Abstract
Background
Various landmarks can guide tibial component rotational alignment in routine TKA, but with the deeper tibial resection levels common in complex primary and revision TKAs, it is unknown whether these landmarks remain reliable.
Questions/purposes
We asked whether three techniques for determining tibial component rotation based on local anatomic landmarks are reliable deeper tibial resection levels.
Patients and Methods
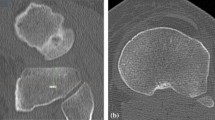
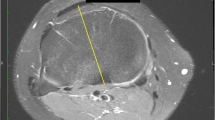
The femoral transepicondylar axis was identified by three independent reviewers on MR images of knees from 24 men and 24 women and transposed at a traditional tibial resection level and at the level of the proximal, middle, and distal parts of the proximal tibiofibular joint. Three axes were drawn on axial slices at these levels: the geometric center of the tibial plateau to the medial 1/3 of the tubercle, the posterior condylar line of the tibia, and the largest mediolateral dimension of the tibia. These lines were compared with the transposed femoral epicondylar axis line.
Results
The posterior condylar line of the tibia is the least variable local landmark for tibial component positioning at deep resection levels.
Conclusions
Assuming the normal posterior condylar line of the tibia is visible at revision, setting the tibial component at 10° external rotation with respect to the posterior condylar axis of the tibia gets the tibial component within 10° of proper rotation in 86% to 98% of patients, even to the distal part of the proximal tibiofibular joint. The experienced surgeon then can adjust this position based on cues from an assortment of other axes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C. Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;436:172–176.
Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T, Tsujimoto H, Asano T, Hamanishi C. An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;420:213–219.
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;356:144–153.
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS. Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;286:40–47.
Chowdhury EA, Porter ML. A study of the effect of tibial tray rotation on a specific mobile bearing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:793–797.
Dalury DF. Observations of the proximal tibia in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;389:150–155.
Incavo SJ, Coughlin KM, Pappas C, Beynnon BD. Anatomic rotational relationships of the proximal tibia, distal femur, and patella: implications for rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18:643–648.
Incavo SJ, Wild JJ, Coughlin KM, Beynnon BD. Early revision for component malrotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 458:131–136.
Moreland JR. Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;226:49–64.
Nagamine R, Whiteside LA, White SE, McCarthy DS. Patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty: the effect of tibial tray malrotation and articular surface configuration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;304:262–271.
Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH, Shastri S, Jacoby SM. Insall Award paper: Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;404:7–13.
Siston RA, Cromie MJ, Gold GE, Goodman SB, Delp SL, Maloney WJ, Giori NJ. Averaging different alignment axes improves femoral rotational alignment in computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:2098–2104.
Siston RA, Goodman SB, Patel JJ, Delp SL, Giori NJ. The high variability of tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;452:65–69.
Uehara K, Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Ohashi H, Yamano Y. Bone anatomy and rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;402:196–201.
Whiteside LA, Arima J. The anteroposterior axis for femoral rotational alignment in valgus total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;321:168–172.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
This work was performed at the VA Palo Alto Healthcare System.
About this article
Cite this article
Graw, B.P., Harris, A.H., Tripuraneni, K.R. et al. Rotational References for Total Knee Arthroplasty Tibial Components Change with Level of Resection. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 2734–2738 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1330-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1330-8