Abstract
Introduction
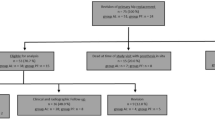
A prospective study was designed to test the hypothesis that short-term results after hip revisions are in association with the surgical approach with lower clinical scores for the transfemoral approach.
Materials and methods
A total of 120 hip revision operations with the modular cementless revision stem “Revitan Curved” (Zimmer GmbH, Winterthur, Switzerland), of which 42 replacements involved an endofemoral (posterolateral) approach and 78 implantations a transfemoral approach, were followed up over a period of at least 24 months.
Results
In the early post-operative stage, stems implanted transfemoral were associated with significantly lower Harris Hip Scores and a significantly more frequent appearance of Trendelenburg signs. The differences lessened at the end of the follow-up period. Within the group of transfemoral implantation, all six stems with a circular fixation zone measuring less than 3 cm had subsided and two of these had become loose; none of the stems with greater fixation zones exhibited these properties. In the case of the endofemoral implants, three stems exhibited sinking but there did not appear to be any relationship between this event and length of fixation zone.
Conclusion
The surgical approach has an association with the short-time outcomes of hip revsions using cementless modular stems. Transfemoral implantation of the “Revitan curved” stem requires a fixation zone of at least 3 cm and a longer period of rehabilitation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bircher HP, Riede U, Lüem M, Ochsner PE (2001) Der Wert der SL-Revisionsprothese nach Wagner zur Überbrückung großer Femurdefekte. Technik und Resultate. Orthopäde 30:294–303
Böhm P, Bischel O (2001) Femoral revision with the Wagner SL revision stem. J Bone Joint Surg 83-A:1023–1031
Böhm P, Bischel O (2001) The uncemented diaphysal fixation of femoral revision stems in case of large bone defects—analysis of twelve years experience with the Wagner SL revision stem. Z Orthop 139:229–239
Böhm P, Bischel O (2004) The use of tapered stems for femoral revision surgery. Clin Orthop Rel Res 420:148–159
Challgahan JJ, Slavati EA, Pellicci PM, Wilson PD, Ranawat CS (1985) Results of revision for mechanical failure after cemented total hip replacement, 1979 to 1982. A two to five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg 67-A:1074–1085
Chen WM, McAuley JP, Engh CA Jr, Hopper RH Jr, Engh CA (2000) Extended slide trochanteric osteotomy for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 82-A:1215–1219
Della Valle CJ, Berger RA, Rosenberg AG, Jacobs JJ, Sheinkop MB, Paprosky WG (2003) Extended trochanteric osteotomy in complex primary total hip arthroplasty. A brief note. J Bone Joint Surg 85-A:2385–2390
Dohmae Y, Bechthold JE, Sherman RE, Puno RM, Gustilo RB (1988) Reduction in cement-bone interface shear strength between primary and revision arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 36:214–220
Duncan DP, Masri BA (1995) Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect 44:293–304
Fink B, Hahn M, Fuerst M, Thybaut L, Delling G (2005) Principle of fixation of the cementless modular revision stem Revitan. Unfallchirurg 108:1029–1037
Fink B, Grossmann A (2007) Modified transfemoral approach to revision arthroplasty with uncemented modular revision stems. Oper Orthop Traumatol 19:32–55
Fink B, Grossmann A, Schubring S, Schulz MS, Fuerst M (2007) A modified transfemoral approach using modular cementless revision stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res 462:105–114
Glassman AH (2004) Exposure for revision total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:39–47
Grünig R, Morscher E, Ochsner PE (1997) Three- to 7-year results with the uncemented SL femoral revision prosthesis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 116:187–197
Gustilo RB, Pasternak HS (1988) Revision total hip arthroplasty with titanium ingrowth prosthesis and bone grafting for failed cemented femoral component loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res 235:111–119
Hartwig C-H, Böhm P, Czecg U, Reize P, Küsswetter W (1996) The Wagner revision stem in alloarthroplasty of the hip. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 115:5–9
Hedley AD, Gruen TA, Ruoff OP (1988) Revision of failed total hip arthroplasties with uncemented porous-coated anatomic components. Clin Orthop Relat Res 235:75–90
Huffman GR, Ries MD (2003) Combined vertical and horizontal cable fixation of an extended trochanteric osteotomy site. J Bone Joint Surg 85-A:273–277
Isacson J, Stark A, Wallensten R (2000) The Wagner revision prosthesis consistently restores femoral bone structure. Int Orthop 24:139–142
Kolstad K, Adalberth G, Mallmin H, Milbrink J, Sahlsted B (1996) The Wagner revision stem for severe osteolysis. 31 hips followed for 1.5–5 years. Acta Orthop Scand 67:541–544
Krishnamurthy AB, MacDonald SJ, Paprosky WG (1997) 5- to 13-year follow-up study on cementless femoral components in revisions surgery. J Arthroplasty 12:839–847
Le Béguec P (2000) Système PFM-revision pour reprise d’une prothèse fémorale descellée. Maîtrise orthopédique 91
Mardones R, Gonzalez C, Cabanela ME, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ (2005) Extended femoral osteotomy for revision of hip arthroplasty: results and complications. J Arthroplasty 20:79–83
Miner TM, Momberger NG, Chong D, Paprosky WL (2001) The extended trochanteric osteotomy in revision hip arthroplasty: a critical review of 166 cases at mean 3-year, 9-month follow-up. J Arthroplasty 16:188–194
Moreland JR, Bernstein ML (1995) Femoral revison hip arthroplasty with uncemented, porous-coated stems. Clin Orthop Rel Res 319:141–150
Paprosky WG, Lawrence J, Cameron H (1990) Femoral defect classification. Clinical application. Orthop Rev 19(Suppl):9–15
Paprosky WG, Greidanus NV, Antoniou J (1999) Minimum 10-year results of extensively porous-coated stems in revision hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 369:230–242
Paprosky WG, Weeden SH, Bowling JW Jr (2001) Component removal in revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 393:181–193
Peters PC Jr, Head WC, Emerson RH Jr (1993) An extended trochanteric osteotomy for revision total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg 75-Br:158–159
Sieber HP, Le Bèguec P (2001) Einsatz des PFM-R-Schaftes bei Revisionseingriffen. In: Perka C, Zippel H (eds) Revisionsendoprothetik des Hüftgelenkes. Schaftrekonstruktion und perioperatives Management. Einhorn-Presse Verlag, pp 174–184
Wagner H (1987) Revisionsprothese für das Hüftgelenk bei schwerem Knochenverlust. Orthopäde 16:295–300
Wagner H (1989) Revisionsprothese für das Hüftgelenk. Orthopäde 18:438–453
Wagner H, Wagner M (1993) Femur-Revisionsprothese. Z Orthop 131:574–577
Wagner H, Wagner M (1997) Hüftprothesenwechsel mit der Femur-Revisionsprothese. Erfahrungen von 10 Jahren. Med Orthop Tech 117:138–148
Warren PJ, Thompson P, Flechter MDA (2002) Transfemoral implantation of the Wagner SL stem. The abolition of subsidence and enhancement of osteotomy union rate using Dall-Miles cables. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122:557–560
Weber M, Hempfing A, Orler R (2002) Femoral revision using the Wagener stem: results at 2–9 years. Int Orthop 26:36–39
Weeden SH, Paprosky WG (2002) Minimal 11-year follow-up of extensively porous-coated stems in femoral revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 17(4 Suppl 1):134–137
Wilkes RA, Birch J, Pearse MF, Lee M, Atkins RM (1994) The Wagner technique for revision arthroplasty of the hip: a review of 24 cases. J Orthop Rheum 7:196–198
Wirtz DC, Niethard FU (1997) Ursachen, Diagnostik und Therapie der aseptischen Hüftendoprothesenlockerung—eine Standortbestimmung. Z Orthop 135:270–280
Younger TI, Bradford MS, Magnus RE, Paprosky WG (1995) Extended proximal femoral osteotomy. A new technique for femoral revision arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 10:329–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0785-5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fink, B., Grossmann, A., Schubring, S. et al. Short-term results of hip revisions with a curved cementless modular stem in association with the surgical approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129, 65–73 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0617-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0617-7