external to the MBTT in the PCL-retaining design and 1.62° internal divergence in the PCL-substituting design. The TRA showed an internal divergence of 0.88° in the PCL-retaining design and an internal divergence of 2.12° in the PCL-substituting design. There were no significant differences between the two designs.
Conclusions
The MBTT might be regarded as a reliable landmark for obtaining an acceptable tibial rotational setting in mobile-bearing TKA despite PCL retention.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puloski SK, McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB (2001) Tibial post wear in posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. An unrecognized source of polyethylene debris. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:390–397
Westrich GH, Laskin RS, Haas SB, Sculco TP (1994) Resection specimen analysis of tibial coverage in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 309:163–175
Merkow RL, Soundry M, Insall JN (1985) Patellar dislocation following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67:1321–1327
Insall JN, Easley ME (2001) Surgical techniques and instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. In: Insall JN, Scott WN (eds) Surgery of the knee, 3rd edn. Churchill-Livingstone, New York, pp 1553–1620
Dalury DF, Jiranek W, Pierson J, Pearson SE (2003) The long-term outcome of total knee patients with moderate loss of motion. J Knee Surg 16:215–220
Insall JN (1993) Surgical techniques and instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. In: Insall JN, Windsor RE, Scott WN, Kelly M, Aglietti P (eds) Surgery of the knee, 2nd edn. Churchill-Livingstone, New York, pp 739–804
Matsui Y, Kadoya Y, Uehara K, Kobayashi A, Takaoka K (2005) Rotational deformity in varus osteoarthritis of the knee: analysis with computed tomography. Clin Orthop Relat Res 433:147–151
Matziolis G, Krocker D, Weiss U, Tohtz S, Perka C (2007) A prospective, randomized study of computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty. Three-dimensional evaluation of implant alignment and rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:236–243
Uehara K, Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Ohashi H, Yamano Y (2002) Bone anatomy and rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 402:196–201
Aglietti P, Sensi L, Cuomo P, Ciardullo A (2008) Rotational position of femoral and tibial components in TKA using the femoral transepicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2751–2755
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Ikeuchi M, Yamanaka N, Okanoue Y, Ueta E, Tani T (2007) Determining the rotational alignment of the tibial component at total knee replacement: a comparison of two techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:45–49
Kawahara S, Matsuda S, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Mitsuyasu H, Nakahara H, Iwamoto Y (2012) Relationship between the tibial anteroposterior axis and the surgical epicondylar axis in varus and valgus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:2077–2081
Moreland JR (1988) Mechanism of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:49–64
Eckhoff DG, Metzger RJ, Stamm ER, Kilcoyne RE, Wiedel JD (1994) Version of osteoarthritic knee. J Arthroplasty 9:73–79
Yoshioka K, Siu DW, Scudamore RA, Cooke TD (1989) Tibial anatomy and functional axes. J Orthop Res 7:132–137
Sahin N, Atıcı T, Kurtoğlu Ü, Turgut A, Ozkaya G, Ozkan Y (2013) Centre of the posterior cruciate ligament and the sulcus between tubercle spines are reliable landmarks for tibial component placement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2384–2391
Hutter EE, Granger JF, Beal MD, Siston RA (2013) Is there a gold standard for TKA tibial component rotational alignment? Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:1646–1653
Nagamine R, Miyanishi K, Miura H, Urabe K, Matsuda S, Iwamoto Y (2003) Medial torsion of the tibia in Japanese patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 408:218–224
Lützner J, Krummenauer F, Günther KP, Kirschner S (2010) Rotational alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty is better at the medial third of tibial tuberosity than at the medial border. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:57
Ishii Y, Terajima K, Koga Y, Bechtold JE (1999) Screw home motion after total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 358:181–187
Mikashima Y, Ishii Y, Takeda M, Noguchi H, Momohara S, Banks SA (2013) Does mobile-bearing knee arthroplasty motion change with activity? Knee 20:422–425
Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Takeda M, Ishii H, Toyabe S (2011) Changes in the medial and lateral posterior condylar offset in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 26:255–259
Sato T, Koga Y, Omori G (2004) Three-dimensional lower extremity alignment assessment system: application to evaluation of component positioning after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 19:620–628
Sato T, Koga Y, Sobue T, Omori G, Tanabe Y, Sakamoto M (2007) Quantitative 3-dimensional analysis of preoperative and postoperative joint lines in total knee arthroplasty: a new concept for evaluation of component alignment. J Arthroplasty 22:560–568
Ariumi A, Sato T, Kobayashi K, Koga Y, Omori G, Minato I, Endo N (2010) Three-dimensional lower extremity alignment in the weight-bearing standing position in healthy elderly subjects. J Orthop Sci 15:64–70
Kobayashi K, Sakamoto M, Tanabe Y, Ariumi A, Sato T, Omori G, Koga Y (2009) Automated image registration for assessing three-dimensional alignment of entire lower extremity and implant position using bi-plane radiography. J Biomech 42:2818–2822
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:40–47
Churchill DL, Incavo SL, Johnson CC, Beynnon BD (1998) The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:111–118
Mantas JP, Bloebaum RD, Skedros JG, Hofmann AA (1992) Implications of reference axes used for rotational alignment of the femoral component in primary and revision knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 7:531–535
Siston RA, Goodman Patel JJ, Delp SL, Giori NJ (2006) The high variety of tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Ortho Relat Res 452:65–69
Eckhoff DG, Metzger RG, Vandewalle MV (1995) Malrotation associated with implant alignment technique in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 321:28–31
Banks SA, Hodge WA (2004) Implant design affects knee arthroplasty kinematics during stair-stepping. Clin Orthop Relat Res 426:187–193
Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Mahfouz MR, Outten JT, Sharma A (2005) Mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: do the polyethylene bearings rotate? Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:88–95
Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Matsuda Y, Takeda M, Walker SA, Komistek RD (2007) Effect of knee laxity on in vivo kinematics of meniscal-bearing knee prostheses. Knee 14:269–274
Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Mahfouz MR, Walker S, Outten J (2004) In vivo polyethylene bearing mobility is maintained in posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:207–213
Stiehl JB, Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Crane HS (1999) In vivo determination of condylar lift-off and screw-home in a mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 14:293–299
Dalury DF (2001) Observations of the proximal tibia in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:150–155
Kawahara S, Okazaki K, Matsuda S, Mitsuyasu H, Nakahara H, Okamoto S, Iwamoto Y (2014) Medial sixth of the patellar tendon at the tibial attachment is useful for the anterior reference in rotational alignment of the tibial component. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:1070–1075
Graw BP, Harris AH, Tripuraneni KR, Giori NJ (2010) Rotational references for total knee arthroplasty tibial components change with level of resection. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:2734–2738
Huddleston JI, Scott RD, Wimberley DW (2005) Determination of neutral tibial rotational alignment in rotational rotating platform TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:101–106
Cates HE, Komistek RD, Mahfouz MR, Schmidt MA, Anderle M (2008) In vivo comparison of knee kinematics for subjects having either a posterior stabilized or cruciate retaining high-flexion total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 23:1057–1067
Ishii Y, Terajima K, Koga Y, Takahashi HE, Bechtold JE (1996) Influence of total knee replacement design on screw home movement: comparison of five designs for total knee replacement prostheses. J Orthop Sci 1:313–317
Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Takeda M, Sato J, Toyabe S (2011) Prediction of range of motion 2 years after mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: PCL-retaining versus PCL-sacrificing. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:2002–2008
Incavo SJ, Ronchetti PJ, Howe JG, Tranowski JP (1994) Tibial plateau coverage in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:81–85
Westrich GH, Laskin RS, Haas SB, Sculco TP (1994) Resection specimen analysis of tibial coverage in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 309:163–175
Martin S, Saurez A, Ismaily S, Ashfaq K, Noble P, Incavo SJ (2014) Maximizing tibial coverage is detrimental to proper rotational alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:121–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No benefit or funds were received in support of the study.
Additional information
The present work was performed at the Ishii Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Clinic, 1089 Shimo-Oshi, Gyoda, Saitama 361-0037, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishii, Y., Noguchi, H., Sato, J. et al. Rotational alignment of tibial components in mobile-bearing TKA: posterior substituted vs. PCL retaining. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 135, 1299–1305 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-015-2275-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-015-2275-x