Abstract
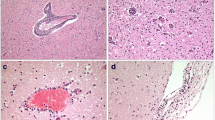
Eight dogs originating from different regions of Austria [all of them known as tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) areas] with severe neurological signs were either euthanatized or died spontaneously. Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) antigen was detected in the brains of five of these dogs by immunohistology, but not in the others. All of the dogs, however, had identical neuropathological changes. There were moderate lymphohistiocytic meningitis, widespread neuronal necroses, karyorrhexis of glial cells, numerous neuronophagic nodules, and extensive microgliosis. In the cerebellum, loss of Purkinje cells and proliferation of microglial cells in the molecular layer were found. All brain regions showed numerous perivascular cuffs consisting of lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells and, occasionally, red blood cells. The blood-derived cells were not restricted to the perivascular spaces but diffusely infiltrated the neuropil. The most severe changes were localized in the neuroparenchyma surrounding the fourth ventricle. Lesions were less severe in basal ganglia, thalamus, mesencephalon, nuclei of pons and medulla oblongata. Moderate lesions were found in the gray matter of neocortex and allocortex, hippocampus and molecular and Purkinje cell layers of the cerebellum. White matter was slightly to moderately affected. The choroid plexus was free of inflammation. Due to rapid virus clearance mechanisms in this disease, antigen was not detectable in all cases. Neuropathological changes identical with those of immunohistologically proven cases justified the diagnosis TBE in these cases. In addition, the neuropathological diagnosis was supported by the origin of the affected dogs from endemic areas, the seasonal occurrence of the disease and a clinical history of a highly febrile neurological disease with short duration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 July 1997 / Revised: 16 October 1997 / Accepted: 20 October 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weissenböck, H., Suchy, A. & Holzmann, H. Tick-borne encephalitis in dogs: neuropathological findings and distribution of antigen. Acta Neuropathol 95, 361–366 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050811
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010050811