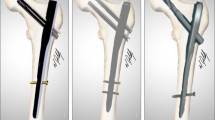
Abstract
Introduction: In this study, we initiated a prospective, randomised, clinical trial comparing the AMBI, TGN and PFN operations used for treatment of unstable fractures, for differences in intra-operative use, consolidation, complications and functional outcome. Materials and methods: We have compared the pre-, intra- and post-operating variables of AMBI, TGN and PFN operations that were used for treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures, of 120 patients all above 60 years old diagnosed with extracapsular hip fractures classified as AO Type 31-A2 or Type 31-A3. Results: According to our results the three methods are comparable in the treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures of patients above 60 years old. Conclusion: The AMBI remains the gold standard for the fractures of trochanteric region. TGN has an easier and faster procedure, facilitates early weight bearing and had minor late complications. An improper use of the PFN system was the reason for the most complications and the longer operation time of the device. PFN is also an accepted minimally invasive implant for unstable proximal femoral fractures but future modification of the implant to avoid Z-effect phenomenon, careful surgical technique and selection of the patients should reduce its high complication rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-yassari G, Langstaff RJ, Jones JWM, Al-Lami M (2002) The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN) for the treatment of unstable trochanteric femoral fracture. Injury 33:395
Banan H, Al-Sabti A, Jimulia T, Hart AJ (2002) The treatment of unstable, extracapsular hip fractures with the AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail (PFN)—our first 60 cases. Injury 33:401
Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM (1998) Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation for the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin Orthop 348:87–94
Bellabarba C, Herscovici D Jr, Ricci WM (2000) Percutaneous treatment of peritrochanteric fractures using the Gamma nail. Clin Orthop 375:30–42
Bess RJ, Jolly SA (1997) Comparison of compression hip screw and gamma nail for treatment of peritrochanteric fractures. J South Orthop Assoc 6:173–179
Boldin C, Seibert F, Fankhauser F, Peicha G, Grechening W, Szyszkowitz R (2003) The proximal femoral nail (PFN)-a minimal invasive treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. A prospective study of 55 patients wit a follow-up of 15 months. Acta Orthop Scand 74:53–58
Bridle SH, Patel AD, Bircher M, Calvert PT (1991) Fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73B:330
Butt MS, Krikler SJ, Nafie S, Ali MS (1995) Comparison of dynamic hip screw and gamma nail: a prospective randomized controlled trail. Injury 26:615
Docquier PL, Manche E, Autrique JC, Geulette B (2002) Complications associated with gamma nailing. A review of 439 cases. Acta Orthop Belg 68:251–257
Domingo L, Cecilia D, Herrera A, Resines C (2001) Trochanteric fractures treated with a proximal femoral nail. Int Orthop 25:298–301
Fogagnolo F, Kfuri M Jr, Paccola C (2004) Intramedullary fixation of pertrochanteric hip fractures with the short AO-ASIF proximal femoral nail. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124:31–37
Guyer P, Landolt M, Eberle C et al (1991) Der Gamma-nagel als belastungsstabile alternative zur DHS bei der instabilen proximalen femurfraktur des alten menschen. Helv Chir Acta 58:697–703
Haberneck H, Wallner T, Aschauer E, Schmid L (2000) Comparison of ender nails, dynamic hip screws, and Gamma nails in the treatment of peritrochanteric femoral fractures. Orthopedics 23:121–127
Haynes RC, Poll RG, Miles AW, Weston RB (1997) Failure of femoral head fixation: a cadaveric analysis of lag screw cut out with the gamma locking nail and AO DHS. Injury 28:337
Herrera A, Domingo LJ, Calvo A, Martínez A, Cuenca J (2002) A comparative study of trochanteric fractures treated with the Gamma nail or the proximal femoral nail. Int Orthop 26:365–369
Leung KS, So WS, Shen WY et al (1992) Gamma nails and dynamic hip screws for peritrochanteric fractures: a randomized prospective study in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 74:345–351
Muller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J (eds) (1990) The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, p 120
O’Brien PJ, Meek RN, Blachut PA et al (1995) Fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: gamma nail versus dynamic hip screw. A randomized, prospective study. Can J Surg 38:516–520
Parker MJ, Pryor GA (1996) Gamma versus DHS nailing for extracapsular femoral fractures: meta-analysis of ten randomised trials. Int Orthop 20:163–168
Radford PJ, Needoff M, Webb JK (1993) A prospective randomised comparison of the dynamic hip screw and the gamma locking nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75:789–793
Salvati A, Wilson D (1973) Long-term results of femoral-head replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 55A:516–524
Saudan M, Lübbeke A, Sadowski C, Riand N, Stern R, Hoffmeyer P (2002) Pertrochanteric fractures: is there an advantage to an intramedullary nail? A randomized, prospective study of 206 patients comparing the dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail. J Orthop Trauma 16:386–393
Schipper IB, Steyerberg EW, Castelein RM, van der Heijden FH, den Hoed PT, Kerver AJ, van Vugt AB (2004) Treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Randomized comparison of the gamma nail and the proximal femoral nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:86–94
Simmermacher RKJ, Bosch AM, Van de Werken Chr (1999) The AO/ASIF-poximal femoral nail (PFN): a new device for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury 30:327
Velasco RV, Comfort TH (1978) Analysis of treatment problems in subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Trauma 18:513
Werner-Tutschku W, Lajtai G, Schmiedhuber G, Lang T, Pirkl C, Orthner E (2002) Intra-und perioperative Komplikationen bei der Stabilisierung von per-und subtrochantären Femurfracturen mittels PFN. Unfallchirurg 105:881–885
Williams WW, Parker BC (1992) Complications associated with the use of the gamma nail. Injury 23:291–292
Wolfrang GL, Bryant MH, Oneil JP (1982) Treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur using sliding screw plate fixation. Clin Orthop 163:148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papasimos, S., Koutsojannis, C.M., Panagopoulos, A. et al. A randomised comparison of AMBI, TGN and PFN for treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 125, 462–468 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-005-0021-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-005-0021-5