Abstract
The number of patients with neurodegenerative diseases is increasing significantly worldwide. Thus, intense research is being pursued to uncover mechanisms of disease development in an effort to identify molecular targets for therapeutic intervention. Analysis of postmortem tissue from patients has yielded important histological and biochemical markers of disease progression. However, this approach is inherently limited because it is not possible to study patient neurons prior to degeneration. As such, transgenic and knockout models of neurodegenerative diseases are commonly employed. While these animal models have yielded important insights into some molecular mechanisms of disease development, they do not provide the opportunity to study mechanisms of neurodegeneration in human neurons at risk and thus, it is often difficult or even impossible to replicate human pathogenesis with this approach. The generation of patient-specific induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells offers a unique opportunity to overcome these obstacles. By expanding and differentiating iPS cells, it is possible to generate large numbers of functional neurons in vitro, which can then be used to study the disease of the donating patient. Here, we provide an overview of human stem cell models of neurodegeneration using iPS cells from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal dementia, Huntington’s disease, spinal muscular atrophy and other neurodegenerative diseases. In addition, we describe how further refinements of reprogramming technology resulted in the generation of patient-specific induced neurons, which have also been used to model neurodegenerative changes in vitro.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sarraj S, King A, Troakes C, Smith B, Maekawa S, Bodi I, Rogelj B, Al-Chalabi A, Hortobagyi T, Shaw CE (2011) p62 positive, TDP-43 negative, neuronal cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusions in the cerebellum and hippocampus define the pathology of C9orf72-linked FTLD and MND/ALS. Acta Neuropathol 122(6):691–702. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0911-2
Almeida S, Gascon E, Tran H, Chou HJ, Gendron TF, Degroot S, Tapper AR, Sellier C, Charlet-Berguerand N, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Boxer AL, Petrucelli L, Miller BL, Gao FB (2013) Modeling key pathological features of frontotemporal dementia with C9ORF72 repeat expansion in iPSC-derived human neurons. Acta Neuropathol 126(3):385–399. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1149-y
Almeida S, Zhang Z, Coppola G, Mao W, Futai K, Karydas A, Geschwind MD, Tartaglia MC, Gao F, Gianni D, Sena-Esteves M, Geschwind DH, Miller BL, Farese RV Jr, Gao FB (2012) Induced pluripotent stem cell models of progranulin-deficient frontotemporal dementia uncover specific reversible neuronal defects. Cell Rep 2(4):789–798. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.09.007
An MC, Zhang N, Scott G, Montoro D, Wittkop T, Mooney S, Melov S, Ellerby LM (2012) Genetic correction of Huntington’s disease phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 11(2):253–263. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.04.026
Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Mann D, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Oda T (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351(3):602–611. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093
Armstrong RA, Carter D, Cairns NJ (2012) A quantitative study of the neuropathology of 32 sporadic and familial cases of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 proteinopathy (FTLD-TDP). Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38(1):25–38. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2011.01188.x
Arrasate M, Finkbeiner S (2011) Protein aggregates in Huntington’s disease. Exp Neurol 238(1):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.12.013
Ash PE, Bieniek KF, Gendron TF, Caulfield T, Lin WL, Dejesus-Hernandez M, van Blitterswijk MM, Jansen-West K, Paul JW 3rd, Rademakers R, Boylan KB, Dickson DW, Petrucelli L (2013) Unconventional translation of C9ORF72 GGGGCC expansion generates insoluble polypeptides specific to c9FTD/ALS. Neuron 77(4):639–646. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.004
Aubry L, Bugi A, Lefort N, Rousseau F, Peschanski M, Perrier AL (2008) Striatal progenitors derived from human ES cells mature into DARPP32 neurons in vitro and in quinolinic acid-lesioned rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(43):16707–16712. doi:10.1073/pnas.0808488105
Baker M, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown SM, Gass J, Rademakers R, Lindholm C, Snowden J, Adamson J, Sadovnick AD, Rollinson S, Cannon A, Dwosh E, Neary D, Melquist S, Richardson A, Dickson D, Berger Z, Eriksen J, Robinson T, Zehr C, Dickey CA, Crook R, McGowan E, Mann D, Boeve B, Feldman H, Hutton M (2006) Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature 442(7105):916–919. doi:10.1038/nature05016
Barnes DE, Yaffe K (2011) The projected effect of risk factor reduction on Alzheimer’s disease prevalence. Lancet Neurol 10(9):819–828. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70072-2
Battaglia G, Cannella M, Riozzi B, Orobello S, Maat-Schieman ML, Aronica E, Busceti CL, Ciarmiello A, Alberti S, Amico E, Sassone J, Sipione S, Bruno V, Frati L, Nicoletti F, Squitieri F (2011) Early defect of transforming growth factor beta1 formation in Huntington’s disease. J Cell Mol Med 15(3):555–571. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01011.x
Bilican B, Serio A, Barmada SJ, Nishimura AL, Sullivan GJ, Carrasco M, Phatnani HP, Puddifoot CA, Story D, Fletcher J, Park IH, Friedman BA, Daley GQ, Wyllie DJ, Hardingham GE, Wilmut I, Finkbeiner S, Maniatis T, Shaw CE, Chandran S (2012) Mutant induced pluripotent stem cell lines recapitulate aspects of TDP-43 proteinopathies and reveal cell-specific vulnerability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(15):5803–5808. doi:10.1073/pnas.1202922109
Bilican B, Serio A, Barmada SJ, Nishimura AL, Sullivan GJ, Carrasco M, Phatnani HP, Puddifoot CA, Story D, Fletcher J, Park IH, Friedman BA, Daley GQ, Wyllie DJ, Hardingham GE, Wilmut I, Finkbeiner S, Maniatis T, Shaw CE, Chandran S (2013) Comment on “Drug screening for ALS using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells”. Sci Transl Med 5(188):188le182. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3005065
Bilsland LG, Nirmalananthan N, Yip J, Greensmith L, Duchen MR (2008) Expression of mutant SOD1 in astrocytes induces functional deficits in motoneuron mitochondria. J Neurochem 107(5):1271–1283. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05699.x
Boch J (2011) TALEs of genome targeting. Nat Biotechnol 29(2):135–136. doi:10.1038/nbt.1767
Boillee S, Vande Velde C, Cleveland DW (2006) ALS: a disease of motor neurons and their nonneuronal neighbors. Neuron 52(1):39–59. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.018
Boulting GL, Kiskinis E, Croft GF, Amoroso MW, Oakley DH, Wainger BJ, Williams DJ, Kahler DJ, Yamaki M, Davidow L, Rodolfa CT, Dimos JT, Mikkilineni S, MacDermott AB, Woolf CJ, Henderson CE, Wichterle H, Eggan K (2011) A functionally characterized test set of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 29(3):279–286. doi:10.1038/nbt.1783
Bradley CK, Scott HA, Chami O, Peura TT, Dumevska B, Schmidt U, Stojanov T (2010) Derivation of Huntington’s disease-affected human embryonic stem cell lines. Stem Cells Dev 20(3):495–502. doi:10.1089/scd.2010.0120
Brady RO, Gal AE, Kanfer JN, Bradley RM (1965) The metabolism of glucocerebrosides. 3. Purification and properties of a glucosyl- and galactosylceramide-cleaving enzyme from rat intestinal tissue. J Biol Chem 240(10):3766–3770
Brennand KJ, Simone A, Jou J, Gelboin-Burkhart C, Tran N, Sangar S, Li Y, Mu Y, Chen G, Yu D, McCarthy S, Sebat J, Gage FH (2011) Modelling schizophrenia using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 473(7346):221–225. doi:10.1038/nature09915
Brichta L, Hofmann Y, Hahnen E, Siebzehnrubl FA, Raschke H, Blumcke I, Eyupoglu IY, Wirth B (2003) Valproic acid increases the SMN2 protein level: a well-known drug as a potential therapy for spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet 12(19):2481–2489. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg256
Brown RH Jr (1997) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Insights from genetics. Arch Neurol 54(10):1246–1250
Brunk I, Blex C, Speidel D, Brose N, Ahnert-Hilger G (2009) Ca2+-dependent activator proteins of secretion promote vesicular monoamine uptake. J Biol Chem 284(2):1050–1056. doi:10.1074/jbc.M805328200
Burger PC, Vogel FS (1973) The development of the pathologic changes of Alzheimer’s disease and senile dementia in patients with Down’s syndrome. Am J Pathol 73(2):457–476
Burkhardt MF, Martinez FJ, Wright S, Ramos C, Volfson D, Mason M, Garnes J, Dang V, Lievers J, Shoukat-Mumtaz U, Martinez R, Gai H, Blake R, Vaisberg E, Grskovic M, Johnson C, Irion S, Bright J, Cooper B, Nguyen L, Griswold-Prenner I, Javaherian A (2013) A cellular model for sporadic ALS using patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 56C:355–364. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2013.07.007
Byers B, Cord B, Nguyen HN, Schule B, Fenno L, Lee PC, Deisseroth K, Langston JW, Pera RR, Palmer TD (2011) SNCA triplication Parkinson’s patient’s iPSC-derived DA neurons accumulate alpha-synuclein and are susceptible to oxidative stress. PLoS One 6(11):e26159. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026159
Caiazzo M, Dell’Anno MT, Dvoretskova E, Lazarevic D, Taverna S, Leo D, Sotnikova TD, Menegon A, Roncaglia P, Colciago G, Russo G, Carninci P, Pezzoli G, Gainetdinov RR, Gustincich S, Dityatev A, Broccoli V (2011) Direct generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nature 476(7359):224–227. doi:10.1038/nature10284
Camnasio S, Delli Carri A, Lombardo A, Grad I, Mariotti C, Castucci A, Rozell B, Lo Riso P, Castiglioni V, Zuccato C, Rochon C, Takashima Y, Diaferia G, Biunno I, Gellera C, Jaconi M, Smith A, Hovatta O, Naldini L, Di Donato S, Feki A, Cattaneo E (2012) The first reported generation of several induced pluripotent stem cell lines from homozygous and heterozygous Huntington’s disease patients demonstrates mutation related enhanced lysosomal activity. Neurobiol Dis 46(1):41–51. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.042
Campuzano V, Montermini L, Lutz Y, Cova L, Hindelang C, Jiralerspong S, Trottier Y, Kish SJ, Faucheux B, Trouillas P, Authier FJ, Durr A, Mandel JL, Vescovi A, Pandolfo M, Koenig M (1997) Frataxin is reduced in Friedreich ataxia patients and is associated with mitochondrial membranes. Hum Mol Genet 6(11):1771–1780
Campuzano V, Montermini L, Molto MD, Pianese L, Cossee M, Cavalcanti F, Monros E, Rodius F, Duclos F, Monticelli A, Zara F, Canizares J, Koutnikova H, Bidichandani SI, Gellera C, Brice A, Trouillas P, De Michele G, Filla A, De Frutos R, Palau F, Patel PI, Di Donato S, Mandel JL, Cocozza S, Koenig M, Pandolfo M (1996) Friedreich’s ataxia: autosomal recessive disease caused by an intronic GAA triplet repeat expansion. Science 271(5254):1423–1427
Carballo-Carbajal I, Weber-Endress S, Rovelli G, Chan D, Wolozin B, Klein CL, Patenge N, Gasser T, Kahle PJ (2010) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 induces alpha-synuclein expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Cell Signal 22(5):821–827. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.006
Cataldo A, Rebeck GW, Ghetri B, Hulette C, Lippa C, Van Broeckhoven C, van Duijn C, Cras P, Bogdanovic N, Bird T, Peterhoff C, Nixon R (2001) Endocytic disturbances distinguish among subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Ann Neurol 50(5):661–665
Cataldo AM, Peterhoff CM, Troncoso JC, Gomez-Isla T, Hyman BT, Nixon RA (2000) Endocytic pathway abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease and Down syndrome: differential effects of APOE genotype and presenilin mutations. Am J Pathol 157(1):277–286. doi:S0002-9440(10)64538-5
Chae JI, Kim DW, Lee N, Jeon YJ, Jeon I, Kwon J, Kim J, Soh Y, Lee DS, Seo KS, Choi NJ, Park BC, Kang SH, Ryu J, Oh SH, Shin DA, Lee DR, Do JT, Park IH, Daley GQ, Song J (2012) Quantitative proteomic analysis of induced pluripotent stem cells derived from a human Huntington’s disease patient. Biochem J 446(3):359–371. doi:10.1042/BJ20111495
Chambers SM, Fasano CA, Papapetrou EP, Tomishima M, Sadelain M, Studer L (2009) Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat Biotechnol 27(3):275–280. doi:10.1038/nbt.1529
Chang T, Zheng W, Tsark W, Bates S, Huang H, Lin RJ, Yee JK (2011) Brief report: phenotypic rescue of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motoneurons of a spinal muscular atrophy patient. Stem Cells 29(12):2090–2093. doi:10.1002/stem.749
Cheng PH, Li CL, Chang YF, Tsai SJ, Lai YY, Chan AW, Chen CM, Yang SH (2013) miR-196a Ameliorates Phenotypes of Huntington Disease in Cell, Transgenic Mouse, and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Models. Am J Hum Genet. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.05.025
Chung CY, Khurana V, Auluck PK, Tardiff DF, Mazzulli JR, Soldner F, Baru V, Lou Y, Freyzon Y, Cho S, Mungenast AE, Muffat J, Mitalipova M, Pluth MD, Jui NT, Schule B, Lippard SJ, Tsai LH, Krainc D, Buchwald SL, Jaenisch R, Lindquist S (2013) Identification and Rescue of alpha-Synuclein Toxicity in Parkinson Patient-Derived Neurons. Science. doi:10.1126/science.1245296
Close P, Hawkes N, Cornez I, Creppe C, Lambert CA, Rogister B, Siebenlist U, Merville MP, Slaugenhaupt SA, Bours V, Svejstrup JQ, Chariot A (2006) Transcription impairment and cell migration defects in elongator-depleted cells: implication for familial dysautonomia. Mol Cell 22(4):521–531. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.04.017
Consortium H (1993) A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell 72(6):971–983. doi:0092-8674(93)90585-E
Consortium THi (2012) Induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with Huntington’s disease show CAG-repeat-expansion-associated phenotypes. Cell Stem Cell 11(2):264–278. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.04.027
Cookson MR (2010) The role of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(12):791–797. doi:10.1038/nrn2935
Cooper O, Hargus G, Deleidi M, Blak A, Osborn T, Marlow E, Lee K, Levy A, Perez-Torres E, Yow A, Isacson O (2010) Differentiation of human ES and Parkinson’s disease iPS cells into ventral midbrain dopaminergic neurons requires a high activity form of SHH, FGF8a and specific regionalization by retinoic acid. Mol Cell Neurosci 45(3):258–266. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2010.06.017
Cooper O, Seo H, Andrabi S, Guardia-Laguarta C, Graziotto J, Sundberg M, McLean JR, Carrillo-Reid L, Xie Z, Osborn T, Hargus G, Deleidi M, Lawson T, Bogetofte H, Perez-Torres E, Clark L, Moskowitz C, Mazzulli J, Chen L, Volpicelli-Daley L, Romero N, Jiang H, Uitti RJ, Huang Z, Opala G, Scarffe LA, Dawson VL, Klein C, Feng J, Ross OA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Marder K, Surmeier DJ, Wszolek ZK, Przedborski S, Krainc D, Dawson TM, Isacson O (2012) Pharmacological rescue of mitochondrial deficits in iPSC-derived neural cells from patients with familial Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med 4 (141):141ra190. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003985
Corti S, Nizzardo M, Simone C, Falcone M, Nardini M, Ronchi D, Donadoni C, Salani S, Riboldi G, Magri F, Menozzi G, Bonaglia C, Rizzo F, Bresolin N, Comi GP (2012) Genetic correction of human induced pluripotent stem cells from patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Sci Transl Med 4 (165):165ra162. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3004108
Cruts M, Kumar-Singh S, Van Broeckhoven C (2006) Progranulin mutations in ubiquitin-positive frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17q21. Curr Alzheimer Res 3(5):485–491
Cruts M, van Duijn CM, Backhovens H, Van den Broeck M, Wehnert A, Serneels S, Sherrington R, Hutton M, Hardy J, St George-Hyslop PH, Hofman A, Van Broeckhoven C (1998) Estimation of the genetic contribution of presenilin-1 and -2 mutations in a population-based study of presenile Alzheimer disease. Hum Mol Genet 7(1):43–51. pii:ddb004
Davies SW, Turmaine M, Cozens BA, DiFiglia M, Sharp AH, Ross CA, Scherzinger E, Wanker EE, Mangiarini L, Bates GP (1997) Formation of neuronal intranuclear inclusions underlies the neurological dysfunction in mice transgenic for the HD mutation. Cell 90(3):537–548. pii:S0092-8674(00)80513-9
de Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5(6):525–535. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70471-9
DeJesus-Hernandez M, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF, Boxer AL, Baker M, Rutherford NJ, Nicholson AM, Finch NA, Flynn H, Adamson J, Kouri N, Wojtas A, Sengdy P, Hsiung GY, Karydas A, Seeley WW, Josephs KA, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, Wszolek ZK, Feldman H, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Miller BL, Dickson DW, Boylan KB, Graff-Radford NR, Rademakers R (2011) Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in noncoding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked FTD and ALS. Neuron 72(2):245–256. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.011
Denton KR, Lei L, Grenier J, Rodionov V, Blackstone C, Li XJ (2013) Loss of spastin function results in disease-specific axonal defects in human pluripotent stem cell-based models of hereditary spastic paraplegia. Stem Cells. doi:10.1002/stem.1569
Devine MJ, Ryten M, Vodicka P, Thomson AJ, Burdon T, Houlden H, Cavaleri F, Nagano M, Drummond NJ, Taanman JW, Schapira AH, Gwinn K, Hardy J, Lewis PA, Kunath T (2011) Parkinson’s disease induced pluripotent stem cells with triplication of the alpha-synuclein locus. Nat Commun 2:440. doi:10.1038/ncomms1453
Di Giorgio FP, Boulting GL, Bobrowicz S, Eggan KC (2008) Human embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons are sensitive to the toxic effect of glial cells carrying an ALS-causing mutation. Cell Stem Cell 3(6):637–648. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2008.09.017
Di Giorgio FP, Carrasco MA, Siao MC, Maniatis T, Eggan K (2007) Non-cell autonomous effect of glia on motor neurons in an embryonic stem cell-based ALS model. Nat Neurosci 10(5):608–614. doi:10.1038/nn1885
Dickson DW (2001) Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Clin Geriatr Med 17(2):209–228
Dimos JT, Rodolfa KT, Niakan KK, Weisenthal LM, Mitsumoto H, Chung W, Croft GF, Saphier G, Leibel R, Goland R, Wichterle H, Henderson CE, Eggan K (2008) Induced pluripotent stem cells generated from patients with ALS can be differentiated into motor neurons. Science 321(5893):1218–1221. doi:10.1126/science.1158799
Donnelly CJ, Zhang PW, Pham JT, Heusler AR, Mistry NA, Vidensky S, Daley EL, Poth EM, Hoover B, Fines DM, Maragakis N, Tienari PJ, Petrucelli L, Traynor BJ, Wang J, Rigo F, Bennett CF, Blackshaw S, Sattler R, Rothstein JD (2013) RNA toxicity from the ALS/FTD C9ORF72 expansion is mitigated by antisense intervention. Neuron 80(2):415–428. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.015
Dragileva E, Hendricks A, Teed A, Gillis T, Lopez ET, Friedberg EC, Kucherlapati R, Edelmann W, Lunetta KL, MacDonald ME, Wheeler VC (2009) Intergenerational and striatal CAG repeat instability in Huntington’s disease knock-in mice involve different DNA repair genes. Neurobiol Dis 33(1):37–47. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.09.014
Draper H, Chadwick R (1999) Beware! Preimplantation genetic diagnosis may solve some old problems but it also raises new ones. J Med Ethics 25(2):114–120
Du J, Campau E, Soragni E, Ku S, Puckett JW, Dervan PB, Gottesfeld JM (2012) Role of mismatch repair enzymes in GAA.TTC triplet-repeat expansion in Friedreich ataxia induced pluripotent stem cells. J Biol Chem 287(35):29861–29872. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.391961
Ebert AD, Yu J, Rose FF Jr, Mattis VB, Lorson CL, Thomson JA, Svendsen CN (2009) Induced pluripotent stem cells from a spinal muscular atrophy patient. Nature 457(7227):277–280. doi:10.1038/nature07677
Egawa N, Kitaoka S, Tsukita K, Naitoh M, Takahashi K, Yamamoto T, Adachi F, Kondo T, Okita K, Asaka I, Aoi T, Watanabe A, Yamada Y, Morizane A, Takahashi J, Ayaki T, Ito H, Yoshikawa K, Yamawaki S, Suzuki S, Watanabe D, Hioki H, Kaneko T, Makioka K, Okamoto K, Takuma H, Tamaoka A, Hasegawa K, Nonaka T, Hasegawa M, Kawata A, Yoshida M, Nakahata T, Takahashi R, Marchetto MC, Gage FH, Yamanaka S, Inoue H (2012) Drug screening for ALS using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Transl Med 4(145):145ra104. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3004052
Egawa N, Kitaoka S, Tsukita K, Naitoh M, Takahashi K, Yamamoto T, Adachi F, Kondo T, Okita K, Asaka I, Aoi T, Watanabe A, Yamada Y, Morizane A, Takahashi J, Ayaki T, Ito H, Yoshikawa K, Yamawaki S, Suzuki S, Watanabe D, Hioki H, Kaneko T, Makioka K, Okamoto K, Takuma H, Tamaoka A, Hasegawa K, Nonaka T, Hasegawa M, Kawata A, Yoshida M, Nakahata T, Takahashi R, Marchetto MC, Gage FH, Yamanaka S, Inoue H (2013) Response to comment on “Drug screening for ALS using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells”. Sci Transl Med 5(188):188lr182. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3005697
Fassier C, Tarrade A, Peris L, Courageot S, Mailly P, Dalard C, Delga S, Roblot N, Lefevre J, Job D, Hazan J, Curmi PA, Melki J (2012) Microtubule-targeting drugs rescue axonal swellings in cortical neurons from spastin knockout mice. Dis Model Mech 6(1):72–83. doi:10.1242/dmm.008946
Fink JK (2002) Hereditary spastic paraplegia. Neurol Clin 20(3):711–726
Fong H, Wang C, Knoferle J, Walker D, Balestra ME, Tong LM, Leung L, Ring KL, Seeley WW, Karydas A, Kshirsagar MA, Boxer AL, Kosik KS, Miller BL, Huang Y (2013) Genetic correction of tauopathy phenotypes in neurons derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports 1(3):1–9. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2013.08.001
Gabanella F, Butchbach ME, Saieva L, Carissimi C, Burghes AH, Pellizzoni L (2007) Ribonucleoprotein assembly defects correlate with spinal muscular atrophy severity and preferentially affect a subset of spliceosomal snRNPs. PLoS One 2(9):e921. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000921
Games D, Adams D, Alessandrini R, Barbour R, Berthelette P, Blackwell C, Carr T, Clemens J, Donaldson T, Gillespie F et al (1995) Alzheimer-type neuropathology in transgenic mice overexpressing V717F beta-amyloid precursor protein. Nature 373(6514):523–527. doi:10.1038/373523a0
Gatchel JR, Zoghbi HY (2005) Diseases of unstable repeat expansion: mechanisms and common principles. Nat Rev Genet 6(10):743–755. doi:10.1038/nrg1691
Han DW, Tapia N, Hermann A, Hemmer K, Hoing S, Arauzo-Bravo MJ, Zaehres H, Wu G, Frank S, Moritz S, Greber B, Yang JH, Lee HT, Schwamborn JC, Storch A, Scholer HR (2012) Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into neural stem cells by defined factors. Cell Stem Cell 10(4):465–472. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.02.021
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297(5580):353–356. doi:10.1126/science.1072994
Hargus G, Cooper O, Deleidi M, Levy A, Lee K, Marlow E, Yow A, Soldner F, Hockemeyer D, Hallett PJ, Osborn T, Jaenisch R, Isacson O (2010) Differentiated Parkinson patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells grow in the adult rodent brain and reduce motor asymmetry in Parkinsonian rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(36):15921–15926. doi:10.1073/pnas.1010209107
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P, Sims R, Gerrish A, Hamshere ML, Pahwa JS, Moskvina V, Dowzell K, Williams A, Jones N, Thomas C, Stretton A, Morgan AR, Lovestone S, Powell J, Proitsi P, Lupton MK, Brayne C, Rubinsztein DC, Gill M, Lawlor B, Lynch A, Morgan K, Brown KS, Passmore PA, Craig D, McGuinness B, Todd S, Holmes C, Mann D, Smith AD, Love S, Kehoe PG, Hardy J, Mead S, Fox N, Rossor M, Collinge J, Maier W, Jessen F, Schurmann B, van den Bussche H, Heuser I, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J, Dichgans M, Frolich L, Hampel H, Hull M, Rujescu D, Goate AM, Kauwe JS, Cruchaga C, Nowotny P, Morris JC, Mayo K, Sleegers K, Bettens K, Engelborghs S, De Deyn PP, Van Broeckhoven C, Livingston G, Bass NJ, Gurling H, McQuillin A, Gwilliam R, Deloukas P, Al-Chalabi A, Shaw CE, Tsolaki M, Singleton AB, Guerreiro R, Muhleisen TW, Nothen MM, Moebus S, Jockel KH, Klopp N, Wichmann HE, Carrasquillo MM, Pankratz VS, Younkin SG, Holmans PA, O’Donovan M, Owen MJ, Williams J (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41(10):1088–1093. doi:10.1038/ng.440
Hermel E, Gafni J, Propp SS, Leavitt BR, Wellington CL, Young JE, Hackam AS, Logvinova AV, Peel AL, Chen SF, Hook V, Singaraja R, Krajewski S, Goldsmith PC, Ellerby HM, Hayden MR, Bredesen DE, Ellerby LM (2004) Specific caspase interactions and amplification are involved in selective neuronal vulnerability in Huntington’s disease. Cell Death Differ 11(4):424–438. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401358
Hick A, Wattenhofer-Donze M, Chintawar S, Tropel P, Simard JP, Vaucamps N, Gall D, Lambot L, Andre C, Reutenauer L, Rai M, Teletin M, Messaddeq N, Schiffmann SN, Viville S, Pearson CE, Pandolfo M, Puccio H (2013) Neurons and cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells as a model for mitochondrial defects in Friedreich’s ataxia. Dis Model Mech 6(3):608–621. doi:10.1242/dmm.010900
Hims MM, Ibrahim EC, Leyne M, Mull J, Liu L, Lazaro C, Shetty RS, Gill S, Gusella JF, Reed R, Slaugenhaupt SA (2007) Therapeutic potential and mechanism of kinetin as a treatment for the human splicing disease familial dysautonomia. J Mol Med (Berl) 85(2):149–161. doi:10.1007/s00109-006-0137-2
Huang HP, Chen PH, Hwu WL, Chuang CY, Chien YH, Stone L, Chien CL, Li LT, Chiang SC, Chen HF, Ho HN, Chen CH, Kuo HC (2011) Human Pompe disease-induced pluripotent stem cells for pathogenesis modeling, drug testing and disease marker identification. Hum Mol Genet 20(24):4851–4864. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr424
Imaizumi Y, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Koike M, Kuzumaki N, Hayakawa H, Nihira T, Kobayashi T, Ohyama M, Sato S, Takanashi M, Funayama M, Hirayama A, Soga T, Hishiki T, Suematsu M, Yagi T, Ito D, Kosakai A, Hayashi K, Shouji M, Nakanishi A, Suzuki N, Mizuno Y, Mizushima N, Amagai M, Uchiyama Y, Mochizuki H, Hattori N, Okano H (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with increased oxidative stress and alpha-synuclein accumulation in PARK2 iPSC-derived neurons and postmortem brain tissue. Mol Brain 5:35. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-5-35
Israel MA, Yuan SH, Bardy C, Reyna SM, Mu Y, Herrera C, Hefferan MP, Van Gorp S, Nazor KL, Boscolo FS, Carson CT, Laurent LC, Marsala M, Gage FH, Remes AM, Koo EH, Goldstein LS (2012) Probing sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease using induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 482(7384):216–220. doi:10.1038/nature10821
Iwata A, Nagashima Y, Matsumoto L, Suzuki T, Yamanaka T, Date H, Deoka K, Nukina N, Tsuji S (2009) Intranuclear degradation of polyglutamine aggregates by the ubiquitin–proteasome system. J Biol Chem 284(15):9796–9803. doi:10.1074/jbc.M809739200
Jablonka S, Rossoll W, Schrank B, Sendtner M (2000) The role of SMN in spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol 247(Suppl 1):I37–I42
Jang J, Kang HC, Kim HS, Kim JY, Huh YJ, Kim DS, Yoo JE, Lee JA, Lim B, Lee J, Yoon TM, Park IH, Hwang DY, Daley GQ, Kim DW (2011) Induced pluripotent stem cell models from X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy patients. Ann Neurol 70(3):402–409. doi:10.1002/ana.22486
Jeon I, Lee N, Li JY, Park IH, Park KS, Moon J, Shim SH, Choi C, Chang DJ, Kwon J, Oh SH, Shin DA, Kim HS, Do JT, Lee DR, Kim M, Kang KS, Daley GQ, Brundin P, Song J (2012) Neuronal properties, in vivo effects, and pathology of a Huntington’s disease patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 30(9):2054–2062. doi:10.1002/stem.1135
Jiang H, Ren Y, Yuen EY, Zhong P, Ghaedi M, Hu Z, Azabdaftari G, Nakaso K, Yan Z, Feng J (2012) Parkin controls dopamine utilization in human midbrain dopaminergic neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Commun 3:668. doi:10.1038/ncomms1669
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337(6096):816–821. doi:10.1126/science.1225829
Jmoudiak M, Futerman AH (2005) Gaucher disease: pathological mechanisms and modern management. Br J Haematol 129(2):178–188. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05351.x
Joyce PI, Fratta P, Fisher EM, Acevedo-Arozena A (2011) SOD1 and TDP-43 animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: recent advances in understanding disease toward the development of clinical treatments. Mamm Genome 22(7–8):420–448. doi:10.1007/s00335-011-9339-1
Kabashi E, Lin L, Tradewell ML, Dion PA, Bercier V, Bourgouin P, Rochefort D, Bel Hadj S, Durham HD, Vande Velde C, Rouleau GA, Drapeau P (2010) Gain and loss of function of ALS-related mutations of TARDBP (TDP-43) cause motor deficits in vivo. Hum Mol Genet 19(4):671–683. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp534
Kandasamy M, Couillard-Despres S, Raber KA, Stephan M, Lehner B, Winner B, Kohl Z, Rivera FJ, Nguyen HP, Riess O, Bogdahn U, Winkler J, von Horsten S, Aigner L (2010) Stem cell quiescence in the hippocampal neurogenic niche is associated with elevated transforming growth factor-beta signaling in an animal model of Huntington disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69(7):717–728. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181e4f733
Kasher PR, De Vos KJ, Wharton SB, Manser C, Bennett EJ, Bingley M, Wood JD, Milner R, McDermott CJ, Miller CC, Shaw PJ, Grierson AJ (2009) Direct evidence for axonal transport defects in a novel mouse model of mutant spastin-induced hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) and human HSP patients. J Neurochem 110(1):34–44. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06104.x
Kim J, Efe JA, Zhu S, Talantova M, Yuan X, Wang S, Lipton SA, Zhang K, Ding S (2011) Direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts to neural progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(19):7838–7843. doi:10.1073/pnas.1103113108
Koch P, Breuer P, Peitz M, Jungverdorben J, Kesavan J, Poppe D, Doerr J, Ladewig J, Mertens J, Tuting T, Hoffmann P, Klockgether T, Evert BO, Wullner U, Brustle O (2011) Excitation-induced ataxin-3 aggregation in neurons from patients with Machado–Joseph disease. Nature 480(7378):543–546. doi:10.1038/nature10671
Kondo T, Asai M, Tsukita K, Kutoku Y, Ohsawa Y, Sunada Y, Imamura K, Egawa N, Yahata N, Okita K, Takahashi K, Asaka I, Aoi T, Watanabe A, Watanabe K, Kadoya C, Nakano R, Watanabe D, Maruyama K, Hori O, Hibino S, Choshi T, Nakahata T, Hioki H, Kaneko T, Naitoh M, Yoshikawa K, Yamawaki S, Suzuki S, Hata R, Ueno S, Seki T, Kobayashi K, Toda T, Murakami K, Irie K, Klein WL, Mori H, Asada T, Takahashi R, Iwata N, Yamanaka S, Inoue H (2013) Modeling Alzheimer’s disease with iPSCs reveals stress phenotypes associated with intracellular Abeta and differential drug responsiveness. Cell Stem Cell 12(4):487–496. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2013.01.009
Kramer PR, Pearson CE, Sinden RR (1996) Stability of triplet repeats of myotonic dystrophy and fragile X loci in human mutator mismatch repair cell lines. Hum Genet 98(2):151–157
Kriks S, Shim JW, Piao J, Ganat YM, Wakeman DR, Xie Z, Carrillo-Reid L, Auyeung G, Antonacci C, Buch A, Yang L, Beal MF, Surmeier DJ, Kordower JH, Tabar V, Studer L (2011) Dopamine neurons derived from human ES cells efficiently engraft in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 480(7378):547–551. doi:10.1038/nature10648
Ku S, Soragni E, Campau E, Thomas EA, Altun G, Laurent LC, Loring JF, Napierala M, Gottesfeld JM (2010) Friedreich’s ataxia induced pluripotent stem cells model intergenerational GAATTC triplet repeat instability. Cell Stem Cell 7(5):631–637. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.09.014
Kwiatkowski TJ Jr, Bosco DA, Leclerc AL, Tamrazian E, Vanderburg CR, Russ C, Davis A, Gilchrist J, Kasarskis EJ, Munsat T, Valdmanis P, Rouleau GA, Hosler BA, Cortelli P, de Jong PJ, Yoshinaga Y, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Yan J, Ticozzi N, Siddique T, McKenna-Yasek D, Sapp PC, Horvitz HR, Landers JE, Brown RH Jr (2009) Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 323(5918):1205–1208. doi:10.1126/science.1166066
Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D, Sleegers K, Hiltunen M, Combarros O, Zelenika D, Bullido MJ, Tavernier B, Letenneur L, Bettens K, Berr C, Pasquier F, Fievet N, Barberger-Gateau P, Engelborghs S, De Deyn P, Mateo I, Franck A, Helisalmi S, Porcellini E, Hanon O, de Pancorbo MM, Lendon C, Dufouil C, Jaillard C, Leveillard T, Alvarez V, Bosco P, Mancuso M, Panza F, Nacmias B, Bossu P, Piccardi P, Annoni G, Seripa D, Galimberti D, Hannequin D, Licastro F, Soininen H, Ritchie K, Blanche H, Dartigues JF, Tzourio C, Gut I, Van Broeckhoven C, Alperovitch A, Lathrop M, Amouyel P (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41(10):1094–1099. doi:10.1038/ng.439
Lazarov O, Demars MP (2012) All in the family: how the APPs regulate neurogenesis. Front Neurosci 6:81. doi:10.3389/fnins.2012.00081
Lee EB, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2011) Gains or losses: molecular mechanisms of TDP43-mediated neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(1):38–50. doi:10.1038/nrn3121
Lee G, Papapetrou EP, Kim H, Chambers SM, Tomishima MJ, Fasano CA, Ganat YM, Menon J, Shimizu F, Viale A, Tabar V, Sadelain M, Studer L (2009) Modelling pathogenesis and treatment of familial dysautonomia using patient-specific iPSCs. Nature 461(7262):402–406. doi:10.1038/nature08320
Lee G, Ramirez CN, Kim H, Zeltner N, Liu B, Radu C, Bhinder B, Kim YJ, Choi IY, Mukherjee-Clavin B, Djaballah H, Studer L (2012) Large-scale screening using familial dysautonomia induced pluripotent stem cells identifies compounds that rescue IKBKAP expression. Nat Biotechnol 30(12):1244–1248. doi:10.1038/nbt.2435
Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Reboullet S, Clermont O, Burlet P, Viollet L, Benichou B, Cruaud C, Millasseau P, Zeviani M et al (1995) Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 80(1):155–165 pii:0092-8674(95)90460-3
Lesage S, Brice A (2009) Parkinson’s disease: from monogenic forms to genetic susceptibility factors. Hum Mol Genet 18 (R1):R48-59. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp012
Li J, Uversky VN, Fink AL (2001) Effect of familial Parkinson’s disease point mutations A30P and A53T on the structural properties, aggregation, and fibrillation of human alpha-synuclein. Biochemistry 40(38):11604–11613 pii:bi010616g
Lin X, Parisiadou L, Gu XL, Wang L, Shim H, Sun L, Xie C, Long CX, Yang WJ, Ding J, Chen ZZ, Gallant PE, Tao-Cheng JH, Rudow G, Troncoso JC, Liu Z, Li Z, Cai H (2009) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 regulates the progression of neuropathology induced by Parkinson’s-disease-related mutant alpha-synuclein. Neuron 64(6):807–827. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.006
Liu GH, Qu J, Suzuki K, Nivet E, Li M, Montserrat N, Yi F, Xu X, Ruiz S, Zhang W, Wagner U, Kim A, Ren B, Li Y, Goebl A, Kim J, Soligalla RD, Dubova I, Thompson J, Yates J 3rd, Esteban CR, Sancho-Martinez I, Izpisua Belmonte JC (2012) Progressive degeneration of human neural stem cells caused by pathogenic LRRK2. Nature 491(7425):603–607. doi:10.1038/nature11557
Liu J, Verma PJ, Evans-Galea MV, Delatycki MB, Michalska A, Leung J, Crombie D, Sarsero JP, Williamson R, Dottori M, Pebay A (2011) Generation of induced pluripotent stem cell lines from Friedreich ataxia patients. Stem Cell Rev 7(3):703–713. doi:10.1007/s12015-010-9210-x
Lopez Castel A, Cleary JD, Pearson CE (2010) Repeat instability as the basis for human diseases and as a potential target for therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(3):165–170. doi:10.1038/nrm2854
Ma L, Hu B, Liu Y, Vermilyea SC, Liu H, Gao L, Sun Y, Zhang X, Zhang SC (2012) Human embryonic stem cell-derived GABA neurons correct locomotion deficits in quinolinic acid-lesioned mice. Cell Stem Cell 10(4):455–464. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.01.021
MacLeod D, Dowman J, Hammond R, Leete T, Inoue K, Abeliovich A (2006) The familial Parkinsonism gene LRRK2 regulates neurite process morphology. Neuron 52(4):587–593. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.008
Majounie E, Renton AE, Mok K, Dopper EG, Waite A, Rollinson S, Chio A, Restagno G, Nicolaou N, Simon-Sanchez J, van Swieten JC, Abramzon Y, Johnson JO, Sendtner M, Pamphlett R, Orrell RW, Mead S, Sidle KC, Houlden H, Rohrer JD, Morrison KE, Pall H, Talbot K, Ansorge O, Hernandez DG, Arepalli S, Sabatelli M, Mora G, Corbo M, Giannini F, Calvo A, Englund E, Borghero G, Floris GL, Remes AM, Laaksovirta H, McCluskey L, Trojanowski JQ, Van Deerlin VM, Schellenberg GD, Nalls MA, Drory VE, Lu CS, Yeh TH, Ishiura H, Takahashi Y, Tsuji S, Le Ber I, Brice A, Drepper C, Williams N, Kirby J, Shaw P, Hardy J, Tienari PJ, Heutink P, Morris HR, Pickering-Brown S, Traynor BJ (2012) Frequency of the C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol 11(4):323–330. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70043-1
Maries E, Dass B, Collier TJ, Kordower JH, Steece-Collier K (2003) The role of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: insights from animal models. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(9):727–738. doi:10.1038/nrn1199
Mateizel I, De Temmerman N, Ullmann U, Cauffman G, Sermon K, Van de Velde H, De Rycke M, Degreef E, Devroey P, Liebaers I, Van Steirteghem A (2006) Derivation of human embryonic stem cell lines from embryos obtained after IVF and after PGD for monogenic disorders. Hum Reprod 21(2):503–511. doi:10.1093/humrep/dei345
McGivern JV, Patitucci TN, Nord JA, Barabas ME, Stucky CL, Ebert AD (2013) Spinal muscular atrophy astrocytes exhibit abnormal calcium regulation and reduced growth factor production. Glia 61(9):1418–1428. doi:10.1002/glia.22522
Mitne-Neto M, Machado-Costa M, Marchetto MC, Bengtson MH, Joazeiro CA, Tsuda H, Bellen HJ, Silva HC, Oliveira AS, Lazar M, Muotri AR, Zatz M (2011) Downregulation of VAPB expression in motor neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells of ALS8 patients. Hum Mol Genet 20(18):3642–3652. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr284
Mori K, Weng SM, Arzberger T, May S, Rentzsch K, Kremmer E, Schmid B, Kretzschmar HA, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C, Haass C, Edbauer D (2013) The C9orf72 GGGGCC repeat is translated into aggregating dipeptide-repeat proteins in FTLD/ALS. Science 339(6125):1335–1338. doi:10.1126/science.1232927
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183(5):795–803. doi:10.1083/jcb.200809125
Narendra DP, Jin SM, Tanaka A, Suen DF, Gautier CA, Shen J, Cookson MR, Youle RJ (2010) PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol 8(1):e1000298. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000298
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314(5796):130–133. doi:10.1126/science.1134108
Nguyen HN, Byers B, Cord B, Shcheglovitov A, Byrne J, Gujar P, Kee K, Schule B, Dolmetsch RE, Langston W, Palmer TD, Pera RR (2011) LRRK2 mutant iPSC-derived DA neurons demonstrate increased susceptibility to oxidative stress. Cell Stem Cell 8(3):267–280. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2011.01.013
Niclis J, Trounson AO, Dottori M, Ellisdon A, Bottomley SP, Verlinsky Y, Cram D (2009) Human embryonic stem cell models of Huntington disease. Reprod Biomed Online 19(1):106–113
Niclis JC, Pinar A, Haynes JM, Alsanie W, Jenny R, Dottori M, Cram DS (2013) Characterization of forebrain neurons derived from late-onset Huntington’s disease human embryonic stem cell lines. Front Cell Neurosci 7:37. doi:10.3389/fncel.2013.00037
Nihei Y, Ito D, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Yagi T, Yoshizaki T, Okano H, Suzuki N (2013) Enhanced aggregation of androgen receptor in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons from spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. J Biol Chem 288(12):8043–8052. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.408211
Orenstein SJ, Kuo SH, Tasset I, Arias E, Koga H, Fernandez-Carasa I, Cortes E, Honig LS, Dauer W, Consiglio A, Raya A, Sulzer D, Cuervo AM (2013) Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Neurosci 16(4):394–406. doi:10.1038/nn.3350
Pang ZP, Yang N, Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Fuentes DR, Yang TQ, Citri A, Sebastiano V, Marro S, Sudhof TC, Wernig M (2011) Induction of human neuronal cells by defined transcription factors. Nature 476(7359):220–223. doi:10.1038/nature10202
Park IH, Arora N, Huo H, Maherali N, Ahfeldt T, Shimamura A, Lensch MW, Cowan C, Hochedlinger K, Daley GQ (2008) Disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell 134(5):877–886. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.041
Pesiridis GS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2009) Mutations in TDP-43 link glycine-rich domain functions to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 18(R2):R156–R162. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp303
Polymenidou M, Lagier-Tourenne C, Hutt KR, Huelga SC, Moran J, Liang TY, Ling SC, Sun E, Wancewicz E, Mazur C, Kordasiewicz H, Sedaghat Y, Donohue JP, Shiue L, Bennett CF, Yeo GW, Cleveland DW (2011) Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat Neurosci 14(4):459–468. doi:10.1038/nn.2779
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276(5321):2045–2047
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, Nemens E, Garruto RM, Anderson L, Andreadis A, Wiederholt WC, Raskind M, Schellenberg GD (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 43(6):815–825. doi:10.1002/ana.410430617
Popescu IR, Nicaise C, Liu S, Bisch G, Knippenberg S, Daubie V, Bohl D, Pochet R (2013) Neural progenitors derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells survive and differentiate upon transplantation into a rat model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Stem Cells Transl Med 2(3):167–174. doi:10.5966/sctm.2012-0042
Qiang L, Fujita R, Yamashita T, Angulo S, Rhinn H, Rhee D, Doege C, Chau L, Aubry L, Vanti WB, Moreno H, Abeliovich A (2011) Directed conversion of Alzheimer’s disease patient skin fibroblasts into functional neurons. Cell 146(3):359–371. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.007
Rademakers R, Neumann M, Mackenzie IR (2012) Advances in understanding the molecular basis of frontotemporal dementia. Nat Rev Neurol 8(8):423–434. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2012.117
Ramsey CP, Glass CA, Montgomery MB, Lindl KA, Ritson GP, Chia LA, Hamilton RL, Chu CT, Jordan-Sciutto KL (2007) Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66(1):75–85. doi:10.1097/nen.0b013e31802d6da9
Reiner A, Albin RL, Anderson KD, D’Amato CJ, Penney JB, Young AB (1988) Differential loss of striatal projection neurons in Huntington disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85(15):5733–5737
Reinhardt P, Glatza M, Hemmer K, Tsytsyura Y, Thiel CS, Hoing S, Moritz S, Parga JA, Wagner L, Bruder JM, Wu G, Schmid B, Ropke A, Klingauf J, Schwamborn JC, Gasser T, Scholer HR, Sterneckert J (2013) Derivation and expansion using only small molecules of human neural progenitors for neurodegenerative disease modeling. PLoS One 8(3):e59252. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059252
Reinhardt P, Schmid B, Burbulla LF, Schondorf DC, Wagner L, Glatza M, Hoing S, Hargus G, Heck SA, Dhingra A, Wu G, Muller S, Brockmann K, Kluba T, Maisel M, Kruger R, Berg D, Tsytsyura Y, Thiel CS, Psathaki OE, Klingauf J, Kuhlmann T, Klewin M, Muller H, Gasser T, Scholer HR, Sterneckert J (2013) Genetic correction of a LRRK2 mutation in human iPSCs links parkinsonian neurodegeneration to ERK-dependent changes in gene expression. Cell Stem Cell 12(3):354–367. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2013.01.008
Reis SA, Thompson MN, Lee JM, Fossale E, Kim HH, Liao JK, Moskowitz MA, Shaw SY, Dong L, Haggarty SJ, MacDonald ME, Seong IS (2011) Striatal neurons expressing full-length mutant huntingtin exhibit decreased N-cadherin and altered neuritogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 20(12):2344–2355. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr127
Renton AE, Majounie E, Waite A, Simon-Sanchez J, Rollinson S, Gibbs JR, Schymick JC, Laaksovirta H, van Swieten JC, Myllykangas L, Kalimo H, Paetau A, Abramzon Y, Remes AM, Kaganovich A, Scholz SW, Duckworth J, Ding J, Harmer DW, Hernandez DG, Johnson JO, Mok K, Ryten M, Trabzuni D, Guerreiro RJ, Orrell RW, Neal J, Murray A, Pearson J, Jansen IE, Sondervan D, Seelaar H, Blake D, Young K, Halliwell N, Callister JB, Toulson G, Richardson A, Gerhard A, Snowden J, Mann D, Neary D, Nalls MA, Peuralinna T, Jansson L, Isoviita VM, Kaivorinne AL, Holtta-Vuori M, Ikonen E, Sulkava R, Benatar M, Wuu J, Chio A, Restagno G, Borghero G, Sabatelli M, Heckerman D, Rogaeva E, Zinman L, Rothstein JD, Sendtner M, Drepper C, Eichler EE, Alkan C, Abdullaev Z, Pack SD, Dutra A, Pak E, Hardy J, Singleton A, Williams NM, Heutink P, Pickering-Brown S, Morris HR, Tienari PJ, Traynor BJ (2011) A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD. Neuron 72(2):257–268. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.010
Ring KL, Tong LM, Balestra ME, Javier R, Andrews-Zwilling Y, Li G, Walker D, Zhang WR, Kreitzer AC, Huang Y (2012) Direct reprogramming of mouse and human fibroblasts into multipotent neural stem cells with a single factor. Cell Stem Cell 11(1):100–109. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.05.018
Roberson ED, Scearce-Levie K, Palop JJ, Yan F, Cheng IH, Wu T, Gerstein H, Yu GQ, Mucke L (2007) Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid beta-induced deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Science 316(5825):750–754. doi:10.1126/science.1141736
Rogaeva E, Meng Y, Lee JH, Gu Y, Kawarai T, Zou F, Katayama T, Baldwin CT, Cheng R, Hasegawa H, Chen F, Shibata N, Lunetta KL, Pardossi-Piquard R, Bohm C, Wakutani Y, Cupples LA, Cuenco KT, Green RC, Pinessi L, Rainero I, Sorbi S, Bruni A, Duara R, Friedland RP, Inzelberg R, Hampe W, Bujo H, Song YQ, Andersen OM, Willnow TE, Graff-Radford N, Petersen RC, Dickson D, Der SD, Fraser PE, Schmitt-Ulms G, Younkin S, Mayeux R, Farrer LA, St George-Hyslop P (2007) The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 39(2):168–177. doi:10.1038/ng1943
Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D, Figlewicz DA, Sapp P, Hentati A, Donaldson D, Goto J, O’Regan JP, Deng HX et al (1993) Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362(6415):59–62. doi:10.1038/362059a0
Rossoll W, Jablonka S, Andreassi C, Kroning AK, Karle K, Monani UR, Sendtner M (2003) Smn, the spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene product, modulates axon growth and localization of beta-actin mRNA in growth cones of motoneurons. J Cell Biol 163(4):801–812. doi:10.1083/jcb.200304128
Sanchez-Danes A, Richaud-Patin Y, Carballo-Carbajal I, Jimenez-Delgado S, Caig C, Mora S, Di Guglielmo C, Ezquerra M, Patel B, Giralt A, Canals JM, Memo M, Alberch J, Lopez-Barneo J, Vila M, Cuervo AM, Tolosa E, Consiglio A, Raya A (2012) Disease-specific phenotypes in dopamine neurons from human iPS-based models of genetic and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 4(5):380–395. doi:10.1002/emmm.201200215
Sanders LH, Laganiere J, Cooper O, Mak SK, Vu BJ, Huang YA, Paschon DE, Vangipuram M, Sundararajan R, Urnov FD, Langston JW, Gregory PD, Zhang HS, Greenamyre JT, Isacson O, Schule B (2013) LRRK2 mutations cause mitochondrial DNA damage in iPSC-derived neural cells from Parkinson’s disease patients: reversal by gene correction. Neurobiol Dis. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2013.10.013
Sandoe J, Eggan K (2013) Opportunities and challenges of pluripotent stem cell neurodegenerative disease models. Nat Neurosci 16(7):780–789. doi:10.1038/nn.3425
Sapp E, Schwarz C, Chase K, Bhide PG, Young AB, Penney J, Vonsattel JP, Aronin N, DiFiglia M (1997) Huntingtin localization in brains of normal and Huntington’s disease patients. Ann Neurol 42(4):604–612. doi:10.1002/ana.410420411
Sareen D, Ebert AD, Heins BM, McGivern JV, Ornelas L, Svendsen CN (2012) Inhibition of apoptosis blocks human motor neuron cell death in a stem cell model of spinal muscular atrophy. PLoS One 7(6):e39113. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039113
Sareen D, O’Rourke JG, Meera P, Muhammad AK, Grant S, Simpkinson M, Bell S, Carmona S, Ornelas L, Sahabian A, Gendron T, Petrucelli L, Baughn M, Ravits J, Harms MB, Rigo F, Bennett CF, Otis TS, Svendsen CN, Baloh RH (2013) Targeting RNA foci in iPSC-derived motor neurons from ALS patients with a C9ORF72 repeat expansion. Sci Transl Med 5(208):208ra149. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007529
Scheuner D, Eckman C, Jensen M, Song X, Citron M, Suzuki N, Bird TD, Hardy J, Hutton M, Kukull W, Larson E, Levy-Lahad E, Viitanen M, Peskind E, Poorkaj P, Schellenberg G, Tanzi R, Wasco W, Lannfelt L, Selkoe D, Younkin S (1996) Secreted amyloid beta-protein similar to that in the senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease is increased in vivo by the presenilin 1 and 2 and APP mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 2(8):864–870
Schmucker S, Puccio H (2010) Understanding the molecular mechanisms of Friedreich’s ataxia to develop therapeutic approaches. Hum Mol Genet 19(R1):R103–R110. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq165
Seibler P, Graziotto J, Jeong H, Simunovic F, Klein C, Krainc D (2011) Mitochondrial Parkin recruitment is impaired in neurons derived from mutant PINK1 induced pluripotent stem cells. J Neurosci 31(16):5970–5976. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4441-10.2011
Serio A, Bilican B, Barmada SJ, Ando DM, Zhao C, Siller R, Burr K, Haghi G, Story D, Nishimura AL, Carrasco MA, Phatnani HP, Shum C, Wilmut I, Maniatis T, Shaw CE, Finkbeiner S, Chandran S (2013) Astrocyte pathology and the absence of non-cell autonomy in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of TDP-43 proteinopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(12):4697–4702. doi:10.1073/pnas.1300398110
Sherrington R, Rogaev EI, Liang Y, Rogaeva EA, Levesque G, Ikeda M, Chi H, Lin C, Li G, Holman K, Tsuda T, Mar L, Foncin JF, Bruni AC, Montesi MP, Sorbi S, Rainero I, Pinessi L, Nee L, Chumakov I, Pollen D, Brookes A, Sanseau P, Polinsky RJ, Wasco W, Da Silva HA, Haines JL, Perkicak-Vance MA, Tanzi RE, Roses AD, Fraser PE, Rommens JM, St George-Hyslop PH (1995) Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 375(6534):754–760. doi:10.1038/375754a0
Shi Y, Kirwan P, Smith J, MacLean G, Orkin SH, Livesey FJ (2012) A human stem cell model of early Alzheimer’s disease pathology in Down syndrome. Sci Transl Med 4(124):124ra129. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003771
Shi Y, Kirwan P, Smith J, Robinson HP, Livesey FJ (2012) Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses. Nat Neurosci 15(3):477–486. doi:10.1038/nn.3041 (S471)
Shih JC, Chen K, Ridd MJ (1999) Monoamine oxidase: from genes to behavior. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:197–217. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.197
Shimura H, Hattori N, Kubo S, Mizuno Y, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Iwai K, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Suzuki T (2000) Familial Parkinson disease gene product, parkin, is a ubiquitin-protein ligase. Nat Genet 25(3):302–305. doi:10.1038/77060
Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Bras JM, Sharma M, Gibbs JR, Berg D, Paisan-Ruiz C, Lichtner P, Scholz SW, Hernandez DG, Kruger R, Federoff M, Klein C, Goate A, Perlmutter J, Bonin M, Nalls MA, Illig T, Gieger C, Houlden H, Steffens M, Okun MS, Racette BA, Cookson MR, Foote KD, Fernandez HH, Traynor BJ, Schreiber S, Arepalli S, Zonozi R, Gwinn K, van der Brug M, Lopez G, Chanock SJ, Schatzkin A, Park Y, Hollenbeck A, Gao J, Huang X, Wood NW, Lorenz D, Deuschl G, Chen H, Riess O, Hardy JA, Singleton AB, Gasser T (2009) Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 41(12):1308–1312. doi:10.1038/ng.487
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K (2003) alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302(5646):841. doi:10.1126/science.1090278
Slaugenhaupt SA, Mull J, Leyne M, Cuajungco MP, Gill SP, Hims MM, Quintero F, Axelrod FB, Gusella JF (2004) Rescue of a human mRNA splicing defect by the plant cytokinin kinetin. Hum Mol Genet 13(4):429–436. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh046
Slowinski J, Dominik J, Uitti RJ, Ahmed Z, Dickson DD, Wszolek ZK (2007) Frontotemporal dementia and Parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 with the N279K tau mutation. Neuropathology 27(1):73–80
Snowden JS, Neary D, Mann DM (2002) Frontotemporal dementia. Br J Psychiatry 180:140–143
Soldner F, Hockemeyer D, Beard C, Gao Q, Bell GW, Cook EG, Hargus G, Blak A, Cooper O, Mitalipova M, Isacson O, Jaenisch R (2009) Parkinson’s disease patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells free of viral reprogramming factors. Cell 136(5):964–977. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.013
Soldner F, Laganiere J, Cheng AW, Hockemeyer D, Gao Q, Alagappan R, Khurana V, Golbe LI, Myers RH, Lindquist S, Zhang L, Guschin D, Fong LK, Vu BJ, Meng X, Urnov FD, Rebar EJ, Gregory PD, Zhang HS, Jaenisch R (2011) Generation of isogenic pluripotent stem cells differing exclusively at two early onset Parkinson point mutations. Cell 146(2):318–331. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.019
Sonntag KC, Pruszak J, Yoshizaki T, van Arensbergen J, Sanchez-Pernaute R, Isacson O (2007) Enhanced yield of neuroepithelial precursors and midbrain-like dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells using the bone morphogenic protein antagonist noggin. Stem Cells 25(2):411–418. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2006-0380
Sorolla MA, Reverter-Branchat G, Tamarit J, Ferrer I, Ros J, Cabiscol E (2008) Proteomic and oxidative stress analysis in human brain samples of Huntington disease. Free Radic Biol Med 45(5):667–678. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.05.014
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow MR, Klug A, Ghetti B (1998) Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(13):7737–7741
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388(6645):839–840. doi:10.1038/42166
Sreedharan J, Blair IP, Tripathi VB, Hu X, Vance C, Rogelj B, Ackerley S, Durnall JC, Williams KL, Buratti E, Baralle F, de Belleroche J, Mitchell JD, Leigh PN, Al-Chalabi A, Miller CC, Nicholson G, Shaw CE (2008) TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 319(5870):1668–1672. doi:10.1126/science.1154584
Sreedharan J, Brown RH Jr (2013) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: problems and prospects. Ann Neurol 74(3):309–316. doi:10.1002/ana.24012
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126(4):663–676. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024
Takata K, Kitamura Y, Tsuchiya D, Kawasaki T, Taniguchi T, Shimohama S (2004) High mobility group box protein-1 inhibits microglial Abeta clearance and enhances Abeta neurotoxicity. J Neurosci Res 78(6):880–891. doi:10.1002/jnr.20340
Tanzi RE, Bertram L (2005) Twenty years of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid hypothesis: a genetic perspective. Cell 120(4):545–555. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.008
Tardiff DF, Jui NT, Khurana V, Tambe MA, Thompson ML, Chung CY, Kamadurai HB, Kim HT, Lancaster AK, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA, Rochet JC, Buchwald SL, Lindquist S (2013) Yeast reveal a “Druggable” Rsp5/Nedd4 network that ameliorates alpha-synuclein toxicity in neurons. Science. doi:10.1126/science.1245321
Thier M, Worsdorfer P, Lakes YB, Gorris R, Herms S, Opitz T, Seiferling D, Quandel T, Hoffmann P, Nothen MM, Brustle O, Edenhofer F (2012) Direct conversion of fibroblasts into stably expandable neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 10(4):473–479. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.03.003
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282(5391):1145–1147
Tiscornia G, Vivas EL, Matalonga L, Berniakovich I, Barragan Monasterio M, Eguizabal C, Gort L, Gonzalez F, Ortiz Mellet C, Garcia Fernandez JM, Ribes A, Veiga A, Izpisua Belmonte JC (2012) Neuronopathic Gaucher’s disease: induced pluripotent stem cells for disease modelling and testing chaperone activity of small compounds. Hum Mol Genet 22(4):633–645. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds471
Tollervey JR, Curk T, Rogelj B, Briese M, Cereda M, Kayikci M, Konig J, Hortobagyi T, Nishimura AL, Zupunski V, Patani R, Chandran S, Rot G, Zupan B, Shaw CE, Ule J (2011) Characterizing the RNA targets and position-dependent splicing regulation by TDP-43. Nat Neurosci 14(4):452–458. doi:10.1038/nn.2778
Trilck M, Hubner R, Seibler P, Klein C, Rolfs A, Frech MJ (2013) Niemann–Pick type C1 patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells display disease specific hallmarks. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8(1):144. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-144
Urbach A, Bar-Nur O, Daley GQ, Benvenisty N (2010) Differential modeling of fragile X syndrome by human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 6(5):407–411. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.04.005
Vance C, Rogelj B, Hortobagyi T, De Vos KJ, Nishimura AL, Sreedharan J, Hu X, Smith B, Ruddy D, Wright P, Ganesalingam J, Williams KL, Tripathi V, Al-Saraj S, Al-Chalabi A, Leigh PN, Blair IP, Nicholson G, de Belleroche J, Gallo JM, Miller CC, Shaw CE (2009) Mutations in FUS, an RNA processing protein, cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 6. Science 323(5918):1208–1211. doi:10.1126/science.1165942
Verlinsky Y, Strelchenko N, Kukharenko V, Rechitsky S, Verlinsky O, Galat V, Kuliev A (2005) Human embryonic stem cell lines with genetic disorders. Reprod Biomed Online 10(1):105–110
Vierbuchen T, Wernig M (2011) Direct lineage conversions: unnatural but useful? Nat Biotechnol 29(10):892–907. doi:10.1038/nbt.1946
Vives-Bauza C, Zhou C, Huang Y, Cui M, de Vries RL, Kim J, May J, Tocilescu MA, Liu W, Ko HS, Magrane J, Moore DJ, Dawson VL, Grailhe R, Dawson TM, Li C, Tieu K, Przedborski S (2010) PINK1-dependent recruitment of Parkin to mitochondria in mitophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(1):378–383. doi:10.1073/pnas.0911187107
Wang XM, Yik WY, Zhang P, Lu W, Dranchak PK, Shibata D, Steinberg SJ, Hacia JG (2012) The gene expression profiles of induced pluripotent stem cells from individuals with childhood cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy are consistent with proposed mechanisms of pathogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther 3(5):39. doi:10.1186/scrt130
Wolstencroft EC, Mattis V, Bajer AA, Young PJ, Lorson CL (2005) A non-sequence-specific requirement for SMN protein activity: the role of aminoglycosides in inducing elevated SMN protein levels. Hum Mol Genet 14(9):1199–1210. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi131
Wong K, Sidransky E, Verma A, Mixon T, Sandberg GD, Wakefield LK, Morrison A, Lwin A, Colegial C, Allman JM, Schiffmann R (2004) Neuropathology provides clues to the pathophysiology of Gaucher disease. Mol Genet Metab 82(3):192–207. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2004.04.011
Woods YL, Cohen P, Becker W, Jakes R, Goedert M, Wang X, Proud CG (2001) The kinase DYRK phosphorylates protein-synthesis initiation factor eIF2Bepsilon at Ser539 and the microtubule-associated protein tau at Thr212: potential role for DYRK as a glycogen synthase kinase 3-priming kinase. Biochem J 355(Pt 3):609–615
Yagi T, Ito D, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Nihei Y, Yoshizaki T, Yamanaka S, Okano H, Suzuki N (2011) Modeling familial Alzheimer’s disease with induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum Mol Genet 20(23):4530–4539. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr394
Yagi T, Kosakai A, Ito D, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Nihei Y, Nabetani A, Ishikawa F, Arai Y, Hirose N, Okano H, Suzuki N (2012) Establishment of induced pluripotent stem cells from centenarians for neurodegenerative disease research. PLoS One 7(7):e41572. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041572
Yang YM, Gupta SK, Kim KJ, Powers BE, Cerqueira A, Wainger BJ, Ngo HD, Rosowski KA, Schein PA, Ackeifi CA, Arvanites AC, Davidow LS, Woolf CJ, Rubin LL (2013) A small molecule screen in stem-cell-derived motor neurons identifies a kinase inhibitor as a candidate therapeutic for ALS. Cell Stem Cell 12(6):713–726. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2013.04.003
Young JE, Goldstein LS (2012) Alzheimer’s disease in a dish: promises and challenges of human stem cell models. Hum Mol Genet 21(R1):R82–R89. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds319
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, Llorens V, Gomez Tortosa E, del Ser T, Munoz DG, de Yebenes JG (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol 55(2):164–173. doi:10.1002/ana.10795
Zhang N, An MC, Montoro D, Ellerby LM (2010) Characterization of Human Huntington’s Disease Cell Model from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. PLoS Curr 2:RRN1193. doi:10.1371/currents.RRN1193
Zuccato C, Valenza M, Cattaneo E (2010) Molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutical targets in Huntington’s disease. Physiol Rev 90(3):905–981. doi:10.1152/physrev.00041.2009
Acknowledgments
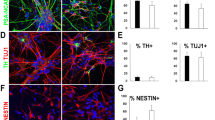
We would like to thank Dr. Jared Sterneckert, Dr. Holm Zaehres and Dr. Vincent Ruland for critical reading of this manuscript and Dr. Peter Reinhardt for providing images of differentiated neural cells. This work was supported by the IMF at University Hospital Münster (I-HA-111219; to GH) and the German Research Foundation (DFG; SFB-TRR128-B7; to TK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hargus, G., Ehrlich, M., Hallmann, AL. et al. Human stem cell models of neurodegeneration: a novel approach to study mechanisms of disease development. Acta Neuropathol 127, 151–173 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1222-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1222-6