Abstract
Purpose/introduction
Urinary incontinence (UI) affects some 20 % of community-dwelling older people and 30–60 % of people in institutional care. UI is known as an independent predictor of falls, and likely impacts fracture rates. The aim of the study was to measure the prevalence of UI in a typical fragility fracture population, to evaluate the relationship of UI with functional disability in the post-acute setting.
Methods
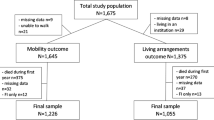
Our study is a retrospective cross-sectional study of patients admitted to rehabilitation setting after inpatient hospital management for a fragility fracture. We included all consecutively admitted fragility fracture patients aged over 65. All patients underwent standard clinical examination and Geriatric Assessment. We assessed UI using a two-stage process with a six-item UI screening questionnaire followed by an interview.
Results
1,857 (80.7 % female) patients were available for analysis, mean age was 81.7 years. UI was identified in 59.2 % of all fragility fracture patients, and was more prevalent in females. Patients suffering from UI differed significantly in almost all measured functional and cognitive tests, with increased dependency/lower ADL scores, increased rates of immobility, and higher rates of cognitive dysfunction and depression.
Conclusion
This study confirms the high prevalence of UI in older fragility fracture patients, and the association between UI and functional impairments. The diagnostic work-up and treatment of patients should be focused on the special needs of these older patients. More efforts are needed to increase awareness about prevalence and consequences of UI among older fragility fracture patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leung F, Blauth M, Bavonratanavech S (2010) Surgery for fragility hip fracture—streamlining the process. Osteoporos Int 21(Suppl 4):519–521
Elliott J, Beringer T, Kee F, Marsh D, Willis C, Stevenson M (2003) Predicting survival after treatment for fracture of the proximal femur and the effect of delays to surgery. J Clin Epidemio 56(8):788–795
Marks R (2011) Physical activity and hip fracture disability: a review. J Aging Res 741918
Thomas TM, Plymat KR, Blannin J et al (1980) Prevalence of urinary incontinence. Br Med J 281:1243–1245
Perry S, Shaw C, Assassa P et al (2000) An epidemiological study to establish the prevalence of urinary symptoms and felt need in the community: the leicestershire MRC Incontinence Study. J Public Health Med 22:427–434
Peet SM, Castleden SM, McGrother CW (1995) Prevalence of urinary and facial incontinence in hospitals and residential and nursing homes for older people. Br Med J 311:1063–1064
Dugan E, Roberts CP, Cohen SJ et al (2001) Why older community-dwelling adults do not discuss urinary incontinence with their primary physicians. J Am Geriatr Soc 49:462–465
Wagg AS, Malone-Lee JG (1998) Urinary incontinence in the elderly. Br J Urol 82(Suppl. 1):11–17
Teunissen TA, de Jong A, van Weel C et al (2004) Treating urinary incontinence in the elderly—conservative therapies that work: a systematic review. J Fam Pract 53:25–32
Burgio K, Locher JL, Goode PS (2000) Combined behavioural and drug therapy for urge incontinence in older women. J Am Geriatr Soc 48:370–374
Rubenstein LZ (2006) Falls in older people: epidemiology, risk factors and strategies for prevention. Age Ageing 35(S2):ii37–ii41
Sattin RW, Lambert Huber DA, DeVito CA et al (1990) The incidence of fall injury events among the elderly in a defined population. Am J Epidemiol 131:1028–1037
Stalenhoef PA, Cremholder HFJM, Knottnerus JA, van der Horst FGEM (1997) Incidence, risk factors and consequences of falls among elderly subjects living in the community. Eur J Public Health 7:328334
Chiarelli PE, Mackenzie LA, Osmotherly PG (2009) Urinary incontinence is associated with an increase in falls: a systematic review. Aust J Physiother 55:89–95
Delbaere K, Close JCT, Menz HB et al (2008) Development and validation of fall risk screening tools fort he use in residential aged care facilities. MJA 189:193–196
Dubeau CE, Kuchel GA, Johnson T et al (2010) Incontinence in frail elderly: report from the 4th international consultation. Neurourol Urodyn 29:165–178
Ouslander JG, Johnson TM (1999) Inconetinence. In: Hazzard WR, Blass JP, Ettinger WH et al (eds). Principles of geriatric medicine and gerontology, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1595–1613
Goode PS, Burgio KL, Richter HE et al (2010) Incontinence in older women. JAMA 303:2172–2181
Fung C, Spencer B, Eslami M et al (2007) Quality indicators for the screening and care of urinary incontinence in vulnerable elders. J Am Geriatr Soc 55:443–449
Woodford H, George J (2007) NICE guidelines on urinary incontinence in women. Age Ageing 36:49–50
Ellis G, Langhorne P (2004) Comprehensive geriatric assessment for older hospital patients. Br Med Bull 71:45–59
Bogoch ER, Elliot-Gibson V, Beaton DE, Jamal SA, Josse RG, Murray TM (2006) Effective initiation of osteoporosis diagnosis and treatment for patients with a fragility fracture in an orthopaedic environment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(1):25–34
Talasz H, Jansen SC, Kofler M, Lechleitner M (2012) High prevalence of pelvic floor muscle dysfunction in hospitalized elderly women with urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J 23(9):1231–1237
Bright E, Cotterill N, Drake M, Abrams P (2014) Developing and validating the international consultation on incontinence questionnaire bladder diary. Eur Urol 66(2):294–300
Khandelwal C, Kistler C (2013) Diagnosis of Urinary Incontinence. Ann Fam Physician 87(8):543–550
Pils K, Umek W (2014). Harninkontinenz der älteren Frau, Leitfaden für Abklärung und Therapie,Urinary incontinence, Guideline for diagnosis and treatment, Facultas, ISBN 978-3-7089-1141-0, S 10
Abrams P, Andersson KE, Birder L, Brubaker L, Cardozo L, Chapple C, Cottenden A, Davila W, de Ridder D, Dmochowski R, Drake M, Dubeau C, Fry C, Hanno P, Smith JH, Herschorn S, Hosker G, Kelleher C, Koelbl H, Khoury S, Madoff R, Milsom I, Moore K, Newman D, Nitti V, Norton C, Nygaard I, Payne C, Smith A, Staskin D, Tekgul S, Thuroff J, Tubaro A, Vodusek D, Wein A, Wyndaele JJ, Members of Committees, Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence (2010) Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and fecal incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 29(1):213–240
Sorbye LW, Grue EV (2013) Hip fracture and urinary incontinence—use of indwelling catheter postsurgery. Scand J Caring Sci 27:632–642
Mahoney FI, Barthel DW (1965) Functional evaluation: the Barthel index. Md State Med J. 14:61–65
Bryant DM, Sanders DW, Coles CP, Petrisor BA, Jeray KJ, Laflamme GY (2009) Selection of outcome measures for patients with hip fracture. J Orthop Trauma 23(6):434–441
Kasner SE (2006) Clinical interpretation and use of stroke scales. Lancet Neurol 5(7):603–612
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR et al (1975) „Mini-mental state“: a practical method for grading the cognitive status of patients for the clinicians. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL et al (1982) Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. J Psychiatr Res 17:37–49
Podsiadlo D, Richardson S (1991) The timed “up and go”: a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 39:142–148
Visser M, Kritchevsky SB, Goodpaster BH et al (2002) Leg muscle mass and composition in relation to lower extremity performance in men and women aged 70 to 79: the health, aging and boy composition study. J Am Geriatr Soc 50:897–904
Cruz-jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM et al (2010) Report of the European working group on sarcopenia in older people. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 39:412–423
Guigoz Y, Garry JP (1994) Mini nutritional assessment: A practical assessment tool for grading the nutritional state of elderly patients. Facts Res Gerontol. pp 15–59
Palmer MH, Baumgarten M, Langenberg P, Carson JL (2002) Risk factors for hospital-acquired incontinence in elderly female hip fracture patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 57(10):M672–M677
Klausner AP, Vapnek JM (2003) Urinary incontinence in the geriatric population. Mt Sinai J Med 70(1):54–61 (review)
Landi F, Cesari M, Russo A, Onder G, Lattanzio F, Bernabei R, Silvernet-HC Study Group (2003) Potentially reversible risk factors and urinary incontinence in frail older people living in community. Age Ageing 32(2):194–199
Kwong PW, Cumming RG, Chan L, Seibel MJ, Naganathan V, Creasey H, Le Couteur D, Waite LM, Sambrook PN, Handelsman D (2010) Urinary incontinence and quality of life among older community-dwelling Australian men: the CHAMP study. Age Ageing 39(3):349–354
Bliuc D, Nguyen TV, Eisman JA, Center JR (2014) The impact of nonhip nonvertebral fractures in elderly women and men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99(2):415–423
Kammerlander C, Riedmüller P, Gosch M, Zegg M, Kammerlander-Knauer U, Schmid R, Roth T (2012) Functional outcome and mortality in geriatric distal femoral fractures. Injury 43(7):1096–1101
Gibson W, Wagg A (2014) New horizons: urinary incontinence in older people. Age Ageing 43(2):157–163
Min LC, Reuben DB, Adams J, Shekelle PG, Ganz DA, Roth CP, Wenger NS (2011) Does better quality of care for falls and urinary incontinence result in better participant-reported outcomes? J Am Geriatr Soc 59(8):1435–1443
Thüroff JW, Abrams P, Andersson KE et al (2011) EAU guidelines on urinary incontinence. Eur Urol 59:387–400
Scheife R, Takeda M (2005) Central nervous system safety of anticholinergic drugs for the treatment of overactive bladder in the elderly. Clin Ther 27(2):144–153
Salahudeen MS, Duffull SB, Nishtala PS (2014) Impact of anticholinergic discontinuation on cognitive outcomes in older people: a systematic review. Drugs Aging 31(3):185–192
Schnelle JF, Leung FW, Rao SS, Beuscher L, Keeler E, Clift JW, Simmons S (2010) A controlled trial of an intervention to improve urinary and fecal incontinence and constipation. J Am Geriatr Soc 58(8):1504–1511
Palmer MH, Baumgarten M, Langenberg P, Carson JL (2002) Risk factors for hospital-acquired incontinence in elderly female hip fracture patients. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 57(10):M672–M677
Inelmen EM, Sergi G, Enzi G (2007) When are indwelling urinary catheters appropriate in elderly patients? Geriatrics 62(10):18–22
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gosch, M., Talasz, H., Nicholas, J.A. et al. Urinary incontinence and poor functional status in fragility fracture patients: an underrecognized and underappreciated association. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 135, 59–67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2113-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2113-6