Abstract
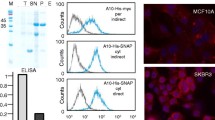
Camelids produce antibodies made of homodimeric heavy chains, and the antigen-binding region being composed of a single domain called VHH. These VHHs are much smaller than complete IgG. They are also more thermostable and more soluble in water; they should, therefore, diffuse more readily in the tissues. VHHs, expressed in bacteria, are easier to produce than conventional monoclonal antibodies. Because of these special characteristics, these antibody fragments could have interesting developments in immunohistochemistry and in the development of biomarkers. To test the possibility of their use in immunohistochemistry (IHC), we selected the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a well-known marker of astrocytes. One alpaca (Lama pacos) was immunized against GFAP. Lymphocytes were isolated; the DNA was extracted; the VHH-coding sequences were selectively amplified. Three VHHs with a high affinity for GFAP and their corresponding mRNA were selected by ribosome display. Large quantities of the recombinant VHHs coupled with different tags were harvested from transfected bacteria. One of them was shown to immunolabel strongly and specifically to GFAP of human astrocytes in tissue sections. The quality of the IHC was comparable or, in some aspects, superior to the quality obtained with conventional IgG. The VHH was shown to diffuse on a longer distance than conventional monoclonal antibodies in fixed cortical tissue: a property that may be useful in immunolabeling of thick sections.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achour I, Cavelier P, Tichit M et al (2008) Tetrameric and homodimeric camelid IgGs originate from the same IgH locus. J Immunol 181:2001–2009
Arbabi Ghahroudi M, Desmyter A, Wyns L, Hamers R, Muyldermans S (1997) Selection and identification of single domain antibody fragments from camel heavy-chain antibodies. FEBS Lett 414:521–526
Cardoso DF, Nato F, England P et al (2000) Neutralizing human anti crotoxin scFv isolated from a nonimmunized phage library. Scand J Immunol 51:337–344
Conrath KE, Lauwereys M, Galleni M et al (2001) beta-Lactamase inhibitors derived from single-domain antibody fragments elicited in the Camelidae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:2807–2812
Conrath KE, Wernery U, Muyldermans S, Nguyen VK (2003) Emergence and evolution of functional heavy-chain antibodies in Camelidae. Dev Comp Immunol 27:87–103
De Genst E, Saerens D, Muyldermans S, Conrath K (2006) Antibody repertoire development in camelids. Dev Comp Immunol 30:187–198
De Genst E, Silence K, Decanniere K et al (2006) Molecular basis for the preferential cleft recognition by dromedary heavy-chain antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4586–4591
DeArmond SJ, Fajardo M, Naughton SA, Eng LF (1983) Degradation of glial fibrillary acidic protein protein by a calcium dependent proteinase: an electroblot study. Brain Res 262:275–282
Desmyter A, Spinelli S, Payan F et al (2002) Three camelid VHH domains in complex with porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase: inhibition and versatility of binding topology. J Biol Chem 277:23645–23650
Desmyter A, Transue TR, Ghahroudi MA et al (1996) Crystal structure of a camel single-domain VH antibody fragment in complex with lysozyme. Nat Struct Biol 3:803–811
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS, Lee YL (2000) Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem Res 25:1439–1451
Frenken LG, van der Linden RH, Hermans PW et al (2000) Isolation of antigen specific llama VHH antibody fragments and their high level secretion by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotech 78:11–21
Friguet B, Chaffote AF, Djavadi-Ohaniance L, Goldberg ME (1985) Measurements of the true affinity constant in solution of antigen-antibody complexes by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods 77:305–319
Gabbot PL, Somogyi J (1984) The ‘single’ section Golgi-impregnation procedure: methodological description. J Neurosci Methods 11:221–230
Hamers-Casterman C, Atarhouch T, Muyldermans S et al (1993) Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 363:446–448
Hanes J, Pluckthun A (1997) In vitro selection and evolution of functional proteins by using ribosome display. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4937–4942
Harmsen MM, de Haard HJW (2007) Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments. Appl Microb Biotech 77:13–22
Harmsen MM, van Solt CB, Fijten HPD et al (2007) Passive immunization of guinea pigs with llama single-domain antibody fragments against foot-and-mouth disease. Vet Microbiol 120:193–206
Hoogenboom HR, Winter G (1992) By-passing immunisation: human antibodies from synthetic repertoires of germline VH gene segments rearranged in vitro. J Mol Biol 227:381–388
Lafaye P, Achour I, England P, Duyckaerts C, Rougeon F (2009) Single-domain antibodies recognize selectively small oligomeric forms of amyloid β, prevent Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and inhibit fibril formation. Mol Immunol 46:695–704
Lafaye P, Nato F, Mazié J-C, Doyen N (1995) Similar binding activity for a neutralizing anti-tetanus toxoid human monoclonal antibody and its bacterially expressed Fab. Res Immunol 146:373–382
Lefranc M-P, Giudicelli V, Ginestoux C et al (1999) IMGT, the international ImMunoGeneTics database. Nucleic Acids Res 27:209–212
Mao S, Gao C, Lo C et al (1999) Phage display library selection of high-affinity human single-chain antibodies to tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens sialyl Lewisx and Lewisx. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6953–6958
Mouratou B, Schaeffer F, Guilvout I et al (2007) Remodeling a DNA-binding protein as a specific in vivo inhibitor of bacterial secretin PulD. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:17983–17988
Muyldermans S (2001) Single domain camel antibodies: current status. Rev Mol Biotechnol 74:277–302
Muyldermans S, Atarhouch T, Saldanha J, Barbosa JA, Hamers R (1994) Sequence and structure of VH domain from naturally occurring camel heavy chain immunoglobulins lacking light chains. Prot Eng 7:1129–1135
Muyldermans S, Lauwereys M (1999) Unique single-domain antigen binding fragments derived from naturally occurring camel heavy-chain antibodies. J Mol Rec 12:131–140
Nguyen VK, Su C, Muyldermans S, van der Loo W (2002) Heavy-chain antibodies in Camelidae; a case of evolutionary innovation. Immunogenetics 54:39–47
Olichon A, Schweizer D, Muyldermans S, de Marco A (2007) Heating as a rapid purification method for recovering correctly-folded thermotolerant VH and VHH domains. BMC Biotechnol 7:7
Perez JM, Renisio JG, Prompers JJ et al (2001) Thermal unfolding of a llama antibody fragment: a two-state reversible process. Biochemistry 40:74–83
Saerens D, Kinne J, Bosmans E et al (2004) Single domain antibodies derived from dromedary lymph node and peripheral blood lymphocytes sensing conformational variants of prostate-specific antigen. J Biol Chem 279:51965–51972
Schlaepfer WW, Zimmerman V-JP (1981) Calcium mediated breakdown of glial filaments and neurofilaments in rat optic nerve and spinal cord. Neurochem Res 6:243–255
Stijlemans B, Conrath K, Cortez-Retamozo V et al (2004) Efficient targeting of conserved cryptic epitopes of infectious agents by single domain antibodies. African trypanosomes as paradigm. J Biol Chem 279:1256–1261
Tanha J, Dubuc G, Hirama T, Narang SA, MacKenzie CR (2002) Selection by phage display of llama conventional VH fragments with heavy chain antibody VHH properties. J Immunol Methods 263:97–109
van der Linden RH, Frenken LG, de Geus B et al (1999) Comparison of physical chemical properties of llama VHH antibody fragments and mouse monoclonal antibodies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1431:37–46
Zahnd C, Amstutz P, Pluckthun A (2007) Ribosome display: selecting and evolving proteins in vitro that specifically bind to a target. Nat Methods 4:269–279
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Brainbank GIE Neuro-CEB of Hôpital de la Pitié-Salpétrière for providing human cortical brain tissue. We want also thank Dr Agathe Subtil from Pasteur Institute for the gift of the rabbit anti-His antibodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perruchini, C., Pecorari, F., Bourgeois, JP. et al. Llama VHH antibody fragments against GFAP: better diffusion in fixed tissues than classical monoclonal antibodies. Acta Neuropathol 118, 685–695 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0572-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0572-6