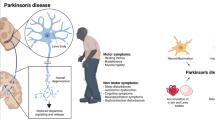
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive movement disorder of adults and the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathologic diagnosis of PD requires moderate-to-marked neuronal loss in the ventrolateral substantia nigra pars compacta and α-synuclein (αS) Lewy body pathology. Nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration correlates with the Parkinsonian motor features, but involvement of other peripheral and central nervous system regions leads to a wide range of non-motor features. Nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration is shared with other parkinsonian disorders, including some genetic forms of parkinsonism, but many of these disorders do not have Lewy bodies. An ideal animal model for PD, therefore, should exhibit age-dependent and progressive dopaminergic neurodegeneration, motor dysfunction, and abnormal αS pathology. Rodent models of PD using genetic or toxin based strategies have been widely used in the past several decades to investigate the pathogenesis and therapeutics of PD, but few recapitulate all the major clinical and pathologic features of PD. It is likely that new strategies or better understanding of fundamental disease processes may facilitate development of better animal models. In this review, we highlight progress in generating rodent models of PD based on impairments of four major cellular functions: mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, autophagy-lysosomal metabolism, ubiquitin–proteasome protein degradation, and endoplasmic reticulum stress/unfolded protein response. We attempt to evaluate how impairment of these major cellular systems contribute to PD and how they can be exploited in rodent models. In addition, we review recent cell biological studies suggesting a link between αS aggregation and impairment of nuclear membrane integrity, as observed during cellular models of apoptosis. We also briefly discuss the role of incompetent phagocytic clearance and how this may be a factor to consider in developing new rodent models of PD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon-Peretz J, Rosenbaum H, Gershoni-Baruch R (2004) Mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene and Parkinson’s disease in Ashkenazi Jews. New Engl J Med 351:1972–1977. https://doi.org/10.1056/Nejmoa033277
Ahmed I, Liang Y, Schools S, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Savitt JM (2012) Development and characterization of a new Parkinson’s disease model resulting from impaired autophagy. J Neurosci 32:16503–16509. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0209-12.2012
Alafuzoff I, Ince PG, Arzberger T, Al-Sarraj S, Bell J, Bodi I, Bogdanovic N, Bugiani O, Ferrer I, Gelpi E, Gentleman S, Giaccone G, Ironside JW, Kavantzas N, King A, Korkolopoulou P, Kovacs GG, Meyronet D, Monoranu C, Parchi P, Parkkinen L, Patsouris E, Roggendorf W, Rozemuller A, Stadelmann-Nessler C, Streichenberger N, Thal DR, Kretzschmar H (2009) Staging/typing of Lewy body related alpha-synuclein pathology: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Acta Neuropathol 117:635–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0523-2
Andres-Mateos E, Perier C, Zhang L, Blanchard-Fillion B, Greco TM, Thomas B, Ko HS, Sasaki M, Ischiropoulos H, Przedborski S, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2007) DJ-1 gene deletion reveals that DJ-1 is an atypical peroxiredoxin-like peroxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14807–14812. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0703219104
Anglade P, Vyas S, JavoyAgid F, Herrero MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, MouattPrigent A, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (1997) Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol Histopathol 12:25–31
Ariga H, Takahashi-Niki K, Kato I, Maita H, Niki T, Iguchi-Ariga SM (2013) Neuroprotective function of DJ-1 in Parkinson’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:683920. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/683920
Baiguera C, Alghisi M, Pinna A, Bellucci A, De Luca MA, Frau L, Morelli M, Ingrassia R, Benarese M, Porrini V, Pellitteri M, Bertini G, Fabene PF, Sigala S, Spillantini MG, Liou HC, Spano PF, Pizzi M (2012) Late-onset Parkinsonism in NFkappaB/c-Rel-deficient mice. Brain 135:2750–2765. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws193
Barrientos A, Moraes CT (1999) Titrating the effects of mitochondrial complex I impairment in the cell physiology. J Biol Chem 274:16188–16197. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.23.16188
Beach TG, Adler CH, Lue L, Sue LI, Bachalakuri J, Henry-Watson J, Sasse J, Boyer S, Shirohi S, Brooks R, Eschbacher J, White CL 3rd, Akiyama H, Caviness J, Shill HA, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG (2009) Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 117:613–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0538-8
Beach TG, Adler CH, Serrano G, Sue LI, Walker DG, Dugger BN, Shill HA, Driver-Dunckley E, Caviness JN, Intorcia A, Filon J, Scott S, Garcia A, Hoffman B, Belden CM, Davis KJ, Sabbagh MN (2016) Prevalence of submandibular gland synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and other Lewy body disorders. J Parkinsons Dis 6:153–163. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-150680
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Vedders L, Lue L, White Iii CL, Akiyama H, Caviness JN, Shill HA, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG (2010) Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 119:689–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-010-0664-3
Bedford L, Hay D, Devoy A, Paine S, Powe DG, Seth R, Gray T, Topham I, Fone K, Rezvani N, Mee M, Soane T, Layfield R, Sheppard PW, Ebendal T, Usoskin D, Lowe J, Mayer RJ (2008) Depletion of 26S proteasomes in mouse brain neurons causes neurodegeneration and Lewy-like inclusions resembling human pale bodies. J Neurosci 28:8189–8198. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2218-08.2008
Beecham GW, Dickson DW, Scott WK, Martin ER, Schellenberg G, Nuytemans K, Larson EB, Buxbaum JD, Trojanowski JQ, Van Deerlin VM, Hurtig HI, Mash DC, Beach TG, Troncoso JC, Pletnikova O, Frosch MP, Ghetti B, Foroud TM, Honig LS, Marder K, Vonsattel JP, Goldman SM, Vinters HV, Ross OA, Wszolek ZK, Wang L, Dykxhoorn DM, Pericak-Vance MA, Montine TJ, Leverenz JB, Dawson TM, Vance JM (2015) PARK10 is a major locus for sporadic neuropathologically confirmed Parkinson disease. Neurology 84:972–980. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001332
Belal C, Ameli NJ, El Kommos A, Bezalel S, Al’Khafaji AM, Mughal MR, Mattson MP, Kyriazis GA, Tyrberg B, Chan SL (2012) The homocysteine-inducible endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress protein Herp counteracts mutant alpha-synuclein-induced ER stress via the homeostatic regulation of ER-resident calcium release channel proteins. Hum Mol Genet 21:963–977. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr502
Bennett MC, Bishop JF, Leng Y, Chock PB, Chase TN, Mouradian MM (1999) Degradation of alpha-synuclein by proteasome. J Biol Chem 274:33855–33858
Bentea E, Van der Perren A, Van Liefferinge J, El Arfani A, Albertini G, Demuyser T, Merckx E, Michotte Y, Smolders I, Baekelandt V, Massie A (2015) Nigral proteasome inhibition in mice leads to motor and non-motor deficits and increased expression of Ser129 phosphorylated alpha-synuclein. Front Behav Neurosci 9:68. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00068
Bhattacharjee N, Borah A (2016) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are the underlying events of dopaminergic neurodegeneration in homocysteine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 101:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.10.001
Blandini F, Armentero MT, Martignoni E (2008) The 6-hydroxydopamine model: news from the past. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14(Suppl 2):S124–S129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.04.015
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1077209
Bove J, Zhou C, Jackson-Lewis V, Taylor J, Chu Y, Rideout HJ, Wu DC, Kordower JH, Petrucelli L, Przedborski S (2006) Proteasome inhibition and Parkinson’s disease modeling. Ann Neurol 60:260–264. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20937
Braak H, Bohl JR, Muller CM, Rub U, de Vos RA, Del Tredici K (2006) Stanley Fahn Lecture 2005: the staging procedure for the inclusion body pathology associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease reconsidered. Mov Disord 21:2042–2051. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21065
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2017) Neuropathological staging of brain pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease: separating the wheat from the chaff. J Parkinsons Dis 7:S73–S87. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-179001
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Brooks AI, Chadwick CA, Gelbard HA, Cory-Slechta DA, Federoff HJ (1999) Paraquat elicited neurobehavioral syndrome caused by dopaminergic neuron loss. Brain Res 823:1–10
Bukhatwa S, Zeng BY, Rose S, Jenner P (2010) A comparison of changes in proteasomal subunit expression in the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain Res 1326:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.02.045
Casadei N, Sood P, Ulrich T, Fallier-Becker P, Kieper N, Helling S, May C, Glaab E, Chen J, Nuber S, Wolburg H, Marcus K, Rapaport D, Ott T, Riess O, Kruger R, Fitzgerald JC (2016) Mitochondrial defects and neurodegeneration in mice overexpressing wild-type or G399S mutant HtrA2. Hum Mol Genet. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw353
Casey DE (1997) The relationship of pharmacology to side effects. J Clin Psychiatry 58:55–62
Chan NC, Salazar AM, Pham AH, Sweredoski MJ, Kolawa NJ, Graham RL, Hess S, Chan DC (2011) Broad activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by Parkin is critical for mitophagy. Hum Mol Genet 20:1726–1737. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr048
Chandran JS, Lin X, Zapata A, Hoke A, Shimoji M, Moore SO, Galloway MP, Laird FM, Wong PC, Price DL, Bailey KR, Crawley JN, Shippenberg T, Cai H (2008) Progressive behavioral deficits in DJ-1-deficient mice are associated with normal nigrostriatal function. Neurobiol Dis 29:505–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2007.11.011
Chen L, Cagniard B, Mathews T, Jones S, Koh HC, Ding Y, Carvey PM, Ling Z, Kang UJ, Zhuang X (2005) Age-dependent motor deficits and dopaminergic dysfunction in DJ-1 null mice. J Biol Chem 280:21418–21426. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M413955200
Chen Q, Vazquez EJ, Moghaddas S, Hoppel CL, Lesnefsky EJ (2003) Production of reactive oxygen species by mitochondria: central role of complex III. J Biol Chem 278:36027–36031. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304854200
Chesselet MF, Richter F, Zhu C, Magen I, Watson MB, Subramaniam SR (2012) A progressive mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: the Thy1-aSyn (“Line 61”) mice. Neurotherapeutics 9:297–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-012-0104-2
Chu VT, Weber T, Graf R, Sommermann T, Petsch K, Sack U, Volchkov P, Rajewsky K, Kuhn R (2016) Efficient generation of Rosa26 knock-in mice using CRISPR/Cas9 in C57BL/6 zygotes. BMC Biotechnol 16:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-016-0234-4
Cicchetti F, Drouin-Ouellet J, Gross RE (2009) Environmental toxins and Parkinson’s disease: what have we learned from pesticide-induced animal models? Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:475–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2009.06.005
Conn KJ, Gao W, McKee A, Lan MS, Ullman MD, Eisenhauer PB, Fine RE, Wells JM (2004) Identification of the protein disulfide isomerase family member PDIp in experimental Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body pathology. Brain Res 1022:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.07.026
Coppola-Segovia V, Cavarsan C, Maia FG, Ferraz AC, Nakao LS, Lima MM, Zanata SM (2016) ER stress induced by tunicamycin triggers alpha-synuclein oligomerization, dopaminergic neurons death and locomotor impairment: a new model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0114-x
Cullen V, Lindfors M, Ng J, Paetau A, Swinton E, Kolodziej P, Boston H, Saftig P, Woulfe J, Feany MB, Myllykangas L, Schlossmacher MG, Tyynela J (2009) Cathepsin D expression level affects alpha-synuclein processing, aggregation, and toxicity in vivo. Mol Brain 2:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-2-5
Daher JP, Ying M, Banerjee R, McDonald RS, Hahn MD, Yang L, Flint Beal M, Thomas B, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Moore DJ (2009) Conditional transgenic mice expressing C-terminally truncated human alpha-synuclein (alphaSyn119) exhibit reduced striatal dopamine without loss of nigrostriatal pathway dopaminergic neurons. Mol Neurodegener 4:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-4-34
Dave KD, De Silva S, Sheth NP, Ramboz S, Beck MJ, Quang C, Switzer RC 3rd, Ahmad SO, Sunkin SM, Walker D, Cui X, Fisher DA, McCoy AM, Gamber K, Ding X, Goldberg MS, Benkovic SA, Haupt M, Baptista MA, Fiske BK, Sherer TB, Frasier MA (2014) Phenotypic characterization of recessive gene knockout rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 70:190–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.06.009
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Rare genetic mutations shed light on the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. J Clin Investig 111:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI17575
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2010) The role of parkin in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25(Suppl 1):S32–S39. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22798
Decressac M, Mattsson B, Lundblad M, Weikop P, Bjorklund A (2012) Progressive neurodegenerative and behavioural changes induced by AAV-mediated overexpression of alpha-synuclein in midbrain dopamine neurons. Neurobiol Dis 45:939–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.013
Dehay B, Bove J, Rodriguez-Muela N, Perier C, Recasens A, Boya P, Vila M (2010) Pathogenic lysosomal depletion in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 30:12535–12544. https://doi.org/10.1523/Jneurosci.1920-10.2010
Dehay B, Martinez-Vicente M, Caldwell GA, Caldwell KA, Yue Z, Cookson MR, Klein C, Vila M, Bezard E (2013) Lysosomal impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 28:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25462
Dickson DW (2017) Neuropathology of Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.07.033
Domico LM, Zeevalk GD, Bernard LP, Cooper KR (2006) Acute neurotoxic effects of mancozeb and maneb in mesencephalic neuronal cultures are associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. Neurotoxicology 27:816–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2006.07.009
Duan W, Ladenheim B, Cutler RG, Kruman II, Cadet JL, Mattson MP (2002) Dietary folate deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels endanger dopaminergic neurons in models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 80:101–110
Ejlerskov P, Hultberg JG, Wang J, Carlsson R, Ambjorn M, Kuss M, Liu Y, Porcu G, Kolkova K, Friis Rundsten C, Ruscher K, Pakkenberg B, Goldmann T, Loreth D, Prinz M, Rubinsztein DC, Issazadeh-Navikas S (2015) Lack of neuronal IFN-beta-IFNAR causes Lewy body- and Parkinson’s disease-like dementia. Cell 163:324–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.069
Ekstrand MI, Terzioglu M, Galter D, Zhu S, Hofstetter C, Lindqvist E, Thams S, Bergstrand A, Hansson FS, Trifunovic A, Hoffer B, Cullheim S, Mohammed AH, Olson L, Larsson NG (2007) Progressive parkinsonism in mice with respiratory-chain-deficient dopamine neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:1325–1330. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605208103
Emmer KL, Waxman EA, Covy JP, Giasson BI (2011) E46K human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop Lewy-like and tau pathology associated with age-dependent, detrimental motor impairment. J Biol Chem 286:35104–35118. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.247965
Enquist IB, Lo Bianco C, Ooka A, Nilsson E, Mansson JE, Ehinger M, Richter J, Brady RO, Kirik D, Karlsson S (2007) Murine models of acute neuronopathic Gaucher disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:17483–17488. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0708086104
Escobar VD, Kuo YM, Orrison BM, Giasson BI, Nussbaum RL (2014) Transgenic mice expressing S129 phosphorylation mutations in alpha-synuclein. Neurosci Lett 563:96–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.01.033
Farrer M, Kachergus J, Forno L, Lincoln S, Wang DS, Hulihan M, Maraganore D, Gwinn-Hardy K, Wszolek Z, Dickson D, Langston JW (2004) Comparison of kindreds with parkinsonism and alpha-synuclein genomic multiplications. Ann Neurol 55:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10846
Fernagut PO, Hutson CB, Fleming SM, Tetreaut NA, Salcedo J, Masliah E, Chesselet MF (2007) Behavioral and histopathological consequences of paraquat intoxication in mice: effects of alpha-synuclein over-expression. Synapse 61:991–1001. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20456
Ferrari CC, Tarelli R (2011) Parkinson’s disease and systemic inflammation. Parkinsons Dis 2011:436813. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/436813
Fifel K, Cooper HM (2014) Loss of dopamine disrupts circadian rhythms in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 71:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.08.024
Fitsanakis VA, Amarnath V, Moore JT, Montine KS, Zhang J, Montine TJ (2002) Catalysis of catechol oxidation by metal-dithiocarbamate complexes in pesticides. Free Radic Biol Med 33:1714–1723
Fornai F, Schluter OM, Lenzi P, Gesi M, Ruffoli R, Ferrucci M, Lazzeri G, Busceti CL, Pontarelli F, Battaglia G, Pellegrini A, Nicoletti F, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Sudhof TC (2005) Parkinson-like syndrome induced by continuous MPTP infusion: convergent roles of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3413–3418. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409713102
Forno LS, DeLanney LE, Irwin I, Langston JW (1993) Similarities and differences between MPTP-induced parkinsonsim and Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathologic considerations. Adv Neurol 60:600–608
Franco-Iborra S, Vila M, Perier C (2016) The Parkinson disease mitochondrial hypothesis: where are we at? Neuroscientist 22:266–277. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858415574600
Gash DM, Rutland K, Hudson NL, Sullivan PG, Bing G, Cass WA, Pandya JD, Liu M, Choi DY, Hunter RL, Gerhardt GA, Smith CD, Slevin JT, Prince TS (2008) Trichloroethylene: Parkinsonism and complex 1 mitochondrial neurotoxicity. Ann Neurol 63:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21288
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Quinn SM, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron 34:521–533
Gispert S, Del Turco D, Garrett L, Chen A, Bernard DJ, Hamm-Clement J, Korf HW, Deller T, Braak H, Auburger G, Nussbaum RL (2003) Transgenic mice expressing mutant A53T human alpha-synuclein show neuronal dysfunction in the absence of aggregate formation. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:419–429
Gispert S, Ricciardi F, Kurz A, Azizov M, Hoepken HH, Becker D, Voos W, Leuner K, Muller WE, Kudin AP, Kunz WS, Zimmermann A, Roeper J, Wenzel D, Jendrach M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Huber L, Rohrer H, Barrera M, Reichert AS, Rub U, Chen A, Nussbaum RL, Auburger G (2009) Parkinson phenotype in aged PINK1-deficient mice is accompanied by progressive mitochondrial dysfunction in absence of neurodegeneration. PLoS One 4:e5777. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005777
Glasl L, Kloos K, Giesert F, Roethig A, Di Benedetto B, Kuhn R, Zhang J, Hafen U, Zerle J, Hofmann A, de Angelis MH, Winklhofer KF, Holter SM, Vogt Weisenhorn DM, Wurst W (2012) Pink1-deficiency in mice impairs gait, olfaction and serotonergic innervation of the olfactory bulb. Exp Neurol 235:214–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.01.002
Goldberg MS, Fleming SM, Palacino JJ, Cepeda C, Lam HA, Bhatnagar A, Meloni EG, Wu N, Ackerson LC, Klapstein GJ, Gajendiran M, Roth BL, Chesselet MF, Maidment NT, Levine MS, Shen J (2003) Parkin-deficient mice exhibit nigrostriatal deficits but not loss of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 278:43628–43635. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M308947200
Goldberg MS, Pisani A, Haburcak M, Vortherms TA, Kitada T, Costa C, Tong Y, Martella G, Tscherter A, Martins A, Bernardi G, Roth BL, Pothos EN, Calabresi P, Shen J (2005) Nigrostriatal dopaminergic deficits and hypokinesia caused by inactivation of the familial Parkinsonism-linked gene DJ-1. Neuron 45:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.041
Goldman SM (2014) Environmental toxins and Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 54:141–164. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011613-135937
Goldman SM, Quinlan PJ, Ross GW, Marras C, Meng C, Bhudhikanok GS, Comyns K, Korell M, Chade AR, Kasten M, Priestley B, Chou KL, Fernandez HH, Cambi F, Langston JW, Tanner CM (2012) Solvent exposures and Parkinson disease risk in twins. Ann Neurol 71:776–784. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22629
Gomez-Isla T, Irizarry MC, Mariash A, Cheung B, Soto O, Schrump S, Sondel J, Kotilinek L, Day J, Schwarzschild MA, Cha JH, Newell K, Miller DW, Ueda K, Young AB, Hyman BT, Ashe KH (2003) Motor dysfunction and gliosis with preserved dopaminergic markers in human alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 24:245–258
Gomez-Suaga P, Fdez E, Blanca Ramirez M, Hilfiker S (2012) A link between autophagy and the pathophysiology of LRRK2 in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis 2012:324521. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/324521
Gonzalez-Reyes LE, Verbitsky M, Blesa J, Jackson-Lewis V, Paredes D, Tillack K, Phani S, Kramer ER, Przedborski S, Kottmann AH (2012) Sonic hedgehog maintains cellular and neurochemical homeostasis in the adult nigrostriatal circuit. Neuron 75:306–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.05.018
Good CH, Hoffman AF, Hoffer BJ, Chefer VI, Shippenberg TS, Backman CM, Larsson NG, Olson L, Gellhaar S, Galter D, Lupica CR (2011) Impaired nigrostriatal function precedes behavioral deficits in a genetic mitochondrial model of Parkinson’s disease. Faseb J 25:1333–1344. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.10-173625
Grozdanov V, Bliederhaeuser C, Ruf WP, Roth V, Fundel-Clemens K, Zondler L, Brenner D, Martin-Villalba A, Hengerer B, Kassubek J, Ludolph AC, Weishaupt JH, Danzer KM (2014) Inflammatory dysregulation of blood monocytes in Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol 128:651–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1345-4
Gu G, Reyes PE, Golden GT, Woltjer RL, Hulette C, Montine TJ, Zhang J (2002) Mitochondrial DNA deletions/rearrangements in parkinson disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:634–639
Guehl D, Bezard E, Dovero S, Boraud T, Bioulac B, Gross C (1999) Trichloroethylene and parkinsonism: a human and experimental observation. Eur J Neurol 6:609–611
Gully JC, Sergeyev VG, Bhootada Y, Mendez-Gomez H, Meyers CA, Zolotukhin S, Gorbatyuk MS, Gorbatyuk OS (2016) Up-regulation of activating transcription factor 4 induces severe loss of dopamine nigral neurons in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 627:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.05.039
Hall K, Yang S, Sauchanka O, Spillantini MG, Anichtchik O (2015) Behavioural deficits in transgenic mice expressing human truncated (1–120 amino acid) alpha-synuclein. Exp Neurol 264:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.11.003
Hashida K, Kitao Y, Sudo H, Awa Y, Maeda S, Mori K, Takahashi R, Iinuma M, Hori O (2012) ATF6alpha promotes astroglial activation and neuronal survival in a chronic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 7:e47950. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047950
Hoozemans JJ, van Haastert ES, Eikelenboom P, de Vos RA, Rozemuller JM, Scheper W (2007) Activation of the unfolded protein response in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:707–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.043
Howell N, Elson JL, Chinnery PF, Turnbull DM (2005) mtDNA mutations and common neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Genet 21:583–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2005.08.012
Hwang DY, Ardayfio P, Kang UJ, Semina EV, Kim KS (2003) Selective loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of Pitx3-deficient aphakia mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 114:123–131
Iglesias-Gonzalez J, Sanchez-Iglesias S, Mendez-Alvarez E, Rose S, Hikima A, Jenner P, Soto-Otero R (2012) Differential toxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells and rat brain mitochondria: protective role of catalase and superoxide dismutase. Neurochem Res 37:2150–2160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0838-6
Ikeda M, Kawarabayashi T, Harigaya Y, Sasaki A, Yamada S, Matsubara E, Murakami T, Tanaka Y, Kurata T, Wuhua X, Ueda K, Kuribara H, Ikarashi Y, Nakazato Y, Okamoto K, Abe K, Shoji M (2009) Motor impairment and aberrant production of neurochemicals in human alpha-synuclein A30P+ A53T transgenic mice with alpha-synuclein pathology. Brain Res 1250:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.10.011
Ikemura M, Saito Y, Sengoku R, Sakiyama Y, Hatsuta H, Kanemaru K, Sawabe M, Arai T, Ito G, Iwatsubo T, Fukayama M, Murayama S (2008) Lewy body pathology involves cutaneous nerves. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:945–953. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e318186de48
Janezic S, Threlfell S, Dodson PD, Dowie MJ, Taylor TN, Potgieter D, Parkkinen L, Senior SL, Anwar S, Ryan B, Deltheil T, Kosillo P, Cioroch M, Wagner K, Ansorge O, Bannerman DM, Bolam JP, Magill PJ, Cragg SJ, Wade-Martins R (2013) Deficits in dopaminergic transmission precede neuron loss and dysfunction in a new Parkinson model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E4016–E4025. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1309143110
Jellinger K, Linert L, Kienzl E, Herlinger E, Youdim MB (1995) Chemical evidence for 6-hydroxydopamine to be an endogenous toxic factor in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 46:297–314
Jiang P, Gan M, Ebrahim AS, Lin WL, Melrose HL, Yen SH (2010) ER stress response plays an important role in aggregation of alpha-synuclein. Mol Neurodegener 5:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-5-56
Jiang P, Gan M, Lin WL, Yen SH (2014) Nutrient deprivation induces alpha-synuclein aggregation through endoplasmic reticulum stress response and SREBP2 pathway. Front Aging Neurosci 6:268. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00268
Jiang P, Gan M, Yen SH, Moussaud S, McLean PJ, Dickson DW (2016) Proaggregant nuclear factor(s) trigger rapid formation of alpha-synuclein aggregates in apoptotic neurons. Acta Neuropathol 132:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1542-4
Kadkhodaei B, Ito T, Joodmardi E, Mattsson B, Rouillard C, Carta M, Muramatsu S, Sumi-Ichinose C, Nomura T, Metzger D, Chambon P, Lindqvist E, Larsson NG, Olson L, Bjorklund A, Ichinose H, Perlmann T (2009) Nurr1 is required for maintenance of maturing and adult midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 29:15923–15932. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3910-09.2009
Kalivendi SV, Cunningham S, Kotamraju S, Joseph J, Hillard CJ, Kalyanaraman B (2004) Alpha-synuclein up-regulation and aggregation during MPP+-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells: intermediacy of transferrin receptor iron and hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem 279:15240–15247. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312497200
Keeney PM, Xie J, Capaldi RA, Bennett JP Jr (2006) Parkinson’s disease brain mitochondrial complex I has oxidatively damaged subunits and is functionally impaired and misassembled. J Neurosci 26:5256–5264. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0984-06.2006
Kett LR, Stiller B, Bernath MM, Tasset I, Blesa J, Jackson-Lewis V, Chan RB, Zhou B, Di Paolo G, Przedborski S, Cuervo AM, Dauer WT (2015) alpha-Synuclein-independent histopathological and motor deficits in mice lacking the endolysosomal Parkinsonism protein Atp13a2. J Neurosci 35:5724–5742. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0632-14.2015
Kim HW, Choi WS, Sorscher N, Park HJ, Tronche F, Palmiter RD, Xia Z (2015) Genetic reduction of mitochondrial complex I function does not lead to loss of dopamine neurons in vivo. Neurobiol Aging 36:2617–2627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.05.008
Kim RH, Smith PD, Aleyasin H, Hayley S, Mount MP, Pownall S, Wakeham A, You-Ten AJ, Kalia SK, Horne P, Westaway D, Lozano AM, Anisman H, Park DS, Mak TW (2005) Hypersensitivity of DJ-1-deficient mice to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrindine (MPTP) and oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5215–5220. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0501282102
Kirik D, Rosenblad C, Burger C, Lundberg C, Johansen TE, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ, Bjorklund A (2002) Parkinson-like neurodegeneration induced by targeted overexpression of alpha-synuclein in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurosci 22:2780–2791
Klein C, Westenberger A (2012) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a008888. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008888
Krige D, Carroll MT, Cooper JM, Marsden CD, Schapira AH (1992) Platelet mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. The Royal Kings and Queens Parkinson Disease Research Group. Ann Neurol 32:782–788. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410320612
Krishnan S, Chi EY, Wood SJ, Kendrick BS, Li C, Garzon-Rodriguez W, Wypych J, Randolph TW, Narhi LO, Biere AL, Citron M, Carpenter JF (2003) Oxidative dimer formation is the critical rate-limiting step for Parkinson’s disease alpha-synuclein fibrillogenesis. Biochemistry 42:829–837. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi026528t
Kuhn W, Roebroek R, Blom H, van Oppenraaij D, Przuntek H, Kretschmer A, Buttner T, Woitalla D, Muller T (1998) Elevated plasma levels of homocysteine in Parkinson’s disease. Eur Neurol 40:225–227
Kupsch A, Schmidt W, Gizatullina Z, Debska-Vielhaber G, Voges J, Striggow F, Panther P, Schwegler H, Heinze HJ, Vielhaber S, Gellerich FN (2014) 6-Hydroxydopamine impairs mitochondrial function in the rat model of Parkinson’s disease: respirometric, histological, and behavioral analyses. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 121:1245–1257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1185-3
Langston JW (2006) The Parkinson’s complex: parkinsonism is just the tip of the iceberg. Ann Neurol 59:591–596. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20834
Langston JW, Langston EB, Irwin I (1984) MPTP-induced parkinsonism in human and non-human primates–clinical and experimental aspects. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 100:49–54
Lauwers E, Beque D, Van Laere K, Nuyts J, Bormans G, Mortelmans L, Casteels C, Vercammen L, Bockstael O, Nuttin B, Debyser Z, Baekelandt V (2007) Non-invasive imaging of neuropathology in a rat model of alpha-synuclein overexpression. Neurobiol Aging 28:248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.12.005
Lee MK, Stirling W, Xu Y, Xu X, Qui D, Mandir AS, Dawson TM, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL (2002) Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson’s disease-linked Ala-53 →Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8968–8973. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.132197599
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 395:451–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/26652
Li Y, Liu W, Oo TF, Wang L, Tang Y, Jackson-Lewis V, Zhou C, Geghman K, Bogdanov M, Przedborski S, Beal MF, Burke RE, Li C (2009) Mutant LRRK2(R1441G) BAC transgenic mice recapitulate cardinal features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci 12:826–828. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2349
Lill CM, Roehr JT, McQueen MB, Kavvoura FK, Bagade S, Schjeide BM, Schjeide LM, Meissner E, Zauft U, Allen NC, Liu T, Schilling M, Anderson KJ, Beecham G, Berg D, Biernacka JM, Brice A, DeStefano AL, Do CB, Eriksson N, Factor SA, Farrer MJ, Foroud T, Gasser T, Hamza T, Hardy JA, Heutink P, Hill-Burns EM, Klein C, Latourelle JC, Maraganore DM, Martin ER, Martinez M, Myers RH, Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Payami H, Satake W, Scott WK, Sharma M, Singleton AB, Stefansson K, Toda T, Tung JY, Vance J, Wood NW, Zabetian CP, Young P, Tanzi RE, Khoury MJ, Zipp F, Lehrach H, Ioannidis JP, Bertram L (2012) Comprehensive research synopsis and systematic meta-analyses in Parkinson’s disease genetics: the PDGene database. PLoS Genet 8:e1002548. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002548
Lim KL (2007) Ubiquitin-proteasome system dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: current evidence and controversies. Expert Rev Proteom 4:769–781. https://doi.org/10.1586/14789450.4.6.769
Lin X, Parisiadou L, Sgobio C, Liu G, Yu J, Sun L, Shim H, Gu XL, Luo J, Long CX, Ding J, Mateo Y, Sullivan PH, Wu LG, Goldstein DS, Lovinger D, Cai H (2012) Conditional expression of Parkinson’s disease-related mutant alpha-synuclein in the midbrain dopaminergic neurons causes progressive neurodegeneration and degradation of transcription factor nuclear receptor related 1. J Neurosci 32:9248–9264. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1731-12.2012
Liu M, Choi DY, Hunter RL, Pandya JD, Cass WA, Sullivan PG, Kim HC, Gash DM, Bing G (2010) Trichloroethylene induces dopaminergic neurodegeneration in Fisher 344 rats. J Neurochem 112:773–783. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06497.x
Lorenc-Koci E, Lenda T, Antkiewicz-Michaluk L, Wardas J, Domin H, Smialowska M, Konieczny J (2011) Different effects of intranigral and intrastriatal administration of the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin on typical neurochemical and histological markers of Parkinson’s disease in rats. Neurochem Int 58:839–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2011.03.013
Lu XH, Fleming SM, Meurers B, Ackerson LC, Mortazavi F, Lo V, Hernandez D, Sulzer D, Jackson GR, Maidment NT, Chesselet MF, Yang XW (2009) Bacterial artificial chromosome transgenic mice expressing a truncated mutant parkin exhibit age-dependent hypokinetic motor deficits, dopaminergic neuron degeneration, and accumulation of proteinase K-resistant alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 29:1962–1976. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5351-08.2009
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209:975–986. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20112457
Luk KC, Lee VM (2014) Modeling Lewy pathology propagation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(Suppl 1):S85–S87. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-8020(13)70022-1
Lynch-Day MA, Mao K, Wang K, Zhao M, Klionsky DJ (2012) The role of autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a009357. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009357
Magnoni R, Palmfeldt J, Christensen JH, Sand M, Maltecca F, Corydon TJ, West M, Casari G, Bross P (2013) Late onset motoneuron disorder caused by mitochondrial Hsp60 chaperone deficiency in mice. Neurobiol Dis 54:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2013.02.012
Manning-Bog AB, Caudle WM, Perez XA, Reaney SH, Paletzki R, Isla MZ, Chou VP, McCormack AL, Miller GW, Langston JW, Gerfen CR, Dimonte DA (2007) Increased vulnerability of nigrostriatal terminals in DJ-1-deficient mice is mediated by the dopamine transporter. Neurobiol Dis 27:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2007.03.014
Manning-Bog AB, McCormack AL, Li J, Uversky VN, Fink AL, Di Monte DA (2002) The herbicide paraquat causes up-regulation and aggregation of alpha-synuclein in mice: paraquat and alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 277:1641–1644. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C100560200
Manzoni C (2012) LRRK2 and autophagy: a common pathway for disease. Biochem Soc Trans 40:1147–1151. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20120126
Maraganore DM, Lesnick TG, Elbaz A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Gasser T, Kruger R, Hattori N, Mellick GD, Quattrone A, Satoh J, Toda T, Wang J, Ioannidis JP, de Andrade M, Rocca WA (2004) UCHL1 is a Parkinson’s disease susceptibility gene. Ann Neurol 55:512–521. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20017
Martella G, Platania P, Vita D, Sciamanna G, Cuomo D, Tassone A, Tscherter A, Kitada T, Bonsi P, Shen J, Pisani A (2009) Enhanced sensitivity to group II mGlu receptor activation at corticostriatal synapses in mice lacking the familial parkinsonism-linked genes PINK1 or Parkin. Exp Neurol 215:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.11.001
Martinez TN, Greenamyre JT (2012) Toxin models of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 16:920–934. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2011.4033
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A, Sagara Y, Sisk A, Mucke L (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287:1265–1269
Matsuoka Y, Vila M, Lincoln S, McCormack A, Picciano M, LaFrancois J, Yu X, Dickson D, Langston WJ, McGowan E, Farrer M, Hardy J, Duff K, Przedborski S, Di Monte DA (2001) Lack of nigral pathology in transgenic mice expressing human alpha-synuclein driven by the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. Neurobiol Dis 8:535–539. https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.2001.0392
McCormack AL, Thiruchelvam M, Manning-Bog AB, Thiffault C, Langston JW, Cory-Slechta DA, Di Monte DA (2002) Environmental risk factors and Parkinson’s disease: selective degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons caused by the herbicide paraquat. Neurobiol Dis 10:119–127
McDowell K, Chesselet MF (2012) Animal models of the non-motor features of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 46:597–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.040
McNaught KS, Belizaire R, Jenner P, Olanow CW, Isacson O (2002) Selective loss of 20S proteasome alpha-subunits in the substantia nigra pars compacta in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 326:155–158
McNaught KS, Jackson T, JnoBaptiste R, Kapustin A, Olanow CW (2006) Proteasomal dysfunction in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 66:S37–S49
McNaught KS, Olanow CW, Halliwell B, Isacson O, Jenner P (2001) Failure of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/35086067
McNaught KS, Perl DP, Brownell AL, Olanow CW (2004) Systemic exposure to proteasome inhibitors causes a progressive model of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 56:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20186
Mercado G, Valdes P, Hetz C (2013) An ERcentric view of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med 19:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2012.12.005
Meredith GE, Rademacher DJ (2011) MPTP mouse models of Parkinson’s disease: an update. J Parkinsons Dis 1:19–33. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-2011-11023
Miller GW (2007) Paraquat: the red herring of Parkinson’s disease research. Toxicol Sci 100:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm223
Mizuno Y, Ohta S, Tanaka M, Takamiya S, Suzuki K, Sato T, Oya H, Ozawa T, Kagawa Y (1989) Deficiencies in complex I subunits of the respiratory chain in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1450–1455
Moisoi N, Fedele V, Edwards J, Martins LM (2014) Loss of PINK1 enhances neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease triggered by mitochondrial stress. Neuropharmacology 77:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.10.009
Moon HE, Paek SH (2015) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 24:103–116. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2015.24.2.103
Moscovitz O, Ben-Nissan G, Fainer I, Pollack D, Mizrachi L, Sharon M (2015) The Parkinson’s-associated protein DJ-1 regulates the 20S proteasome. Nat Commun 6:6609. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7609
Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Lill CM, Do CB, Hernandez DG, Saad M, DeStefano AL, Kara E, Bras J, Sharma M, Schulte C, Keller MF, Arepalli S, Letson C, Edsall C, Stefansson H, Liu X, Pliner H, Lee JH, Cheng R, Ikram MA, Ioannidis JP, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Bis JC, Martinez M, Perlmutter JS, Goate A, Marder K, Fiske B, Sutherland M, Xiromerisiou G, Myers RH, Clark LN, Stefansson K, Hardy JA, Heutink P, Chen H, Wood NW, Houlden H, Payami H, Brice A, Scott WK, Gasser T, Bertram L, Eriksson N, Foroud T, Singleton AB (2014) Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 46:989–993. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3043
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183:795–803. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200809125
Nordstrom U, Beauvais G, Ghosh A, Pulikkaparambil Sasidharan BC, Lundblad M, Fuchs J, Joshi RL, Lipton JW, Roholt A, Medicetty S, Feinstein TN, Steiner JA, Escobar Galvis ML, Prochiantz A, Brundin P (2015) Progressive nigrostriatal terminal dysfunction and degeneration in the engrailed1 heterozygous mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 73:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.09.012
Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE (2003) Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. New Engl J Med 348:1356–1364. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM2003ra020003
Obeso JA, Stamelou M, Goetz CG, Poewe W, Lang AE, Weintraub D, Burn D, Halliday GM, Bezard E, Przedborski S, Lehericy S, Brooks DJ, Rothwell JC, Hallett M, DeLong MR, Marras C, Tanner CM, Ross GW, Langston JW, Klein C, Bonifati V, Jankovic J, Lozano AM, Deuschl G, Bergman H, Tolosa E, Rodriguez-Violante M, Fahn S, Postuma RB, Berg D, Marek K, Standaert DG, Surmeier DJ, Olanow CW, Kordower JH, Calabresi P, Schapira AHV, Stoessl AJ (2017) Past, present, and future of Parkinson’s disease: a special essay on the 200th anniversary of the Shaking Palsy. Mov Disord 32:1264–1310. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27115
Osellame LD, Rahim AA, Hargreaves IP, Gegg ME, Richard-Londt A, Brandner S, Waddington SN, Schapira AH, Duchen MR (2013) Mitochondria and quality control defects in a mouse model of Gaucher disease–links to Parkinson’s disease. Cell Metab 17:941–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.014
Paine SM, Anderson G, Bedford K, Lawler K, Mayer RJ, Lowe J, Bedford L (2013) Pale body-like inclusion formation and neurodegeneration following depletion of 26S proteasomes in mouse brain neurones are independent of alpha-synuclein. PLoS One 8:e54711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054711
Palmeira CM, Moreno AJ, Madeira VMC (1995) Mitochondrial bioenergetics is affected by the herbicide paraquat. Bba Bioenergetics 1229:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2728(94)00202-G
Palomo-Garo C, Gomez-Galvez Y, Garcia C, Fernandez-Ruiz J (2016) Targeting the cannabinoid CB2 receptor to attenuate the progression of motor deficits in LRRK2-transgenic mice. Pharmacol Res 110:181–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.04.004
Pan TH, Kondo S, Le WD, Jankovic J (2008) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:1969–1978. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm318
Park JS, Blair NF, Sue CM (2015) The role of ATP13A2 in Parkinson’s disease: clinical phenotypes and molecular mechanisms. Mov Disord 30:770–779. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26243
Parker WD Jr, Boyson SJ, Parks JK (1989) Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 26:719–723. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410260606
Patterson VL, Zullo AJ, Koenig C, Stoessel S, Jo H, Liu X, Han J, Choi M, DeWan AT, Thomas JL, Kuan CY, Hoh J (2014) Neural-specific deletion of Htra2 causes cerebellar neurodegeneration and defective processing of mitochondrial OPA1. PLoS One 9:e115789. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0115789
Perez FA, Palmiter RD (2005) Parkin-deficient mice are not a robust model of parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2174–2179. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409598102
Perier C, Vila M (2012) Mitochondrial biology and Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a009332. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009332
Pfeiffer RF (2016) Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 22(Suppl 1):S119–S122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.09.004
Pickrell AM, Pinto M, Hida A, Moraes CT (2011) Striatal dysfunctions associated with mitochondrial DNA damage in dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 31:17649–17658. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4871-11.2011
Pollanen MS, Dickson DW, Bergeron C (1993) Pathology and biology of the Lewy body. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52:183–191
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Poulopoulos M, Levy OA, Alcalay RN (2012) The neuropathology of genetic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27:831–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.24962
Przedborski S, Levivier M, Jiang H, Ferreira M, Jackson-Lewis V, Donaldson D, Togasaki DM (1995) Dose-dependent lesions of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway induced by intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Neuroscience 67:631–647
Puschmann A, Fiesel FC, Caulfield TR, Hudec R, Ando M, Truban D, Hou X, Ogaki K, Heckman MG, James ED, Swanberg M, Jimenez-Ferrer I, Hansson O, Opala G, Siuda J, Boczarska-Jedynak M, Friedman A, Koziorowski D, Aasly JO, Lynch T, Mellick GD, Mohan M, Silburn PA, Sanotsky Y, Vilarino-Guell C, Farrer MJ, Chen L, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Wszolek ZK, Ross OA, Springer W (2017) Heterozygous PINK1 p. G411S increases risk of Parkinson’s disease via a dominant-negative mechanism. Brain 140:98–117. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww261
Qiao L, Hamamichi S, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA, Yacoubian TA, Wilson S, Xie ZL, Speake LD, Parks R, Crabtree D, Liang Q, Crimmins S, Schneider L, Uchiyama Y, Iwatsubo T, Zhou Y, Peng L, Lu Y, Standaert DG, Walls KC, Shacka JJ, Roth KA, Zhang J (2008) Lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D protects against alpha-synuclein aggregation and toxicity. Mol Brain 1:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-1-17
Ramirez A, Heimbach A, Grundemann J, Stiller B, Hampshire D, Cid LP, Goebel I, Mubaidin AF, Wriekat AL, Roeper J, Al-Din A, Hillmer AM, Karsak M, Liss B, Woods CG, Behrens MI, Kubisch C (2006) Hereditary parkinsonism with dementia is caused by mutations in ATP13A2, encoding a lysosomal type 5 P-type ATPase. Nat Genet 38:1184–1191. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1884
Ramonet D, Daher JP, Lin BM, Stafa K, Kim J, Banerjee R, Westerlund M, Pletnikova O, Glauser L, Yang L, Liu Y, Swing DA, Beal MF, Troncoso JC, McCaffery JM, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Galter D, Thomas B, Lee MK, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Moore DJ (2011) Dopaminergic neuronal loss, reduced neurite complexity and autophagic abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing G2019S mutant LRRK2. PLoS One 6:e18568. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018568
Richardson JR, Quan Y, Sherer TB, Greenamyre JT, Miller GW (2005) Paraquat neurotoxicity is distinct from that of MPTP and rotenone. Toxicol Sci 88:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfi304
Richter G, Sonnenschein A, Grunewald T, Reichmann H, Janetzky B (2002) Novel mitochondrial DNA mutations in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 109:721–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020200060
Rocha EM, Smith GA, Park E, Cao H, Graham AR, Brown E, McLean JR, Hayes MA, Beagan J, Izen SC, Perez-Torres E, Hallett PJ, Isacson O (2015) Sustained systemic glucocerebrosidase inhibition induces brain alpha-synuclein aggregation, microglia and complement C1q activation in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 23:550–564. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6307
Salganik M, Sergeyev VG, Shinde V, Meyers CA, Gorbatyuk MS, Lin JH, Zolotukhin S, Gorbatyuk OS (2015) The loss of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) during normal aging or from siRNA knockdown augments human alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) toxicity to rat nigral neurons. Neurobiol Aging 36:2213–2223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.018
Salman H, Bergman M, Djaldetti R, Bessler H, Djaldetti M (1999) Decreased phagocytic function in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 53:146–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0753-3322(99)80080-8
Sauer H, Oertel WH (1994) Progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons following intrastriatal terminal lesions with 6-hydroxydopamine: a combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Neuroscience 59:401–415
Schapira AH (2015) Glucocerebrosidase and Parkinson disease: recent advances. Mol Cell Neurosci 66:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2015.03.013
Schapira AH, Cleeter MW, Muddle JR, Workman JM, Cooper JM, King RH (2006) Proteasomal inhibition causes loss of nigral tyrosine hydroxylase neurons. Ann Neurol 60:253–255. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20934
Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Jenner P, Clark JB, Marsden CD (1989) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 1:1269
Schapira AHV, Chaudhuri KR, Jenner P (2017) Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:435–450. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.62
Selvaraj S, Sun Y, Watt JA, Wang S, Lei S, Birnbaumer L, Singh BB (2012) Neurotoxin-induced ER stress in mouse dopaminergic neurons involves downregulation of TRPC1 and inhibition of AKT/mTOR signaling. J Clin Investig 122:1354–1367. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI61332
Setsuie R, Wang YL, Mochizuki H, Osaka H, Hayakawa H, Ichihara N, Li H, Furuta A, Sano Y, Sun YJ, Kwon J, Kabuta T, Yoshimi K, Aoki S, Mizuno Y, Noda M, Wada K (2007) Dopaminergic neuronal loss in transgenic mice expressing the Parkinson’s disease-associated UCH-L1 I93M mutant. Neurochem Int 50:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2006.07.015
Sevlever D, Jiang P, Yen SH (2008) Cathepsin D is the main lysosomal enzyme involved in the degradation of alpha-synuclein and generation of its carboxy-terminally truncated species. Biochemistry 47:9678–9687. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi800699v
Shi CH, Mao CY, Zhang SY, Yang J, Song B, Wu P, Zuo CT, Liu YT, Ji Y, Yang ZH, Wu J, Zhuang ZP, Xu YM (2016) CHCHD2 gene mutations in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 38:217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.10.040 (e219–213)
Shimshek DR, Schweizer T, Schmid P, van der Putten PH (2012) Excess alpha-synuclein worsens disease in mice lacking ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1. Sci Rep 2:262. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00262
Sidransky E, Nalls MA, Aasly JO, Aharon-Peretz J, Annesi G, Barbosa ER, Bar-Shira A, Berg D, Bras J, Brice A, Chen CM, Clark LN, Condroyer C, De Marco EV, Durr A, Eblan MJ, Fahn S, Farrer MJ, Fung HC, Gan-Or Z, Gasser T, Gershoni-Baruch R, Giladi N, Griffith A, Gurevich T, Januario C, Kropp P, Lang AE, Lee-Chen GJ, Lesage S, Marder K, Mata IF, Mirelman A, Mitsui J, Mizuta I, Nicoletti G, Oliveira C, Ottman R, Orr-Urtreger A, Pereira LV, Quattrone A, Rogaeva E, Rolfs A, Rosenbaum H, Rozenberg R, Samii A, Samaddar T, Schulte C, Sharma M, Singleton A, Spitz M, Tan EK, Tayebi N, Toda T, Troiano AR, Tsuji S, Wittstock M, Wolfsberg TG, Wu YR, Zabetian CP, Zhao Y, Ziegler SG (2009) Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson’s Disease. New Engl J Med 361:1651–1661. https://doi.org/10.1056/Nejmoa0901281
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K (2003) Alpha-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:841. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1090278
Slodzinski H, Moran LB, Michael GJ, Wang B, Novoselov S, Cheetham ME, Pearce RK, Graeber MB (2009) Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum protein (herp) is up-regulated in parkinsonian substantia nigra and present in the core of Lewy bodies. Clin Neuropathol 28:333–343
Smith GA, Isacson O, Dunnett SB (2012) The search for genetic mouse models of prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 237:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.06.035
Sokolowski JD, Mandell JW (2011) Phagocytic clearance in neurodegeneration. Am J Pathol 178:1416–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.12.051
Song L, Cortopassi G (2015) Mitochondrial complex I defects increase ubiquitin in substantia nigra. Brain Res 1594:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.013
Song L, Shan Y, Lloyd KC, Cortopassi GA (2012) Mutant twinkle increases dopaminergic neurodegeneration, mtDNA deletions and modulates Parkin expression. Hum Mol Genet 21:5147–5158. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/dds365
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/42166
Strauss KM, Martins LM, Plun-Favreau H, Marx FP, Kautzmann S, Berg D, Gasser T, Wszolek Z, Muller T, Bornemann A, Wolburg H, Downward J, Riess O, Schulz JB, Kruger R (2005) Loss of function mutations in the gene encoding Omi/HtrA2 in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 14:2099–2111. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddi215
Sun F, Anantharam V, Zhang D, Latchoumycandane C, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG (2006) Proteasome inhibitor MG-132 induces dopaminergic degeneration in cell culture and animal models. Neurotoxicology 27:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2006.06.006
Szondy Z, Garabuczi E, Joos G, Tsay GJ, Sarang Z (2014) Impaired clearance of apoptotic cells in chronic inflammatory diseases: therapeutic implications. Front Immunol 5:354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00354
Tagliaferro P, Kareva T, Oo TF, Yarygina O, Kholodilov N, Burke RE (2015) An early axonopathy in a hLRRK2(R1441G) transgenic model of Parkinson disease. Neurobiol Dis 82:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.07.009
Taylor TN, Caudle WM, Miller GW (2011) VMAT2-deficient mice display nigral and extranigral pathology and motor and nonmotor symptoms of parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis 2011:124165. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/124165
Thiruchelvam M, Brockel BJ, Richfield EK, Baggs RB, Cory-Slechta DA (2000) Potentiated and preferential effects of combined paraquat and maneb on nigrostriatal dopamine systems: environmental risk factors for Parkinson’s disease? Brain Res 873:225–234
Thiruchelvam MJ, Powers JM, Cory-Slechta DA, Richfield EK (2004) Risk factors for dopaminergic neuron loss in human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. Eur J Neurosci 19:845–854
Tofaris GK, Garcia Reitbock P, Humby T, Lambourne SL, O’Connell M, Ghetti B, Gossage H, Emson PC, Wilkinson LS, Goedert M, Spillantini MG (2006) Pathological changes in dopaminergic nerve cells of the substantia nigra and olfactory bulb in mice transgenic for truncated human alpha-synuclein (1–120): implications for Lewy body disorders. J Neurosci 26:3942–3950. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4965-05.2006
Toledo JB, Gopal P, Raible K, Irwin DJ, Brettschneider J, Sedor S, Waits K, Boluda S, Grossman M, Van Deerlin VM, Lee EB, Arnold SE, Duda JE, Hurtig H, Lee VM, Adler CH, Beach TG, Trojanowski JQ (2016) Pathological alpha-synuclein distribution in subjects with coincident Alzheimer’s and Lewy body pathology. Acta Neuropathol 131:393–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1526-9
Ungerstedt U (1968) 6-Hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of central monoamine neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 5:107–110
Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG, Albanese A, Nussbaum R, Gonzalez-Maldonado R, Deller T, Salvi S, Cortelli P, Gilks WP, Latchman DS, Harvey RJ, Dallapiccola B, Auburger G, Wood NW (2004) Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304:1158–1160. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1096284
Valente EM, Salvi S, Ialongo T, Marongiu R, Elia AE, Caputo V, Romito L, Albanese A, Dallapiccola B, Bentivoglio AR (2004) PINK1 mutations are associated with sporadic early-onset parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 56:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20256
van den Munckhof P, Luk KC, Ste-Marie L, Montgomery J, Blanchet PJ, Sadikot AF, Drouin J (2003) Pitx3 is required for motor activity and for survival of a subset of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Development 130:2535–2542
Van Rompuy AS, Lobbestael E, Van der Perren A, Van den Haute C, Baekelandt V (2014) Long-term overexpression of human wild-type and T240R mutant Parkin in rat substantia nigra induces progressive dopaminergic neurodegeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 73:159–174. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0000000000000039
Varma D, Sen D (2015) Role of the unfolded protein response in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 75:1–26
Vekrellis K, Xilouri M, Emmanouilidou E, Rideout HJ, Stefanis L (2011) Pathological roles of alpha-synuclein in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 10:1015–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70213-7
Vernon AC, Johansson SM, Modo MM (2010) Non-invasive evaluation of nigrostriatal neuropathology in a proteasome inhibitor rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. BMC Neurosci 11:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-11-1
Villeneuve LM, Purnell PR, Boska MD, Fox HS (2016) Early Expression of Parkinson’s disease-related mitochondrial abnormalities in PINK1 knockout rats. Mol Neurobiol 53:171–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8927-y
Villeneuve LM, Purnell PR, Stauch KL, Fox HS (2016) Neonatal mitochondrial abnormalities due to PINK1 deficiency: proteomics reveals early changes relevant to Parkinsons disease. Data Brief 6:428–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2015.11.070
Wang X, Yen J, Kaiser P, Huang L (2010) Regulation of the 26S proteasome complex during oxidative stress. Sci Signal 3:ra88. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2001232
Webb JL, Ravikumar B, Atkins J, Skepper JN, Rubinsztein DC (2003) Alpha-synuclein is degraded by both autophagy and the proteasome. J Biol Chem 278:25009–25013. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M300227200
Wey MC, Fernandez E, Martinez PA, Sullivan P, Goldstein DS, Strong R (2012) Neurodegeneration and motor dysfunction in mice lacking cytosolic and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenases: implications for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 7:e31522. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031522
Yasuda T, Nihira T, Ren YR, Cao XQ, Wada K, Setsuie R, Kabuta T, Hattori N, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H (2009) Effects of UCH-L1 on alpha-synuclein over-expression mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 108:932–944. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05827.x
Zhang L, Le W, Xie W, Dani JA (2012) Age-related changes in dopamine signaling in Nurr1 deficient mice as a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(1001):e1007–e1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.03.022
Zhu JH, Guo FL, Shelburne J, Watkins S, Chu CT (2003) Localization of phosphorylated ERK/MAP kinases to mitochondria and autophagosomes in Lewy body diseases. Brain Pathol 13:473–481
Zhu XR, Maskri L, Herold C, Bader V, Stichel CC, Gunturkun O, Lubbert H (2007) Non-motor behavioural impairments in parkin-deficient mice. Eur J Neurosci 26:1902–1911. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05812.x
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Muller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.11.005
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Institute of Health (P50-NS072187 and R21-NS099757) and the Mangurian Foundation Lewy Body Dementia Program at Mayo Clinic (Dickson, Jiang). Neither author has actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, P., Dickson, D.W. Parkinson’s disease: experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol 135, 13–32 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1788-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-017-1788-5