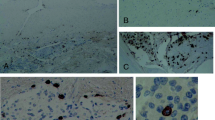
Abstract
Mast cells (MCs) are densely granulated perivascular resident cells of hematopoietic origin and well known for their pathogenetic role in allergic and anaphylactic reactions. In addition, they are also involved in processes of innate and adaptive immunity. MCs can be activated in response to a wide range of stimuli, resulting in the release of not only pro-inflammatory, but also anti-inflammatory mediators. The patterns of secreted mediators depend upon the given stimuli and microenvironmental conditions, accordingly MCs have the ability to promote or attenuate inflammatory processes. Their presence in the central nervous system (CNS) has been recognized for more than a century. Since then a participation of MCs in various pathological processes in the CNS has been well documented. They can aggravate CNS damage in models of brain ischemia and hemorrhage, namely through increased blood–brain barrier damage, brain edema and hemorrhage formation and promotion of inflammatory responses to such events. In contrast, recent evidence suggests that MCs may have a protective role following traumatic brain injury by degrading pro-inflammatory cytokines via specific proteases. In neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis, the role of MCs seems to be ambiguous. MCs have been shown to be damaging, neuroprotective, or even dispensable, depending on the experimental protocols used. The role of MCs in the formation and progression of CNS tumors such as gliomas is complex and both positive and negative relationships between MC activity and tumor progression have been reported. In summary, MCs and their secreted mediators modulate inflammatory processes in multiple CNS pathologies and can thereby either contribute to neurological damage or confer neuroprotection. This review intends to give a concise overview of the regulatory roles of MCs in brain disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arinobu Y, Iwasaki H, Gurish MF, Mizuno S, Shigematsu H, Ozawa H, Tenen DG, Austen KF, Akashi K (2005) Developmental checkpoints of the basophil/mast cell lineages in adult murine hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(50):18105–18110. doi:10.1073/pnas.0509148102
Bennett JL, Blanchet MR, Zhao L, Zbytnuik L, Antignano F, Gold M, Kubes P, McNagny KM (2009) Bone marrow-derived mast cells accumulate in the central nervous system during inflammation but are dispensable for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis pathogenesis. J Immunol 182(9):5507–5514. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0801485
Biran V, Cochois V, Karroubi A, Arrang JM, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Heron A (2008) Stroke induces histamine accumulation and mast cell degranulation in the neonatal rat brain. Brain Pathol 18(1):1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00092.x
Brown MA, Hatfield JK (2012) Mast cells are important modifiers of autoimmune disease: with so much evidence, why is there still controversy? Front Immunol 3:147. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00147
Carlson T, Kroenke M, Rao P, Lane TE, Segal B (2008) The Th17-ELR + CXC chemokine pathway is essential for the development of central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 205(4):811–823. doi:10.1084/jem.20072404
Christy AL, Brown MA (2007) The multitasking mast cell: positive and negative roles in the progression of autoimmunity. J Immunol 179(5):2673–2679 (pii:179/5/2673)
Costa JJ, Weller PF, Galli SJ (1997) The cells of the allergic response: mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. JAMA 278(22):1815–1822
Couturier N, Zappulla JP, Lauwers-Cances V, Uro-Coste E, Delisle MB, Clanet M, Montagne L, Van der Valk P, Bo L, Liblau RS (2008) Mast cell transcripts are increased within and outside multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuroimmunol 195(1–2):176–185. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.01.017
Dropp JJ (1972) Mast cells in the central nervous system of several rodents. Anat Rec 174(2):227–237. doi:10.1002/ar.1091740207
Dropp JJ (1979) Mast cells in the human brain. Acta Anat (Basel) 105(4):505–513
Du T, Friend DS, Austen KF, Katz HR (1996) Tissue-dependent differences in the asynchronous appearance of mast cells in normal mice and in congenic mast cell-deficient mice after infusion of normal bone marrow cells. Clin Exp Immunol 103(2):316–321
Dvorak AM (1997) New aspects of mast cell biology. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 114(1):1–9
Ehrlich P (1879) Über die spezifischen Granulationen des Blutes. Arch Anat Physiol Abteil 571–579
Erdei A, Andrasfalvy M, Peterfy H, Toth G, Pecht I (2004) Regulation of mast cell activation by complement-derived peptides. Immunol Lett 92(1–2):39–42. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2003.11.019
Feyerabend TB, Weiser A, Tietz A, Stassen M, Harris N, Kopf M, Radermacher P, Moller P, Benoist C, Mathis D, Fehling HJ, Rodewald HR (2011) Cre-mediated cell ablation contests mast cell contribution in models of antibody- and t cell-mediated autoimmunity. Immunity 35(5):832–844. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.015
Galinsky DS, Nechushtan H (2008) Mast cells and cancer—no longer just basic science. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 68(2):115–130. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2008.06.001
Galli SJ (1993) New concepts about the mast cell. N Engl J Med 328(4):257–265. doi:10.1056/NEJM199301283280408
Galli SJ, Hammel I (1994) Mast cell and basophil development. Curr Opin Hematol 1(1):33–39
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA, Piliponsky AM, Williams CM, Tsai M (2005) Mast cells as “tunable” effector and immunoregulatory cells: recent advances. Annu Rev Immunol 23:749–786. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141025
Galli SJ, Kitamura Y (1987) Genetically mast-cell-deficient W/Wv and Sl/Sld mice. Their value for the analysis of the roles of mast cells in biologic responses in vivo. Am J Pathol 127(1):191–198
Galli SJ, Nakae S, Tsai M (2005) Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 6(2):135–142. doi:10.1038/ni1158
Galli SJ, Tsai M (2008) Mast cells: versatile regulators of inflammation, tissue remodeling, host defense and homeostasis. J Dermatol Sci 49(1):7–19. doi:1016/j.jdermsci.2007.09.009
Gilfillan AM, Beaven MA (2011) Regulation of mast cell responses in health and disease. Crit Rev Immunol 31(6):475–529 (pii:20591c2466aedc19,222bcdb718a38c7c)
Gilfillan AM, Rivera J (2009) The tyrosine kinase network regulating mast cell activation. Immunol Rev 228(1):149–169. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00742.x
Gordon JR, Galli SJ (1994) Promotion of mouse fibroblast collagen gene expression by mast cells stimulated via the Fc epsilon RI. Role for mast cell-derived transforming growth factor beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med 180(6):2027–2037
Grimbaldeston MA, Chen CC, Piliponsky AM, Tsai M, Tam SY, Galli SJ (2005) Mast cell-deficient W-sash c-kit mutant Kit W-sh/W-sh mice as a model for investigating mast cell biology in vivo. Am J Pathol 167(3):835–848
Grimbaldeston MA, Nakae S, Kalesnikoff J, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2007) Mast cell-derived interleukin 10 limits skin pathology in contact dermatitis and chronic irradiation with ultraviolet B. Nat Immunol 8(10):1095–1104. doi:10.1038/ni1503
Hallgren J, Pejler G (2006) Biology of mast cell tryptase. An inflammatory mediator. FEBS J 273(9):1871–1895. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05211.x
Hedtjarn M, Mallard C, Hagberg H (2004) Inflammatory gene profiling in the developing mouse brain after hypoxia-ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24(12):1333–1351. doi:10.1097/01.WCB.0000141559.17620.36
Hendrix S, Kramer P, Pehl D, Warnke K, Boato F, Nelissen S, Lemmens E, Pejler G, Metz M, Siebenhaar F, Maurer M (2012) Mast cells protect from post-traumatic brain inflammation by the mast cell-specific chymase mouse mast cell protease-4. FASEB J. doi:10.1096/fj.12-204800
Hendrix S, Nitsch R (2007) The role of T helper cells in neuroprotection and regeneration. J Neuroimmunol 184(1–2):100–112. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.11.019
Hendrix S, Warnke K, Siebenhaar F, Peters EM, Nitsch R, Maurer M (2006) The majority of brain mast cells in B10.PL mice is present in the hippocampal formation. Neurosci Lett 392(3):174–177
Henz BM, Maurer M, Lippert U, Worm M, Babina M (2001) Mast cells as initiators of immunity and host defense. Exp Dermatol 10(1):1–10
Hough LB (1988) Cellular localization and possible functions for brain histamine: recent progress. Prog Neurobiol 30(6):469–505 (pii:0301-0082(88)90032-9)
Ibrahim MZ, Reder AT, Lawand R, Takash W, Sallouh-Khatib S (1996) The mast cells of the multiple sclerosis brain. J Neuroimmunol 70(2):131–138 (pii:0165-5728(96)00102-6)
Jin Y, Silverman AJ, Vannucci SJ (2007) Mast cell stabilization limits hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the immature rat. Dev Neurosci 29(4–5):373–384. doi:10.1159/000105478
Jin Y, Silverman AJ, Vannucci SJ (2009) Mast cells are early responders after hypoxia-ischemia in immature rat brain. Stroke 40(9):3107–3112. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.549691
Johnson D, Krenger W (1992) Interactions of mast cells with the nervous system—recent advances. Neurochem Res 17(9):939–951
Karasuyama H, Mukai K, Tsujimura Y, Obata K (2009) Newly discovered roles for basophils: a neglected minority gains new respect. Nat Rev 9(1):9–13. doi:10.1038/nri2458
Kendall JC, Li XH, Galli SJ, Gordon JR (1997) Promotion of mouse fibroblast proliferation by IgE-dependent activation of mouse mast cells: role for mast cell tumor necrosis factor-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta 1. J Allergy Clin Immunol 99(1 Pt 1):113–123 (pii:S0091674997000055)
Korkmaz OT, Tuncel N, Tuncel M, Oncu EM, Sahinturk V, Celik M (2010) Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) treatment of Parkinsonian rats increases thalamic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels and alters the release of nerve growth factor (NGF) by mast cells. J Mol Neurosci 41(2):278–287. doi:10.1007/s12031-009-9307-3
Kulka M, Alexopoulou L, Flavell RA, Metcalfe DD (2004) Activation of mast cells by double-stranded RNA: evidence for activation through Toll-like receptor 3. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114(1):174–182. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.03.049
Lassman AB, DeAngelis LM (2003) Brain metastases. Neurol Clin 21(1):1–23, vii
Li H, Nourbakhsh B, Safavi F, Li K, Xu H, Cullimore M, Zhou F, Zhang G, Rostami A (2011) Kit (W-sh) mice develop earlier and more severe experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis due to absence of immune suppression. J Immunol 187(1):274–282. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003603
Lindsberg PJ, Strbian D, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML (2010) Mast cells as early responders in the regulation of acute blood–brain barrier changes after cerebral ischemia and hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(4):689–702. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.282
Lock C, Hermans G, Pedotti R, Brendolan A, Schadt E, Garren H, Langer-Gould A, Strober S, Cannella B, Allard J, Klonowski P, Austin A, Lad N, Kaminski N, Galli SJ, Oksenberg JR, Raine CS, Heller R, Steinman L (2002) Gene-microarray analysis of multiple sclerosis lesions yields new targets validated in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat Med 8(5):500–508. doi:10.1038/nm0502-500
Lozada A, Maegele M, Stark H, Neugebauer EM, Panula P (2005) Traumatic brain injury results in mast cell increase and changes in regulation of central histamine receptors. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 31(2):150–162. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2004.00622.x
Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (2008) Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol 7(8):728–741. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70164-9
Maltby S, Khazaie K, McNagny KM (2009) Mast cells in tumor growth: angiogenesis, tissue remodelling and immune-modulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1796(1):19–26. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.02.001
Manni L, Micera A, Pistillo L, Aloe L (1998) Neonatal handling in EAE-susceptible rats alters NGF levels and mast cell distribution in the brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 16(1):1–8 (pii:S0736-5748(98)00003-3)
Marshall JS (2004) Mast-cell responses to pathogens. Nat Rev 4(10):787–799
Maslinska D, Laure-Kamionowska M, Maslinski KT, Gujski M, Maslinski S (2007) Distribution of tryptase-containing mast cells and metallothionein reactive astrocytes in human brains with amyloid deposits. Inflamm Res 56(Suppl 1):S17–S18
Maurer M, Wedemeyer J, Metz M, Piliponsky AM, Weller K, Chatterjea D, Clouthier DE, Yanagisawa MM, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2004) Mast cells promote homeostasis by limiting endothelin-1-induced toxicity. Nature 432(7016):512–516. doi:10.1038/nature03085
McCurdy JD, Lin TJ, Marshall JS (2001) Toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of murine mast cells. J Leukoc Biol 70(6):977–984
McDermott JR, Bartram RE, Knight PA, Miller HR, Garrod DR, Grencis RK (2003) Mast cells disrupt epithelial barrier function during enteric nematode infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(13):7761–7766. doi:10.1073/pnas.1231488100
Metcalfe DD, Baram D, Mekori YA (1997) Mast cells. Physiol Rev 77(4):1033–1079
Metz M, Grimbaldeston MA, Nakae S, Piliponsky AM, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2007) Mast cells in the promotion and limitation of chronic inflammation. Immunol Rev 217:304–328. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00520.x
Metz M, Piliponsky AM, Chen CC, Lammel V, Abrink M, Pejler G, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2006) Mast cells can enhance resistance to snake and honeybee venoms. Science 313(5786):526–530. doi:10.1126/science.1128877
Miller HR, Pemberton AD (2002) Tissue-specific expression of mast cell granule serine proteinases and their role in inflammation in the lung and gut. Immunology 105(4):375–390 (pii:1375)
Min B (2008) Basophils: what they ‘can do’ versus what they ‘actually do’. Nat Immunol 9(12):1333–1339. doi:10.1038/ni.f.217
Nautiyal KM, Liu C, Dong X, Silver R (2011) Blood-borne donor mast cell precursors migrate to mast cell-rich brain regions in the adult mouse. J Neuroimmunol 240–241:142–146. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.09.003
Nautiyal KM, Ribeiro AC, Pfaff DW, Silver R (2008) Brain mast cells link the immune system to anxiety-like behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(46):18053–18057. doi:10.1073/pnas.0809479105
Neumann J (1890) Ueber das Vorkommen der sogenannten „Mastzellen” bei pathologischen Veränderungen des Gehirns. Archiv für pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und für klinische Medicin 122(2)
Niederhoffer N, Levy R, Sick E, Andre P, Coupin G, Lombard Y, Gies JP (2009) Amyloid beta peptides trigger CD47-dependent mast cell secretory and phagocytic responses. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 22(2):473–483
Schmidt OI, Infanger M, Hyde CE, Ertel W, Stahel PF (2004) The role of neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury. Eur J Trauma 30:135–149
Olsson Y (1974) Mast cells in plaques of multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 50(5):611–618
Pang X, Letourneau R, Rozniecki JJ, Wang L, Theoharides TC (1996) Definitive characterization of rat hypothalamic mast cells. Neuroscience 73(3):889–902 (pii:0306-4522(95)00606-0)
Panula P, Rinne J, Kuokkanen K, Eriksson KS, Sallmen T, Kalimo H, Relja M (1998) Neuronal histamine deficit in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 82(4):993–997 (pii:S0306452297003539)
Piconese S, Costanza M, Musio S, Tripodo C, Poliani PL, Gri G, Burocchi A, Pittoni P, Gorzanelli A, Colombo MP, Pedotti R (2011) Exacerbated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mast-cell-deficient Kit W-sh/W-sh mice. Lab Invest 91(4):627–641. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2011.3
Polajeva J, Sjosten AM, Lager N, Kastemar M, Waern I, Alafuzoff I, Smits A, Westermark B, Pejler G, Uhrbom L, Tchougounova E (2011) Mast cell accumulation in glioblastoma with a potential role for stem cell factor and chemokine CXCL12. PLoS ONE 6(9):e25222. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025222
Porzionato A, Macchi V, Parenti A, De Caro R (2004) The distribution of mast cells in the human area postrema. J Anat 204(2):141–147. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2004.00256.x
Prodeus AP, Zhou X, Maurer M, Galli SJ, Carroll MC (1997) Impaired mast cell-dependent natural immunity in complement C3-deficient mice. Nature 390(6656):172–175. doi:10.1038/36586
Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9(2):131–141. doi:10.1002/ana.410090206
Rivera J, Fierro NA, Olivera A, Suzuki R (2008) New insights on mast cell activation via the high affinity receptor for IgE. Adv Immunol 98:85–120. doi:1016/S0065-2776(08)00403-3
Robbie-Ryan M, Tanzola MB, Secor VH, Brown MA (2003) Cutting edge: both activating and inhibitory Fc receptors expressed on mast cells regulate experimental allergic encephalomyelitis disease severity. J Immunol 170(4):1630–1634
Rodewald HR, Dessing M, Dvorak AM, Galli SJ (1996) Identification of a committed precursor for the mast cell lineage. Science 271(5250):818–822
Rozniecki JJ, Hauser SL, Stein M, Lincoln R, Theoharides TC (1995) Elevated mast cell tryptase in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. Ann Neurol 37(1):63–66. doi:10.1002/ana.410370112
Sayed BA, Christy AL, Walker ME, Brown MA (2010) Meningeal mast cells affect early T cell central nervous system infiltration and blood-brain barrier integrity through TNF: a role for neutrophil recruitment? J Immunol 184(12):6891–6900. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000126
Sayed BA, Walker ME, Brown MA (2011) Cutting edge: mast cells regulate disease severity in a relapsing-remitting model of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 186(6):3294–3298. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003574
Secor VH, Secor WE, Gutekunst CA, Brown MA (2000) Mast cells are essential for early onset and severe disease in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 191(5):813–822
Shanas U, Bhasin R, Sutherland AK, Silverman AJ, Silver R (1998) Brain mast cells lack the c-kit receptor: immunocytochemical evidence. J Neuroimmunol 90(2):207–211 (pii:S0165572898001374)
Sharma N, Kumar V, Everingham S, Mali RS, Kapur R, Zeng LF, Zhang ZY, Feng GS, Hartmann K, Roers A, Craig AW (2012) SH2 domain-containing phosphatase-2 is a critical regulator of connective tissue mast cell survival and homeostasis in mice. Mol Cell Biol. doi:10.1128/MCB.00308-12
Shimada R, Nakao K, Furutani R, Kibayashi K (2012) A rat model of changes in dural mast cells and brain histamine receptor H3 expression following traumatic brain injury. J Clin Neurosci 19(3):447–451. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2011.06.033
Silver R, Silverman AJ, Vitkovic L, Lederhendler II (1996) Mast cells in the brain: evidence and functional significance. Trends Neurosci 19(1):25–31 (pii:0166223696818637)
Silverman AJ, Sutherland AK, Wilhelm M, Silver R (2000) Mast cells migrate from blood to brain. J Neurosci 20(1):401–408
Skaper SD, Facci L, Romanello S, Leon A (1996) Mast cell activation causes delayed neurodegeneration in mixed hippocampal cultures via the nitric oxide pathway. J Neurochem 66(3):1157–1166
Stelekati E, Bahri R, D’Orlando O, Orinska Z, Mittrucker HW, Langenhaun R, Glatzel M, Bollinger A, Paus R, Bulfone-Paus S (2009) Mast cell-mediated antigen presentation regulates CD8 + T cell effector functions. Immunity 31(4):665–676. doi:1016/j.immuni.2009.08.022
Stokely ME, Orr EL (2008) Acute effects of calvarial damage on dural mast cells, pial vascular permeability, and cerebral cortical histamine levels in rats and mice. J Neurotrauma 25(1):52–61. doi:10.1089/neu.2007.0397
Stone KD, Prussin C, Metcalfe DD (2010) IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125(2 Suppl 2):S73–S80. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.017
Strbian D, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Kovanen PT, Tatlisumak T, Lindsberg PJ (2007) Mast cell stabilization reduces hemorrhage formation and mortality after administration of thrombolytics in experimental ischemic stroke. Circulation 116(4):411–418. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.655423
Strbian D, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Tatlisumak T, Lindsberg PJ (2006) Cerebral mast cells regulate early ischemic brain swelling and neutrophil accumulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26(5):605–612. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600228
Strbian D, Kovanen PT, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Tatlisumak T, Lindsberg PJ (2009) An emerging role of mast cells in cerebral ischemia and hemorrhage. Ann Med 41(6):438–450. doi:10.1080/07853890902887303
Strbian D, Tatlisumak T, Ramadan UA, Lindsberg PJ (2007) Mast cell blocking reduces brain edema and hematoma volume and improves outcome after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(4):795–802. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600387
Sullivan BM, Locksley RM (2009) Basophils: a nonredundant contributor to host immunity. Immunity 30(1):12–20. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.12.006
Taiwo OB, Kovacs KJ, Sun Y, Larson AA (2005) Unilateral spinal nerve ligation leads to an asymmetrical distribution of mast cells in the thalamus of female but not male mice. Pain 114(1–2):131–140. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.12.002
Tanzola MB, Robbie-Ryan M, Gutekunst CA, Brown MA (2003) Mast cells exert effects outside the central nervous system to influence experimental allergic encephalomyelitis disease course. J Immunol 171(8):4385–4391
Theoharides TC (1990) Mast cells: the immune gate to the brain. Life Sci 46(9):607–617
Theoharides TC, Alysandratos KD, Angelidou A, Delivanis DA, Sismanopoulos N, Zhang B, Asadi S, Vasiadi M, Weng Z, Miniati A, Kalogeromitros D (2012) Mast cells and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(1):21–33. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.12.014
Theoharides TC, Conti P (2004) Mast cells: the Jekyll and Hyde of tumor growth. Trends Immunol 25(5):235–241. doi:10.1016/j.it.2004.02.013
Theoharides TC, Donelan JM, Papadopoulou N, Cao J, Kempuraj D, Conti P (2004) Mast cells as targets of corticotropin-releasing factor and related peptides. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25(11):563–568. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2004.09.007
Theoharides TC, Kempuraj D, Tagen M, Conti P, Kalogeromitros D (2007) Differential release of mast cell mediators and the pathogenesis of inflammation. Immunol Rev 217:65–78. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00519.x
Theoharides TC, Rozniecki JJ, Sahagian G, Jocobson S, Kempuraj D, Conti P, Kalogeromitros D (2008) Impact of stress and mast cells on brain metastases. J Neuroimmunol 205(1–2):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.09.014
Tuncel N, Sener E, Cerit C, Karasu U, Gurer F, Sahinturk V, Baycu C, Ak D, Filiz Z (2005) Brain mast cells and therapeutic potential of vasoactive intestinal peptide in a Parkinson’s disease model in rats: brain microdialysis, behavior, and microscopy. Peptides 26(5):827–836. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2004.12.019
Walker ME, Hatfield JK, Brown MA (2011) New insights into the role of mast cells in autoimmunity: evidence for a common mechanism of action? Biochim Biophys Acta. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.02.009
Welle M (1997) Development, significance, and heterogeneity of mast cells with particular regard to the mast cell-specific proteases chymase and tryptase. J Leukoc Biol 61(3):233–245
Zappulla JP, Arock M, Mars LT, Liblau RS (2002) Mast cells: new targets for multiple sclerosis therapy? J Neuroimmunol 131(1–2):5–20
Acknowledgments
This publication was supported in part by grants from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SPP1394) to S.H. and M.M. and from Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek, Vlaanderen to S.H. (G.0834.11N, G.0389.12) and to EL (1.2.703.10N). The authors also acknowledge the support of the COST action BM1007 “Mast cells and basophils—Targets for innovative therapy” which facilitated their collaboration. The authors thank Evelin Hagen for excellent technical assistance to generate the pictures of human MCs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelissen, S., Lemmens, E., Geurts, N. et al. The role of mast cells in neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol 125, 637–650 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1092-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1092-y