Abstract
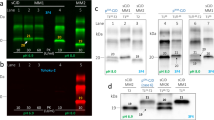
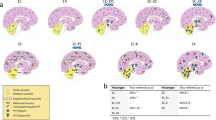
Plaque-type deposition of prion protein (PrP) in the brain has been extremely rare in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease patients with methionine homozygosity at polymorphic codon 129 of the PrP gene and type 1 abnormal isoform of PrP (sCJD-MM1). Here we report three sCJD-MM1 patients who showed prominent PrP-positive amyloid plaques in the cerebral and cerebellar white matter. All three patients showed clinical courses of long duration (2 years ≤), particularly at the end-stage. The white matter of these patients was severely damaged because of the prolonged disease duration. Furthermore, Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein, which accumulates within the axonal swellings under pathological conditions, co-accumulated with the PrP-amyloid plaques. These findings suggest that the axonal damage reflecting the prolonged disease duration causes the deposition of PrP-amyloid plaques in the white matter. The present study shows that PrP-amyloid plaques can occur in the white matter of sCJD-MM1 cases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano M, Mohri S, Ironside JW, Ito M, Tamaoki N, Kitamoto T (2006) vCJD prion acquires altered virulence through trans-species infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:293–299. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.149
Cali I, Castellani R, Yuan J et al (2006) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease revisited. Brain 129:2266–2277. doi:10.1093/brain/awl224
Grathwohl KUD, Horiuchi M, Ishiguro N, Shinagawa M (1996) Improvement of PrPSc-detection in mouse spleen early at the preclinical stage of scrapie with collagenase-completed tissue homogenization and Sarkosyl-NaCl extraction of PrPSc. Arch Virol 141:1863–1874. doi:10.1007/BF01718200
Ishida C, Kakishima A, Okino S et al (2003) Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with MM1-type prion protein and plaques. Neurology 60:514–517
Iwasaki Y, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Kitamoto T, Sobue G (2006) Clinicopathologic characteristics of sporadic Japanese Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease classified according to prion protein gene polymorphism and prion protein type. Acta Neuropathol 112:561–571. doi:10.1007/s00401-006-0111-7
Kitamoto T, Shin RW, Doh-ura K et al (1992) Abnormal isoform of prion proteins accumulates in the synaptic structures of the central nervous system in patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am J Pathol 140:1285–1294
Kitamoto T, Ohta M, Doh-ura K, Hitoshi S, Terao Y, Tateishi J (1993) Novel missense variants of prion protein in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease or Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 191:709–714. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1993.1275
Kobayashi A, Asano M, Mohri S, Kitamoto T (2007) Cross-sequence transmission of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease creates a new prion strain. J Biol Chem 282:30022–30028. doi:10.1074/jbc.M704597200
Koo EH, Sisodia SS, Archer DR et al (1990) Precursor of amyloid protein in Alzheimer disease undergoes fast anterograde axonal transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1561–1565. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.4.1561
Muramoto T, Tanaka T, Kitamoto N et al (2000) Analyasis of Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome with 102Leu219Lys using monoclonal antibodies that specifically detect human prion protein with 219Glu. Neurosci Lett 288:179–182. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01232-5
Murayama H, Shin RW, Higuchi J, Shibuya S, Muramoto T, Kitamoto T (1999) Interaction of aluminum with PHFτ in Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary degeneration evidenced by desferrioxamine-assisted chelating autoclave method. Am J Pathol 155:877–885
Ohgami T, Kitamoto T, Shin RW, Kaneko Y, Ogomori K, Tateishi J (1991) Increased senile plaques without microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 81:242–247. doi:10.1007/BF00305864
Ohgami T, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J (1992) Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein accumulates within axonal swellings in human brain lesions. Neurosci Lett 136:75–78. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(92)90651-M
Parchi P, Castellani R, Capellari S et al (1996) Molecular basis of phenotypic variability in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 39:767–778. doi:10.1002/ana.410390613
Parchi P, Capellari S, Chen SG et al (1997) Typing prion isoforms. Nature 386:232–233. doi:10.1038/386232a0
Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S et al (1999) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol 46:224–233. doi :10.1002/1531-8249(199908)46:2<224::AID-ANA12>3.0.CO;2-W
Parchi P, Zou W, Wang W et al (2000) Genetic influence on the structural variations of the abnormal prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10168–10172. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.18.10168
Pocchiari M, Puopolo M, Croes EA et al (2004) Predictors of survival in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Brain 127:2348–2359. doi:10.1093/brain/awh249
Satoh K, Muramoto T, Tanaka T et al (2003) Association of an 11–12 kDa protease-resistant prion protein fragment with subtypes of dura graft-associated Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other prion diseases. J Gen Virol 84:2885–2893. doi:10.1099/vir.0.19236-0
Shin RW, Iwaki T, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J (1991) Hydrated autoclave pretreatment enhances tau immunoreactivity in formalin-fixed normal and Alzheimer’s disease brain tissues. Lab Invest 64:693–702
Tomita S, Ozaki T, Taru H et al (1999) Interaction of a neuron-specific protein containing PDZ domains with Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem 274:2243–2254. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.4.2243
Acknowledgments
We thank H. Kudo, K. Abe and M. Kimura for their technical assistance, and B. Bell for critical review of the manuscript. We are grateful to Dr. T. Suzuki for providing the UT-18 antibody. This study was supported by the Program for Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences of National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (T.K.), a grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (A.K. and T.K.), and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (A.K. and T.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, A., Arima, K., Ogawa, M. et al. Plaque-type deposition of prion protein in the damaged white matter of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease MM1 patients. Acta Neuropathol 116, 561–566 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0425-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0425-8