Abstract
Introduction
Reverse distal femoral locking compression plates (DF-LCP) have been used as an alternative treatment in complex proximal femur fractures.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to assess the compatibility of reverse DF-LCP with Asian proximal femurs, to determine the matching patterns and integrate information to establish guidelines for correct application.
Methods
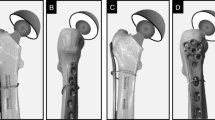
Twenty-eight adult cadaveric femurs were obtained from 5 males and 9 females with an average age of 69.27 years (range 59–85). A contralateral 13-hole DF-LCP was applied with MIPO technique using the vastus ridge as a landmark for Hole A. The first locking screw was inserted through Hole A under fluoroscopic guidance just above the femoral head–neck junction in AP view and centered of the neck in lateral view, followed by three proximal locking screws. The number of screws successfully inserted through the femoral neck, including any penetration of femoral neck, the gap between anterior and posterior borders between plate and bone, the anatomical parameters of proximal femur, and any mismatches between the plate and the bone were recorded.
Results
Most of the screws (82.1%) in Holes A, D, E, and F were put into the femoral neck without breaking through. The average distance from the entry point at the vastus ridge to the anterior cortex of the femur was 17.3 ± 2.3 mm and from the posterior cortex was 19.46 ± 2.55 mm. The anterior gap was 4.93 ± 1.01 mm, and the posterior gap was 13.48 ± 1.44 mm. The mismatch where the distal part of the plate started to lift off from the bone > 2 mm at the 8th hole with an average distance of 2.78 ± 2.01 mm. That distance gradually increased distally to an average of 9.38 ± 6.03 mm at the 13th hole.
Conclusions
Reverse DF-LCP can fit most proximal femurs in the Asian population and can be used as an alternative implant when performed using an appropriate technique. However, as a relatively consistent mismatch was found at the distal part starting at the 8th hole, so if a plate is longer than 9 holes, the plate contouring should be considered.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haq RU, Manhas V, Pankaj A, Srivastava A, Dhammi IK, Jain AK (2014) Proximal femoral nails compared with reverse distal femoral locking plates in intertrochanteric fractures with a compromised lateral wall; a randomised controlled trial. Int Orthop 38(7):1443–1449
Ma KL, Wang X, Luan FJ, Xu HT, Fang Y, Min J et al (2014) Proximal femoral nails antirotation, gamma nails, and dynamic hip screws for fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of femur: a meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 100(8):859–866
Glassner PJ, Tejwani NC (2011) Failure of proximal femoral locking compression plate: a case series. J Orthop Trauma 25(2):76–83
Wieser K, Babst R (2010) Fixation failure of the LCP proximal femoral plate 4.5/5.0 in patients with missing posteromedial support in unstable per-, inter-, and subtrochanteric fractures of the proximal femur. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130(10):1281–1287
Streubel PN, Moustoukas MJ, Obremskey WT (2013) Mechanical failure after locking plate fixation of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2013(27):22–8
Hodel S, Beeres FJP, Babst R, Link BC (2017) Complications following proximal femoral locking compression plating in unstable proximal femur fractures: medium-term follow-up. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 27(8):1117–1124
Shah MD, Kapoor CS, Soni RJ, Patwa JJ, Golwala PP (2017) Evaluation of outcome of proximal femur locking compression plate (PFLCP) in unstable proximal femur fractures. J Clin Orthop Trauma 8(4):308–312
Glassner PJ, MaNCT MD (2011) Failure of proximal femoral locking compression plate: a case series. J Clin Orthop Trauma 25:76–83
Wirtz C, Abbassi F, Evangelopoulos DS, Kohl S, Siebenrock KA, Kruger A (2013) High failure rate of trochanteric fracture osteosynthesis with proximal femoral locking compression plate. Injury 44(6):751–756
Johnson B, Stevenson J, Chamma R, Patel A, Rhee SJ, Lever C et al (2014) Short-term follow-up of pertrochanteric fractures treated using the proximal femoral locking plate. J Orthop Trauma 28(5):283–287
Collinge CA, Hymes R, Archdeacon M, Streubel P, Obremskey W, Weber T et al (2016) Unstable proximal femur fractures treated with proximal femoral locking plates: a retrospective, multicenter study of 111 cases. J Orthop Trauma 30(9):489–495
Streubel PN, Moustoukas MJ, Obremskey WT (2013) Mechanical failure after locking plate fixation of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 27(1):22–28
Pryce Lewis JR, Ashcroft GP (2007) Reverse LISS plating for proximal segmental femoral fractures in the polytrauma patient: a case report. Injury 38(2):235–239
Acklin YP, Bereiter H, Sommer C (2010) Reversed LISS-DF in selected cases of complex proximal femur fractures. Injury 41(4):427–429
Ma CH, Tu YK, Yu SW, Yen CY, Yeh JH, Wu CH (2010) Reverse LISS plates for unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury 41(8):827–833
Zhang CQ, Sun Y, Jin DX, Yao C, Chen SB, Zeng BF (2010) Reverse LISS plating for intertrochanteric hip fractures in elderly patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:166
Ehlinger M, Brinkert D, Besse J, Adam P, Arlettaz Y, Bonnomet F (2011) Reversed anatomic distal femur locking plate for periprosthetic hip fracture fixation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97(5):560–564
Zhou F, Zhang ZS, Yang H, Tian Y, Ji HQ, Guo Y et al (2012) Less invasive stabilization system (LISS) versus proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) in treating proximal femoral fractures: a prospective randomized study. J Orthop Trauma 26(3):155–162
Gogna P, Mukhopadhyay R, Singh A, Devgan A, Arora S, Batra A et al (2015) Contralateral reversed distal femoral locking plate for fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Chin J Traumatol 18(5):279–283
Russo M, Malekzadeh AS, Hampton C, Hymes R, Schwartzbach C, Schulman J (2015) Reversed contralateral liss plate for vancouver b1 periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures. Orthopedics 38(6):e467–e472
Vaishya R, Agarwal AK, Gupta N, Vijay V (2016) Reversed distal femoral locking plate for failed proximal femoral nail with non-union of proximal femoral fractures. Int Orthop 40(8):1709–1715
Lin SJ, Huang KC, Chuang PY, Lee CY, Huang TW, Lee MS et al (2016) The outcome of unstable proximal femoral fracture treated with reverse LISS plates. Injury 47(10):2161–2168
Hwang JH, Oh JK, Oh CW, Yoon YC, Choi HW (2012) Mismatch of anatomically pre-shaped locking plate on Asian femurs could lead to malalignment in the minimally invasive plating of distal femoral fractures: a cadaveric study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132(1):51–56
Apivatthakakul T, Chiewcharntanakit S (2009) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in the treatment of the femoral shaft fracture where intramedullary nailing is not indicated. Int Orthop 33(4):1119–1126
Ying C, Liu Shouyao LP, Yunting W, Jinhui W, Jianfeng T, Rongrong C (2014) Comparative biomechanical study of reversed less invasive stabilization system and proximal femoral nail antirotation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Chin Med J 2014:4124–4129
Sidhom SA, Pinder R, Shaw DL (2006) Reverse LISS plate stabilisation of a subtrochanteric fracture of the femur in a patient with osteopetrosis: is this the answer? Injury Extra 37(3):113–115
Li G, Li Z, Han N, Lu Q (2014) A retrospective analysis of reversed femoral Less Invasive Stable System (LISS) for treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fracture. Int J Surg 12(5):432–436
Jang JH, Ahn JM, Lee HJ, Moon NH (2017) Surgical outcomes of biologic fixation for subtrochanteric fracture using locking compression plates. Hip Pelvis 29(1):68–76
Singh J, Selhi HS, Gupta R, Kaur G (2019) Functional outcomes of reverse distal femoral locking plate in the extra capsular fractures of proximal femur. Int J Res Orthop 5(3):417
Shin YS, Han SB (2017) Periprosthetic fracture around a stable femoral stem treated with locking plate osteosynthesis: distal femoral locking plate alone versus with cerclage cable. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 27(5):623–630
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apivatthakakul, V., Apivatthakakul, T. Reverse distal femoral locking compression plate (DF-LCP), does it fit and how to fit on Asian’s proximal femurs? A cadaveric study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 32, 991–1000 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03072-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-021-03072-3