Abstract
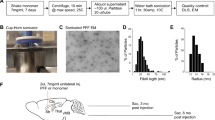
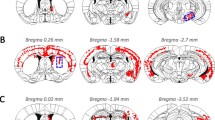
In order to further evaluate the parameters whereby intracerebral administration of recombinant α-synuclein (αS) induces pathological phenotypes in mice, we conducted a series of studies where αS fibrils were injected into the brains of M83 (A53T) and M47 (E46K) αS transgenic (Tg) mice, and non-transgenic (nTg) mice. Using multiple markers to assess αS inclusion formation, we find that injected fibrillar human αS induced widespread cerebral αS inclusion formation in the M83 Tg mice, but in both nTg and M47 Tg mice, induced αS inclusion pathology is largely restricted to the site of injection. Furthermore, mouse αS fibrils injected into nTg mice brains also resulted in inclusion pathology restricted to the site of injection with no evidence for spread. We find no compelling evidence for extensive spread of αS pathology within white matter tracts, and we attribute previous reports of white matter tract spreading to cross-reactivity of the αS pSer129/81A antibody with phosphorylated neurofilament subunit L. These studies suggest that, with the exception of the M83 Tg mice which appear to be uniquely susceptible to induction of inclusion pathology by exogenous forms of αS, there are significant barriers in mice to widespread induction of αS pathology following intracerebral administration of amyloidogenic αS.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Phillips H, Sulzer D, Rosenthal A (2000) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25(1):239–252
Aguzzi A, Heikenwalder M, Polymenidou M (2007) Insights into prion strains and neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(7):552–561. doi:10.1038/nrm2204
Alvarez-Erviti L, Couch Y, Richardson J, Cooper JM, Wood MJ (2011) Alpha-synuclein release by neurons activates the inflammatory response in a microglial cell line. Neurosci Res 69(4):337–342. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2010.12.020
Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, de Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, Diep L, Keim PS, Shen X, Chataway T, Schlossmacher MG, Seubert P, Schenk D, Sinha S, Gai WP, Chilcote TJ (2006) Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 281(40):29739–29752. doi:10.1074/jbc.M600933200
Appel-Cresswell S, Vilarino-Guell C, Encarnacion M, Sherman H, Yu I, Shah B, Weir D, Thompson C, Szu-Tu C, Trinh J, Aasly JO, Rajput A, Rajput AH, Jon SA, Farrer MJ (2013) Alpha-synuclein p. H50Q, a novel pathogenic mutation for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 28:811–813
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Vedders L, Lue L, White Iii CL, Akiyama H, Caviness JN, Shill HA, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG, Arizona Parkinson’s disease C (2010) Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 119(6):689–702. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0664-3
Beraud D, Twomey M, Bloom B, Mittereder A, Ton V, Neitzke K, Chasovskikh S, Mhyre TR, Maguire-Zeiss KA (2011) Alpha-Synuclein alters toll-like receptor expression. Front Neurosci 5:80
Bousset L, Pieri L, Ruiz-Arlandis G, Gath J, Jensen PH, Habenstein B, Madiona K, Olieric V, Bockmann A, Meier BH, Melki R (2013) Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nature Commun 4:2575. doi:10.1038/ncomms3575
Brundin P, Li JY, Holton JL, Lindvall O, Revesz T (2008) Research in motion: the enigma of Parkinson’s disease pathology spread. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(10):741–745
Codolo G, Plotegher N, Pozzobon T, Brucale M, Tessari I, Bubacco L, de Bernard M (2013) Triggering of inflammasome by aggregated alpha-synuclein, an inflammatory response in synucleinopathies. PLoS One 8(1):e55375
Comellas G, Lemkau LR, Nieuwkoop AJ, Kloepper KD, Ladror DT, Ebisu R, Woods WS, Lipton AS, George JM, Rienstra CM (2011) Structured regions of alpha-synuclein fibrils include the early-onset Parkinson’s disease mutation sites. J Mol Biol 411(4):881–895. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.06.026
Conway KA, Harper JD, Lansbury PT (1998) Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat Med 4(11):1318–1320
Cookson MR (2005) The biochemistry of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Biochem 74:29–52
Couch Y, Alvarez-Erviti L, Sibson NR, Wood MJ, Anthony DC (2011) The acute inflammatory response to intranigral alpha-synuclein differs significantly from intranigral lipopolysaccharide and is exacerbated by peripheral inflammation. J Neuroinflammation 8:166. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-8-166
Cremades N, Cohen SI, Deas E, Abramov AY, Chen AY, Orte A, Sandal M, Clarke RW, Dunne P, Aprile FA, Bertoncini CW, Wood NW, Knowles TP, Dobson CM, Klenerman D (2012) Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of alpha-synuclein. Cell 149(5):1048–1059. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.037
Crystal AS, Giasson BI, Crowe A, Kung MP, Zhuang ZP, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2003) A comparison of amyloid fibrillogenesis using the novel fluorescent compound K114. J Neurochem 86(6):1359–1368
Danzer KM, Haasen D, Karow AR, Moussaud S, Habeck M, Giese A, Kretzschmar H, Hengerer B, Kostka M (2007) Different species of alpha-synuclein oligomers induce calcium influx and seeding. J Neurosci 27(34):9220–9232. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2617-07.2007
Davidson WS, Jonas A, Clayton DF, George JM (1998) Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J Biol Chem 273(16):9443–9449
Dryanovski DI, Guzman JN, Xie Z, Galteri DJ, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Lee VM, Miller RJ, Schumacker PT, Surmeier DJ (2013) Calcium entry and alpha-synuclein inclusions elevate dendritic mitochondrial oxidant stress in dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 33(24):10154–10164. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5311-12.2013
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Gur TL, Montine TJ, Robertson D, Biaggioni I, Hurtig HI, Stern MB, Gollomp SM, Grossman M, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ (2000) Immunohistochemical and biochemical studies demonstrate a distinct profile of alpha-synuclein permutations in multiple system atrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59(9):830–841
Duda JE, Giasson BI, Mabon ME, Lee VMY, Trojanoswki JQ (2002) Novel antibodies to oxidized α-synuclein reveal abundant neuritic pathology in Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol 52:205–210
El-Agnaf OM, Jakes R, Curran MD, Middleton D, Ingenito R, Bianchi E, Pessi A, Neill D, Wallace A (1998) Aggregates from mutant and wild-type alpha-synuclein proteins and NAC peptide induce apoptotic cell death in human neuroblastoma cells by formation of beta-sheet and amyloid-like filaments. FEBS Lett 440(1–2):71–75
Emmer KL, Waxman EA, Covy JP, Giasson BI (2011) E46K human alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop Lewy-like and tau pathology associated with age-dependent, detrimental motor impairment. J Biol Chem 286(40):35104–35118
Eyer J, Peterson A (1994) Neurofilament-deficient axons and perikaryal aggregates in viable transgenic mice expressing a neurofilament-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Neuron 12(2):389–405
Farrer M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Hutton M, Hardy J (1999) The genetics of disorders with synuclein pathology and parkinsonism. Hum Mol Genet 8(10):1901–1905
Fellner L, Irschick R, Schanda K, Reindl M, Klimaschewski L, Poewe W, Wenning GK, Stefanova N (2013) Toll-like receptor 4 is required for alpha-synuclein dependent activation of microglia and astroglia. Glia 61(3):349–360
Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T (2002) α-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol 4:160–164
Gao HM, Kotzbauer PT, Uryu K, Leight S, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2008) Neuroinflammation and oxidation/nitration of alpha-synuclein linked to dopaminergic neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 28(30):7687–7698
Gao HM, Zhang F, Zhou H, Kam W, Wilson B, Hong JS (2011) Neuroinflammation and alpha-synuclein dysfunction potentiate each other, driving chronic progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Environ Health Perspect 119(6):807–814
Geisler N, Plessmann U, Weber K (1985) The complete amino acid sequence of the major mammalian neurofilament protein (NF-L). FEBS Lett 182(2):475–478
George JM, Jin H, Woods WS, Clayton DF (1995) Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron 15(2):361–372
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Forman MS, Lee VMY, Trojanoswki JQ (2001) Prominent perikaryal expression of α- and ß-synuclein in neurons of dorsal root ganglion and in medullary neurons. Exp Neurol 172:354–362
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Quinn SM, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2002) Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron 34(4):521–533
Giasson BI, Jakes R, Goedert M, Duda JE, Leight S, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2000) A panel of epitope-specific antibodies detects protein domains distributed throughout human alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 59(4):528–533
Giasson BI, Murray IV, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (2001) A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J Biol Chem 276:2380–2386
Giasson BI, Uryu K, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY (1999) Mutant and wild type human alpha-synucleins assemble into elongated filaments with distinct morphologies in vitro. J Biol Chem 274(12):7619–7622
Goedert M (1997) Familial Parkinson’s disease. The awakening of alpha-synuclein. Nature 388(6639):232–233
Golde TE, Borchelt DR, Giasson BI, Lewis J (2013) Thinking laterally about neurodegenerative proteinopathies. J Clin Invest 123:1847–1855
Greenbaum EA, Graves CL, Mishizen-Eberz AJ, Lupoli MA, Lynch DR, Englander SW, Axelsen PH, Giasson BI (2005) The E46K mutation in alpha-synuclein increases amyloid fibril formation. JBiolChem 280(9):7800–7807
Guo JL, Covell DJ, Daniels JP, Iba M, Stieber A, Zhang B, Riddle DM, Kwong LK, Xu Y, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2013) Distinct alpha-synuclein strains differentially promote tau inclusions in neurons. Cell 154(1):103–117. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.057
Hansen C, Angot E, Bergstrom AL, Steiner JA, Pieri L, Paul G, Outeiro TF, Melki R, Kallunki P, Fog K, Li JY, Brundin P (2011) Alpha-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J Clin Invest 121(2):715–725
Hilton D, Stephens M, Kirk L, Edwards P, Potter R, Zajicek J, Broughton E, Hagan H, Carroll C (2013) Accumulation of alpha-synuclein in the bowel of patients in the pre-clinical phase of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1214-6
Hoyer W, Antony T, Cherny D, Heim G, Jovin TM, Subramaniam V (2002) Dependence of alpha-synuclein aggregate morphology on solution conditions. J Mol Biol 322(2):383–393
Ikemura M, Saito Y, Sengoku R, Sakiyama Y, Hatsuta H, Kanemaru K, Sawabe M, Arai T, Ito G, Iwatsubo T, Fukayama M, Murayama S (2008) Lewy body pathology involves cutaneous nerves. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67(10):945–953. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e318186de48
Ishii A, Nonaka T, Taniguchi S, Saito T, Arai T, Mann D, Iwatsubo T, Hisanaga S, Goedert M, Hasegawa M (2007) Casein kinase 2 is the major enzyme in brain that phosphorylates Ser129 of human alpha-synuclein: implication for alpha-synucleinopathies. FEBS Lett 581(24):4711–4717. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.08.067
Iwai A, Masliah E, Yoshimoto M, Ge N, Flanagan L, de Silva HA, Kittel A, Saitoh T (1995) The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 14(2):467–475
Jakes R, Spillantini MG, Goedert M (1994) Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett 345(1):27–32
Jucker M, Walker LC (2013) Self-propagation of pathogenic protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 501(7465):45–51. doi:10.1038/nature12481
Julien JP, Grosveld F, Yazdanbaksh K, Flavell D, Meijer D, Mushynski W (1987) The structure of a human neurofilament gene (NF-L): a unique exon-intron organization in the intermediate filament gene family. Biochim Biophys Acta 909(1):10–20
Julien JPMD, Flavel D, Hurst J, Grosveld F (1986) Cloning and developmental expression of the murine neurofilament gene family. Mol Brain Res 1:243–250
Kayed R, Head E, Thompson JL, McIntire TM, Milton SC, Cotman CW, Glabe CG (2003) Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis. Science 300(5618):486–489
Kiely AP, Asi YT, Kara E, Limousin P, Ling H, Lewis P, Proukakis C, Quinn N, Lees AJ, Hardy J, Revesz T, Houlden H, Holton JL (2013) Alpha-synucleinopathy associated with G51D SNCA mutation: a link between Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy? Acta Neuropathol 125:753–769
Kim C, Ho DH, Suk JE, You S, Michael S, Kang J, Joong LS, Masliah E, Hwang D, Lee HJ, Lee SJ (2013) Neuron-released oligomeric alpha-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia. Nat Commun 4:1562
Klegeris A, Giasson BI, Zhang H, Maguire J, Pelech S, McGeer PL (2006) Alpha-synuclein and its disease-causing mutants induce ICAM-1 and IL-6 in human astrocytes and astrocytoma cells. FASEB J 20(12):2000–2008
Klegeris A, Pelech S, Giasson BI, Maguire J, Zhang H, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (2008) Alpha-synuclein activates stress signaling protein kinases in THP-1 cells and microglia. Neurobiol Aging 29(5):739–752
Kordower JH, Chu Y, Hauser RA, Freeman TB, Olanow CW (2008) Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med 14(5):504–506
Kruger R, Muller T, Riess O (2000) Involvement of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. J Neural Transm 107(1):31–40
Kuusisto E, Parkkinen L, Alafuzoff I (2003) Morphogenesis of Lewy bodies: dissimilar incorporation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and p62. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62(12):1241–1253
Lebouvier T, Chaumette T, Damier P, Coron E, Touchefeu Y, Vrignaud S, Naveilhan P, Galmiche JP, Bruley des Varannes S, Derkinderen P, Neunlist M (2008) Pathological lesions in colonic biopsies during Parkinson’s disease. Gut 57(12):1741–1743. doi:10.1136/gut.2008.162503
Lee SB, Park SM, Ahn KJ, Chung KC, Paik SR, Kim J (2009) Identification of the amino acid sequence motif of alpha-synuclein responsible for macrophage activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381(1):39–43
Lesage S, Anheim M, Letournel F, Bousset L, Honore A, Rozas N, Pieri L, Madiona K, Durr A, Melki R, Verny C, Brice A (2013) G51D alpha-synuclein mutation causes a novel parkinsonian-pyramidal syndrome. Ann Neurol 73(4):459–471
Li JY, Englund E, Holton JL, Soulet D, Hagell P, Lees AJ, Lashley T, Quinn NP, Rehncrona S, Bjorklund A, Widner H, Revesz T, Lindvall O, Brundin P (2008) Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat Med 14(5):501–503
Li JY, Englund E, Widner H, Rehncrona S, Bjorklund A, Lindvall O, Brundin P (2010) Characterization of Lewy body pathology in 12- and 16-year-old intrastriatal mesencephalic grafts surviving in a patient with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25(8):1091–1096
Liu CW, Giasson BI, Lewis KA, Lee VM, Demartino GN, Thomas PJ (2005) A precipitating role for truncated alpha-synuclein and the proteasome in alpha-synuclein aggregation: implications for pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem 280(24):22670–22678. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501508200
Lowe J, Blanchard A, Morrell K, Lennox G, Reynolds L, Billett M, Landon M, Mayer RJ (1988) Ubiquitin is a common factor in intermediate filament inclusion bodies of diverse type in man, including those of Parkinson’s disease, Pick’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as Rosenthal fibres in cerebellar astrocytomas, cytoplasmic bodies in muscle, and mallory bodies in alcoholic liver disease. J Pathol 155(1):9–15
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 338(6109):949–953
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209(5):975–986
Luk KC, Song C, O’Brien P, Stieber A, Branch JR, Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2009) Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(47):20051–20056
Masuda-Suzukake M, Nonaka T, Hosokawa M, Oikawa T, Arai T, Akiyama H, Mann DM, Hasegawa M (2013) Prion-like spreading of pathological alpha-synuclein in brain. Brain 136(Pt 4):1128–1138
Mougenot AL, Nicot S, Bencsik A, Morignat E, Verchere J, Lakhdar L, Legastelois S, Baron T (2012) Prion-like acceleration of a synucleinopathy in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 33(9):2225–2228
Mu L, Sobotka S, Chen J, Su H, Sanders I, Adler CH, Shill HA, Caviness JN, Samanta JE, Beach TG, Arizona Parkinson’s disease C (2013) Alpha-synuclein pathology and axonal degeneration of the peripheral motor nerves innervating pharyngeal muscles in Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 72(2):119–129. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182801cde
Nakamura Y, Hashimoto R, Kashiwagi Y, Wada Y, Sakoda S, Miyamae Y, Kudo T, Takeda M (1999) Casein kinase II is responsible for phosphorylation of NF-L at Ser-473. FEBS Lett 455(1–2):83–86
Ono K, Ikeda T, Takasaki J, Yamada M (2011) Familial Parkinson disease mutations influence alpha-synuclein assembly. Neurobiol Dis 43(3):715–724
Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW (2012) Prion-like spread of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. J Exp Med 209(5):889–893. doi:10.1084/jem.20120741
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276(5321):2045–2047
Proukakis C, Dudzik CG, Brier T, Mackay DS, Cooper JM, Millhauser GL, Houlden H, Schapira AH (2013) A novel alpha-synuclein missense mutation in Parkinson disease. Neurology 80(11):1062–1064
Recasens A, Dehay B, Bove J, Carballo-Carbajal I, Dovero S, Perez A, Fernagut PO, Blesa J, Parent A, Perier C, Farinas I, Obeso JA, Bezard E, Vila M (2013) Lewy body extracts from Parkinson’s disease brains trigger alpha-synuclein pathology and neurodegeneration in mice and monkeys. Ann Neurol. doi:10.1002/ana.24066
Reynolds AD, Glanzer JG, Kadiu I, Ricardo-Dukelow M, Chaudhuri A, Ciborowski P, Cerny R, Gelman B, Thomas MP, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE (2008) Nitrated alpha-synuclein-activated microglial profiling for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 104(6):1504–1525
Rochet JC, Conway KA, Lansbury PT (2000) Inhibition of fibrillization and accumulation of prefibrillar oligomers in mixtures of human and mouse alpha-synuclein. Biochemistry 39(35):10619–10626
Roodveldt C, Christodoulou J, Dobson CM (2008) Immunological features of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Mol Med 12(5B):1820–1829
Rubartelli A, Lotze MT (2007) Inside, outside, upside down: damage-associated molecular-pattern molecules (DAMPs) and redox. Trends Immunol 28(10):429–436
Sacino AN, Brooks M, McGarvey NH, McKinney AB, Thomas MA, Levites Y, Ran Y, Golde TE, Giasson BI (2013) Induction of CNS alpha-synuclein pathology by fibrillar and non-amyloidogenic recombinant alpha-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol Commun 1(1):38. doi:10.1186/2051-5960-1-38
Sacino AN, Thomas MA, Ceballos-Diaz C, Cruz PE, Rosario AM, Lewis J, Giasson BI, Golde TE (2013) Conformational templating of alpha-synuclein aggregates in neuronal-glial cultures. Mol Neurodegen 8:17. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-8-17
Sengoku R, Saito Y, Ikemura M, Hatsuta H, Sakiyama Y, Kanemaru K, Arai T, Sawabe M, Tanaka N, Mochizuki H, Inoue K, Murayama S (2008) Incidence and extent of Lewy body-related alpha-synucleinopathy in aging human olfactory bulb. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67(11):1072–1083. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e31818b4126
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K (2003) Alpha-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302(5646):841
Su X, Maguire-Zeiss KA, Giuliano R, Prifti L, Venkatesh K, Federoff HJ (2008) Synuclein activates microglia in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 29(11):1690–1701
Tansey MG, Goldberg MS (2010) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol Dis 37(3):510–518
Trimpin S, Mixon AE, Stapels MD, Kim MY, Spencer PS, Deinzer ML (2004) Identification of endogenous phosphorylation sites of bovine medium and low molecular weight neurofilament proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 43(7):2091–2105. doi:10.1021/bi030196q
Tu PH, Robinson KA, de Snoo F, Eyer J, Peterson A, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (1997) Selective degeneration for Purkinje cells with Lewy body-like inclusions in aged NFHLACZ transgenic mice. J Neurosci 17(3):1064–1074
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Patel TP, Tanik SA, Riddle DM, Stieber A, Meaney DF, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2011) Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron 72(1):57–71
Watts JC, Giles K, Oehler A, Middleton L, Dexter DT, Gentleman SM, Dearmond SJ, Prusiner SB (2013) Transmission of multiple system atrophy prions to transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(48):19555–19560. doi:10.1073/pnas.1318268110
Waxman EA, Duda JE, Giasson BI (2008) Characterization of antibodies that selectively detect alpha-synuclein in pathological inclusions. Acta Neuropathol 116(1):37–46
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2008) Molecular mechanisms of alpha-synuclein neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:616–624
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2008) Specificity and regulation of casein kinase-mediated phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67(5):402–416
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2010) A novel, high-efficiency cellular model of fibrillar alpha-synuclein inclusions and the examination of mutations that inhibit amyloid formation. J Neurochem 113(2):374–388
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2011) Characterization of kinases involved in the phosphorylation of aggregated alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci Res 89(2):231–247
Waxman EA, Giasson BI (2011) Induction of intracellular tau aggregation is promoted by alpha-synuclein seeds and provides novel insights into the hyperphosphorylation of tau. J Neurosci 31(21):7604–7618
Waxman EA, Mazzulli JR, Giasson BI (2009) Characterization of hydrophobic residue requirements for alpha-synuclein fibrillization. Biochemistry 48(40):9427–9436
Weinreb PH, Zhen W, Poon AW, Conway KA, Lansbury PT (1996) NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 35(43):13709–13715
Xu ZS, Liu WS, Willard M (1990) Identification of serine 473 as a major phosphorylation site in the neurofilament polypeptide NF-L. J Neurosci 10(6):1838–1846
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gomez TE, del Ser T, Munoz DG, de Yebenes JG (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55(2):164–173
Zhang W, Wang T, Pei Z, Miller DS, Wu X, Block ML, Wilson B, Zhang W, Zhou Y, Hong JS, Zhang J (2005) Aggregated alpha-synuclein activates microglia: a process leading to disease progression in Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J 19(6):533–542
Zhu Q, Couillard-Despres S, Julien JP (1997) Delayed maturation of regenerating myelinated axons in mice lacking neurofilaments. Exp Neurol 148(1):299–316. doi:10.1006/exnr.1997.6654
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ellison Medical Foundation Senior Scholar Award to TEG, the Wilder Family Fellowship to ANS, and funding from the University of Florida. We thank the University of Florida NeuroMedicine Human Tissue Brain Bank, which is supported by a gift from Eve and Joe Wilder, for the patient brain tissues. JR holds a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair and is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sacino, A.N., Brooks, M., Thomas, M.A. et al. Amyloidogenic α-synuclein seeds do not invariably induce rapid, widespread pathology in mice. Acta Neuropathol 127, 645–665 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1268-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-014-1268-0