Abstract
Background
LCP-DF (locking compression plate-distal femur) has been introduced as an anatomically pre-shaped plate that does not require further contouring. However, the LCP-DF was developed based on skeletal measurements in Caucasians. It is unknown whether the LCP-DF fits Asians.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to assess the conformity of the LCP-DF in Asian adult femurs and also to determine the matching pattern of this anatomically pre-shaped LCP-DF in normal Asian adult femurs and the clinical implications of the matching pattern.
Methods
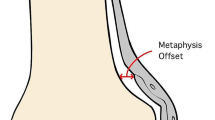
Sixty adult cadaver femurs were obtained from 41 male and 19 female cadavers with an average age of 63 years (31–95). An 11-hole LCP-DF was applied to the lateral surface of the distal femur according to the contour. Any mismatches between the bone and the plate were recorded. Then the distance from the inner surface of the plate to the cortex was measured at the sites of mismatch. C-arm AP image of the distal femur was taken and the angle between the distal most locking screw and the joint line was measured, and it was named as joint screw angle (JSA).
Results
Mismatch was found at the level of proximal 4–5 holes of the plate with an average distance of 11.36 mm (range 0–32 mm) at the tip of the plate. Otherwise, the overall conformity of the LCP-DF was good. The average JSA was 2.15 ± 1.78° (ranged from 0° to 5°).
Conclusion
A rather consistent pattern of mismatch was found at the proximal part of the 11-hole LCP-DF. An attempt to fit the plate to the bone at this level may cause valgus malalignment at the fracture site.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ (2004) Treatment of proximal tibia fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 77 fractures. J Orthop Trauma 18:528–535
Ricci AR, Yue JJ, Taffet R, Catalano JB, DeFalco RA, Wilkens KJ (2004) Less invasive stabilization system for treatment of distal femur fractures. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 33:250–255
Kregor PJ, Stannard J, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA, Alonso J (2001) Distal femoral fracture fixation utilizing the Less Invasive Stabilization System (L.I.S.S.): the technique and early results. Injury 32(Suppl 3):SC32–SC47
Kregor PJ, Stannard JA, Zlowodzki M, Cole PA (2004) Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 103 fractures. J Orthop Trauma 18:509–520
Schutz M, Muller M, Regazzoni P, Hontzsch D, Krettek C, Van der Werken C, Haas N (2005) Use of the less invasive stabilization system (LISS) in patients with distal femoral (AO33) fractures: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 125:102–108
Weight M, Collinge C (2004) Early results of the less invasive stabilization system for mechanically unstable fractures of the distal femur (AO/OTA types A2, A3, C2, and C3). J Orthop Trauma 18:503–508
Frigg R (2003) Development of the locking compression plate. Injury 34(Suppl 2):B6–B10
Frigg R, Appenzeller A, Christensen R, Frenk A, Gilbert S, Schavan R (2001) The development of the distal femur Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Injury 32(Suppl 3):SC24–SC31
Leung KS, Procter P, Robioneck B, Behrens K (1996) Geometric mismatch of the Gamma nail to the Chinese femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res:42-48
Hak DJ, Stewart RL, Lee M (2004) Preliminary stabilization of the less invasive stabilization system. J Orthop Trauma 18:559–561
Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, Bertram R, Holmes W, Tscherne H (1997) Transarticular joint reconstruction and indirect plate osteosynthesis for complex distal supracondylar femoral fractures. Injury 28(Suppl 1):A31–A41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, JH., Oh, JK., Oh, CW. et al. Mismatch of anatomically pre-shaped locking plate on asian femurs could lead to malalignment in the minimally invasive plating of distal femoral fractures: a cadaveric study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132, 51–56 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1375-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1375-5