Abstract
Introduction
The standard treatment of femoral diaphyseal fractures is intramedullary nailing. Torsion error remains a largely unsolved problem. We hypothesized that femoral malrotation would change the coronal alignment of the lower extremity and the center of force (COF) in the tibiofemoral joint as compared to the native state.
Method
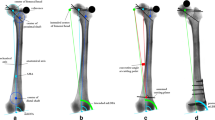
Ten cadaveric legs were used. Intraarticularly placed sensor foil was used to measure contact pressures for each condyle. The resultant pressure of this two-force measurement was calculated as the COF for the joint. Mechanical axis was defined by the navigation system. Two novel devices were used: (1) to simulate bodyweight with leg attachment and fixation to the anterior pelvis and (2) to fix the femur at various degrees of malrotation. A mid-diaphyseal osteotomy was performed and the distal fragment was rotated both internally and externally in 5° increments to a maximum of 25°. COF and axial alignment were assessed at each step with application of a half-bodyweight specific to each specimen.
Results
Internal rotation resulted in valgus deviation of the mechanical axis and a shift in COF towards the lateral condyle (P < 0.05). External rotation caused varus deviation and switched COF towards the medial condyle (P < 0.05). This study shows that femoral malrotation has a significant effect on mechanical axis alignment and force vectors within the knee. Correlation with clinical outcomes is necessary and further research into minimizing such errors of torsion is warranted.
Conclusion
Torsion errors are not merely cosmetic issues, but may result in further morbidity, such as varus or valgus deformity and shifting of the COF, which may lead to joint arthrosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braten M, Terjesen T, Rossvoll I (1993) Torsional deformity after intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. Measurement of anteversion angles in 110 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75:799–803
Braten M, Terjesen T, Rossvoll I (1995) Femoral shaft fractures treated by intramedullary nailing. A follow-up study focusing on problems related to the method. Injury 26:379–383
Citak M, Gardner MJ, Citak M, Krettek C, Hufner T, Kendoff D (2008) Navigated femoral anteversion measurements: a new intraoperative technique. Injury 39:467–471
Citak M, Kendoff D, Citak M, Gardner MJ, Oszwald M, Krettek C, Hufner T (2008) Femoral nail osteosynthesis. Mechanical factors influencing the femoral antetorsion. Unfallchirurg 111:240–246
Citak M, Kendoff D, Pearle AD, O’Loughlin PF, Krettek C, Hufner T, Citak M (2009) Navigated femoral anteversion measurements: general precision and registration options. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129:671–677
Cordier W, Katthagen BD (2000) Femoral torsional deformities. Orthopade 29:795–801
Eckhoff DG (1994) Effect of limb malrotation on malalignment and osteoarthritis. Orthop Clin North Am 25:405–414
Gebhard F, Krettek C, Hufner T, Grutzner PA, Stockle U, Imhoff AB, Lorenz S, Ljungqvist J and Keppler P (2010) Reliability of computer-assisted surgery as an intraoperative ruler in navigated high tibial osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (in press)
Gugenheim JJ, Probe RA, Brinker MR (2004) The effects of femoral shaft malrotation on lower extremity anatomy. J Orthop Trauma 18:658–664
Hazel WA Jr, Rand JA, Morrey BF (1993) Results of meniscectomy in the knee with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Clin Orthop Relat Res 292:232–238
Hulet CH, Locker BG, Schiltz D, Texier A, Tallier E, Vielpeau CH (2001) Arthroscopic medial meniscectomy on stable knees. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83:29–32
Jaarsma RL, Pakvis DF, Verdonschot N, Biert J, van Kampen A (2004) Rotational malalignment after intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma 18:403–409
Janzing HM, Stockman B, Van Damme G, Rommens P, Broos PL (1998) The retrograde intramedullary nail: prospective experience in patients older than sixty-five years. J Orthop Trauma 12:330–333
Kendoff D, Citak M, Gardner MJ, Gosling T, Krettek C, Hufner T (2007) Navigated femoral nailing using noninvasive registration of the contralateral intact femur to restore anteversion. Technique and clinical use. J Orthop Trauma 21:725–730
Kettelkamp DB, Hillberry BM, Murrish DE, Heck DA (1988) Degenerative arthritis of the knee secondary to fracture malunion. Clin Orthop Relat Res 234:159–169
Koch M (1993) Measuring plantar pressure in conventional shoes with the TEKSCAN sensory system. Biomed Tech (Berl) 38:243–248
Krettek C, Miclau T, Blauth M, Lindsey RW, Donow C, Tscherne H (1997) Recurrent rotational deformity of the femur after static locking of intramedullary nails: case reports. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:4–8
Maier DG, Reisig R, Keppler P, Kinzl L, Gebhard F (2005) Post-traumatic torsional differences and functional tests following antegrade or retrograde intramedullary nailing of the distal femoral diaphysis. Unfallchirurg 108:109–117
Ostrum RF, Agarwal A, Lakatos R, Poka A (2000) Prospective comparison of retrograde and antegrade femoral intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma 14:496–501
Paley D, Tetsworth K (1992) Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res 280:48–64
Pena E, Calvo B, Martinez MA, Palanca D, Doblare M (2006) Why lateral meniscectomy is more dangerous than medial meniscectomy. A finite element study. J Orthop Res 24:1001–1010
Ricci WM, Bellabarba C, Lewis R, Evanoff B, Herscovici D, Dipasquale T, Sanders R (2001) Angular malalignment after intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma 15:90–95
Stindel E, Briard JL, Merloz P, Plaweski S, Dubrana F, Lefevre C, Troccaz J (2002) Bone morphing: 3D morphological data for total knee arthroplasty. Comput Aided Surg 7:156–168
van Joost MC, Gastkemper RJ (1972) Malrotation after femoral shaft fractures. Arch Chir Neerl 24:101–115
Wirz D, Becker R, Li SF, Friederich NF, Muller W (2002) Validation of the Tekscan system for statistic and dynamic pressure measurements of the human femorotibial joint. Biomed Tech (Berl) 47:195–201
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Dr. hc. Robert Mathys Foundation for scientific and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bretin, P., O’Loughlin, P.F., Suero, E.M. et al. Influence of femoral malrotation on knee joint alignment and intra-articular contract pressures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131, 1115–1120 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1210-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1210-4